CG--SCI-answers-NJ.ASK - Grade 8 Learning from the Fossil
... 3. B 4. C 5. B 6. C 7. This organism (flies) starts out as an egg, and it starts to grow and becomes maggots (aka larvae). When the organism is an egg, it’s like when humans are babies. When they become maggots, we are children. The flies then mature into pupae. That is around the same stage in huma ...
... 3. B 4. C 5. B 6. C 7. This organism (flies) starts out as an egg, and it starts to grow and becomes maggots (aka larvae). When the organism is an egg, it’s like when humans are babies. When they become maggots, we are children. The flies then mature into pupae. That is around the same stage in huma ...
Stem Cell
... In the mid 1800’s scientists realized that stems cells were basically the building blocks of life and they were capable of producing and forming other adult cells. They then began to make attempts to mammalian fertilise eggs outside of the human body in the 1900’s. That is when they discovered stem ...
... In the mid 1800’s scientists realized that stems cells were basically the building blocks of life and they were capable of producing and forming other adult cells. They then began to make attempts to mammalian fertilise eggs outside of the human body in the 1900’s. That is when they discovered stem ...
Clinical Trials Currently Being Conducted with the Use of Adult Stem
... cell therapy to treat multiple retinal diseases. These trials can be divided into two categories: regenerative and trophic. The regenerative therapies utilize differentiated cells such as RPE or photoreceptors that have been isolated, expanded, and derived from pluripotent embryonic or adult stem ce ...
... cell therapy to treat multiple retinal diseases. These trials can be divided into two categories: regenerative and trophic. The regenerative therapies utilize differentiated cells such as RPE or photoreceptors that have been isolated, expanded, and derived from pluripotent embryonic or adult stem ce ...
A CNIO group produce embryonic stem cells in living adult organisms
... horizon in regenerative medicine. ...
... horizon in regenerative medicine. ...
Cells and Tissues
... System - brain and spinal cord • Peripheral Nervous System - Nerve cells (neurons) • Sends and receives messages (electrical impulses) to and from the brain. ...
... System - brain and spinal cord • Peripheral Nervous System - Nerve cells (neurons) • Sends and receives messages (electrical impulses) to and from the brain. ...
Cell Function CC
... Compound Light Microscope: lets light pass through an object then through 2 or more lenses Electron microscope: for objects way too small to be seen with a light microscope; uses magnetic field to bend beams of electrons and can magnify 1,000,000 times ...
... Compound Light Microscope: lets light pass through an object then through 2 or more lenses Electron microscope: for objects way too small to be seen with a light microscope; uses magnetic field to bend beams of electrons and can magnify 1,000,000 times ...
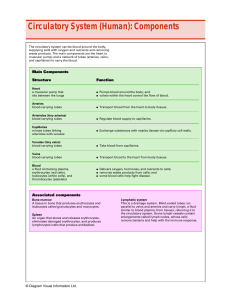
Circulatory System (Human): Components
... similar to blood plasma, from tissues, returning it to the circulatory system. Some lymph vessels contain enlargements called lymph nodes, whose cells remove bacteria and help with the immune response. ...
... similar to blood plasma, from tissues, returning it to the circulatory system. Some lymph vessels contain enlargements called lymph nodes, whose cells remove bacteria and help with the immune response. ...
Introduction to Cells, Tissues, Organs and Systems
... • This is called Cell Theory – the idea that cells are the basic unit of structure of every living thing. ...
... • This is called Cell Theory – the idea that cells are the basic unit of structure of every living thing. ...
Cell Specialization and Organization
... Things Vocab Cells: The smallest unit of life capable of carrying on life's functions Tissues: A group of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function Organs: Consists of different kinds of tissues that function together Organ Systems: A group of organs that work together to perfo ...
... Things Vocab Cells: The smallest unit of life capable of carrying on life's functions Tissues: A group of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function Organs: Consists of different kinds of tissues that function together Organ Systems: A group of organs that work together to perfo ...
TWO TYPES OF CELLS
... Red blood cell • Linear DNA • Big compared to prokaryotic cells Examples: ...
... Red blood cell • Linear DNA • Big compared to prokaryotic cells Examples: ...
C: Endothelial cells incorporate DiI-Ac
... 1. Peripheral or cord blood derived cells, including: ...
... 1. Peripheral or cord blood derived cells, including: ...
Cells to Body Systems
... function form a tissue. • Just as cells that work together form a tissue, tissues that work together form an organ. • Organs that work together to perform a function form a system. Example: circulatory system. • Plant cells also form tissues, such as the bark of a tree. And plant cells work together ...
... function form a tissue. • Just as cells that work together form a tissue, tissues that work together form an organ. • Organs that work together to perform a function form a system. Example: circulatory system. • Plant cells also form tissues, such as the bark of a tree. And plant cells work together ...
Cells - Livingstone High School
... function form a tissue. • Just as cells that work together form a tissue, tissues that work together form an organ. • Organs that work together to perform a function form a system. Example: circulatory system. • Plant cells also form tissues, such as the bark of a tree. And plant cells work together ...
... function form a tissue. • Just as cells that work together form a tissue, tissues that work together form an organ. • Organs that work together to perform a function form a system. Example: circulatory system. • Plant cells also form tissues, such as the bark of a tree. And plant cells work together ...
A1984SU44500002
... the recirculating pool, and antibody-secreting cells. Using F1 hybrid-parental combinations and appropriate antisera, it was found that inoculated thymocytes were not the precursors of antibody-secreting cells.6 However, these studies did not establish the immediate organ of origin of antibody forme ...
... the recirculating pool, and antibody-secreting cells. Using F1 hybrid-parental combinations and appropriate antisera, it was found that inoculated thymocytes were not the precursors of antibody-secreting cells.6 However, these studies did not establish the immediate organ of origin of antibody forme ...
Unit 2: Multi-cellular organisms
... Variation exists amongst the members of a species. When a characteristic can be used to divide the species into distinct groups, it is said to show DISCRETE variation. When the characteristic varies in an UNINTERRUPTED way from one extreme to the other, it is said to show CONTINUOUS variation. ...
... Variation exists amongst the members of a species. When a characteristic can be used to divide the species into distinct groups, it is said to show DISCRETE variation. When the characteristic varies in an UNINTERRUPTED way from one extreme to the other, it is said to show CONTINUOUS variation. ...
Cillia and flagella
... complex organisms ,the fate of the cell becomes more and more restricted as it divides ,through a process called differentiation .Initially ,a cell is capable of performing a variety of functions but as the cell differentiation (literally ,becomes different ),its progressively losses some of its abi ...
... complex organisms ,the fate of the cell becomes more and more restricted as it divides ,through a process called differentiation .Initially ,a cell is capable of performing a variety of functions but as the cell differentiation (literally ,becomes different ),its progressively losses some of its abi ...
organs-on-a-chip - Federation of American Societies for
... magine if, before you ever took a drug, doctors could predict which drug would work best for you, because they already had information on how organs in your body were likely to respond. Organs-on-a-chip research is bringing that day closer. This emerging technology allows scientists to watch the cas ...
... magine if, before you ever took a drug, doctors could predict which drug would work best for you, because they already had information on how organs in your body were likely to respond. Organs-on-a-chip research is bringing that day closer. This emerging technology allows scientists to watch the cas ...
Adult Stem Cells
... Adult cells that have been reprogrammed to an embryonic stem cell-like state By enforced expression of genes and factors important for maintaining the defining properties of embyonic stem cells ...
... Adult cells that have been reprogrammed to an embryonic stem cell-like state By enforced expression of genes and factors important for maintaining the defining properties of embyonic stem cells ...
Identify cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organisms
... Cells A structural unit of all living things. The smallest unit classified as an living organism. ...
... Cells A structural unit of all living things. The smallest unit classified as an living organism. ...
STUDY GUIDE FOR CELLS
... Specialized Cells-Cells made or used for one particular purpose. Example: Muscles cells are specialized to help move your body. Because multicellular cells are specialized (focus on one job), then they depend on other cells to help them survive. Cell- The smallest part of a living thing that can car ...
... Specialized Cells-Cells made or used for one particular purpose. Example: Muscles cells are specialized to help move your body. Because multicellular cells are specialized (focus on one job), then they depend on other cells to help them survive. Cell- The smallest part of a living thing that can car ...
Blood
... In man and in all mammals: they are devoid of a nucleus In the other vertebrates: they have a nucleus the lack of nucleus allows more room for hemoglobin => the shape of a biconcave lens raises the surface and cytoplasm volume ratio. => more efficient the diffusion of oxygen The mean life is about 1 ...
... In man and in all mammals: they are devoid of a nucleus In the other vertebrates: they have a nucleus the lack of nucleus allows more room for hemoglobin => the shape of a biconcave lens raises the surface and cytoplasm volume ratio. => more efficient the diffusion of oxygen The mean life is about 1 ...
Word
... used to fuel all of the body’s activities. The lower right chamber of the heart that pumps blood to the lungs for gas exchange. The smallest functioning units of the lungs in which gas exchange takes place. The smallest and thinnest blood vessels, which surround all of your body’s cells. The special ...
... used to fuel all of the body’s activities. The lower right chamber of the heart that pumps blood to the lungs for gas exchange. The smallest functioning units of the lungs in which gas exchange takes place. The smallest and thinnest blood vessels, which surround all of your body’s cells. The special ...
Hematopoietic stem cell
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are the blood cells that give rise to all the other blood cells and are derived from mesoderm. They are located in the red bone marrow, which is contained in the core of most bones.They give rise to both the myeloid and lymphoid lineages of blood cells. (Myeloid cells include monocytes, macrophages, neutrophils, basophils, eosinophils, erythrocytes, dendritic cells, and megakaryocytes or platelets. Lymphoid cells include T cells, B cells, and natural killer cells.) The definition of hematopoietic stem cells has changed in the last two decades. The hematopoietic tissue contains cells with long-term and short-term regeneration capacities and committed multipotent, oligopotent, and unipotent progenitors. HSCs constitute 1:10.000 of cells in myeloid tissue.HSCs are a heterogeneous population. The third category consists of the balanced (Bala) HSC, whose L/M ratio is between 3 and 10. Only the myeloid-biased and -balanced HSCs have durable self-renewal properties. In addition, serial transplantation experiments have shown that each subtype preferentially re-creates its blood cell type distribution, suggesting an inherited epigenetic program for each subtype.HSC studies through much of the past half century have led to a much deeper understanding. More recent advances have resulted in the use of HSC transplants in the treatment of cancers and other immune system disorders.