seed dispersal
... Pollination Regardless of the type, the process is the same. The pollen settles on the stigma, and a pollen tube grows to the ovary. ...
... Pollination Regardless of the type, the process is the same. The pollen settles on the stigma, and a pollen tube grows to the ovary. ...
part 4: reproduction of flowering plants
... which two distinct fertilization events take place between the male and female gametophyte. Seed Formation 1. After fertilization occurs, the fl ...
... which two distinct fertilization events take place between the male and female gametophyte. Seed Formation 1. After fertilization occurs, the fl ...
Chapter 24: Plant Reproduction and response
... Meiosis produces 4 haploid cells, each undergoing mitosis to produce 2 haploid nuclei per pollen grain Surrounded by thick wall for protection ...
... Meiosis produces 4 haploid cells, each undergoing mitosis to produce 2 haploid nuclei per pollen grain Surrounded by thick wall for protection ...
Bio I Lab Instructor: Dr. Rana Tayyar Lab XI Kingdom Plantae Plants
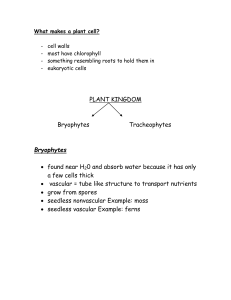
... and a sporophyte develops on top of the female gametophyte. In a mature sporophyte, the sporangium produces and releases haploid spores which will develop into protonema (juvenile stage of gametophyte). Protonema develops into a gametophyte. Division Pterophyta: The ferns Diploid sporophyte is the m ...
... and a sporophyte develops on top of the female gametophyte. In a mature sporophyte, the sporangium produces and releases haploid spores which will develop into protonema (juvenile stage of gametophyte). Protonema develops into a gametophyte. Division Pterophyta: The ferns Diploid sporophyte is the m ...
seed_plants_2
... • Needles retain moisture even during cold seasons. • Grow all year • Can grow in harsh environments (cold, poor soil) • Used for lumber, making paper, wood chips ...
... • Needles retain moisture even during cold seasons. • Grow all year • Can grow in harsh environments (cold, poor soil) • Used for lumber, making paper, wood chips ...
Plants II
... covered by a seed coat (integument) Seeds contain high energy nutrients like fats, carbs, and proteins to help the new plant embryo grow until it has leaves and can do photosynthesis Remain dormant until favorable conditions ...
... covered by a seed coat (integument) Seeds contain high energy nutrients like fats, carbs, and proteins to help the new plant embryo grow until it has leaves and can do photosynthesis Remain dormant until favorable conditions ...
Bacteria to Plants 5-2 Gymnosperms Full
... occurred the female cone and ovule close to seal in pollen Fertilized egg cell develops into an embryo. ...
... occurred the female cone and ovule close to seal in pollen Fertilized egg cell develops into an embryo. ...
Seed Reproduction
... – When pollen blows into a female cone, fertilization and seed formation can occur. – Seed released by a female cone can take two or three years. ...
... – When pollen blows into a female cone, fertilization and seed formation can occur. – Seed released by a female cone can take two or three years. ...
21 - Deepwater.org
... 34. Which of the following represents the male gametophyte of an angiosperm? a. ovule b. microspore mother cell c. pollen d. embryo sac e. fertilized egg 35. A botanist discovers a new species of plant in a tropical rainforest. After observing its anatomy and life cycle, the following characteristic ...
... 34. Which of the following represents the male gametophyte of an angiosperm? a. ovule b. microspore mother cell c. pollen d. embryo sac e. fertilized egg 35. A botanist discovers a new species of plant in a tropical rainforest. After observing its anatomy and life cycle, the following characteristic ...
LS Seeded Vascular Plants Booklet PP
... • Female reproductive organs produce eggs • Male reproductive organs produce sperm ...
... • Female reproductive organs produce eggs • Male reproductive organs produce sperm ...
Kingdom Plantae : “Plants”... - nonmotile eukaryotic, multicellular
... when pollen is made in the spring, some grains land next to an archegonium...it makes a pollen tube into it, sperm cells use this tube to reach the ovum. Seeds are formed after this fertilization. Male cones disintegrate, female cones stay on the tree...maturing a season or two. ...
... when pollen is made in the spring, some grains land next to an archegonium...it makes a pollen tube into it, sperm cells use this tube to reach the ovum. Seeds are formed after this fertilization. Male cones disintegrate, female cones stay on the tree...maturing a season or two. ...
Ch 30 Evolution Seed Plants
... ___3. Which of the following is characterized by a dominant sporophyte, small free-living gametophyte, and swimming sperm? A. Bryophyta B. Pterophyta C. Coniferophyta D. Anthophyta E. Hapatophyta ___4. The following statements are all true of the pine life cycle EXCEPT A. cones are short stems with ...
... ___3. Which of the following is characterized by a dominant sporophyte, small free-living gametophyte, and swimming sperm? A. Bryophyta B. Pterophyta C. Coniferophyta D. Anthophyta E. Hapatophyta ___4. The following statements are all true of the pine life cycle EXCEPT A. cones are short stems with ...
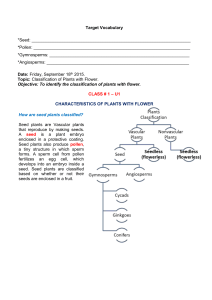
Plant Classification
... used to nourish a plant until it can undergo photosynthesis • Dicotyledons- also called dicots- have 2 seed leaves • Monocotyledons- also called monocots- have 1 seed leaf ...
... used to nourish a plant until it can undergo photosynthesis • Dicotyledons- also called dicots- have 2 seed leaves • Monocotyledons- also called monocots- have 1 seed leaf ...
Target Vocabulary *Seed: *Pollen: *Gymnosperms: *Angiosperms
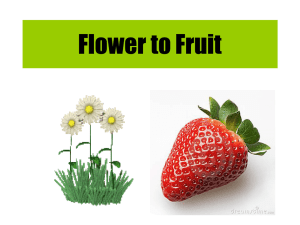
... forms. A sperm cell from pollen fertilizes an egg cell, which develops into an embryo inside a seed. Seed plants are classified based on whether or not their seeds are enclosed in a fruit. ...
... forms. A sperm cell from pollen fertilizes an egg cell, which develops into an embryo inside a seed. Seed plants are classified based on whether or not their seeds are enclosed in a fruit. ...
Green_Plants - Papanui High School
... Two ways: • Insect- pollen sticks to the insect and is transferred to the female part (stigma). • Wind- pollen is blown onto the stigma. ...
... Two ways: • Insect- pollen sticks to the insect and is transferred to the female part (stigma). • Wind- pollen is blown onto the stigma. ...
Green Plants
... Two ways: • Insect- pollen sticks to the insect and is transferred to the female part (stigma). • Wind- pollen is blown onto the stigma. ...
... Two ways: • Insect- pollen sticks to the insect and is transferred to the female part (stigma). • Wind- pollen is blown onto the stigma. ...
Plant Reproduction
... • Conifers (also non-flowering plants) have reduced gametophytes. • Male gametophyte is contained in a dry pollen grain. • Female gametophyte is a few cells inside of the structures that become the seed. ...
... • Conifers (also non-flowering plants) have reduced gametophytes. • Male gametophyte is contained in a dry pollen grain. • Female gametophyte is a few cells inside of the structures that become the seed. ...
Plant Classification
... and phloem) to conduct water and sugars • Have true roots, stems and leaves • Do not produce flowers, pollen or seeds • Reproduce by producing spores that grow into tiny plants that produce eggs and sperm • Sperm swim to eggs and fertilize • Ferns usually grow in places with lots of water ...
... and phloem) to conduct water and sugars • Have true roots, stems and leaves • Do not produce flowers, pollen or seeds • Reproduce by producing spores that grow into tiny plants that produce eggs and sperm • Sperm swim to eggs and fertilize • Ferns usually grow in places with lots of water ...
Coniferophyta
... •Gymnosperms date from the Carboniferous (360-290 millions years ago) and subsequently they dominated the floras of the world until the Cretaceous (65 millions years ago), since when they have been progressively displaced by the angiosperms (flowering plants). •‘Gymnosperm’ is used only informally t ...
... •Gymnosperms date from the Carboniferous (360-290 millions years ago) and subsequently they dominated the floras of the world until the Cretaceous (65 millions years ago), since when they have been progressively displaced by the angiosperms (flowering plants). •‘Gymnosperm’ is used only informally t ...
Pinophyta
The conifers, division Pinophyta, also known as division Coniferophyta or Coniferae, are one of 12 extant division-level taxa within the Kingdom Plantae (Viridiplantae) and 10 within the extant land plants. Pinophytes are gymnosperms, cone-bearing seed plants with vascular tissue. All extant conifers are woody plants with secondary growth, the great majority being trees with just a few being shrubs. Typical examples of conifers include cedars, Douglas-firs, cypresses, firs, junipers, kauri, larches, pines, hemlocks, redwoods, spruces, and yews. The division contains approximately eight families, 68 genera, and 630 living species.Although the total number of species is relatively small, conifers are of immense ecological importance. They are the dominant plants over huge areas of land, most notably the boreal forests of the northern hemisphere, but also in similar cool climates in mountains further south. Boreal conifers have many wintertime adaptations. The narrow conical shape of northern conifers, and their downward-drooping limbs, help them shed snow. Many of them seasonally alter their biochemistry to make them more resistant to freezing, called ""hardening"". While tropical rainforests have more biodiversity and turnover, the immense conifer forests of the world represent the largest terrestrial carbon sink, i.e. where carbon from atmospheric CO2 is bound as organic compounds.They are also of great economic value, primarily for timber and paper production; the wood of conifers is known as softwood.Conifer is a Latin word, a compound of conus (cone) and ferre (to bear), meaning ""the one that bears (a) cone(s)"".