Greece Test Review Power Point
... Greece, it had its golden age under the ruler Pericles. The thing that set Athens apart from the other city-states was its government. Athens was a ...
... Greece, it had its golden age under the ruler Pericles. The thing that set Athens apart from the other city-states was its government. Athens was a ...
Art in the Classroom, January 2013 Subject: Ancient Architecture
... became such a problem that Egyptians stopped building pyramids after this era. Ancient Egyptians didn't bury their Pharoahs and return to their lives. They built cities around the pyramid during its construction called Pyramid Cities which were paid for by the Pharoahs during their lifetimes -- ther ...
... became such a problem that Egyptians stopped building pyramids after this era. Ancient Egyptians didn't bury their Pharoahs and return to their lives. They built cities around the pyramid during its construction called Pyramid Cities which were paid for by the Pharoahs during their lifetimes -- ther ...
Golden Age of Athens
... The _______, dramatic and comedic plays, has its origin in Ancient Greece as _________ _________. During the Golden Age Greek drama became entertainment as ________, _________, and _________, wrote _________ to teach Athenians lessons about life. ____________ wrote ________, or humorous stories with ...
... The _______, dramatic and comedic plays, has its origin in Ancient Greece as _________ _________. During the Golden Age Greek drama became entertainment as ________, _________, and _________, wrote _________ to teach Athenians lessons about life. ____________ wrote ________, or humorous stories with ...
Greek Art and Architecture
... i. Most extinct from . . . 1. Built of _________, mud or brick 2. Nothing left except … ii. By 700 BC, populations large enough … iii. Stone, marble used for _____________________ b. Classical Architecture – three styles i. Doric style 1. Earliest style 2. Formal, austere 3. Spread from . . . 4. Sty ...
... i. Most extinct from . . . 1. Built of _________, mud or brick 2. Nothing left except … ii. By 700 BC, populations large enough … iii. Stone, marble used for _____________________ b. Classical Architecture – three styles i. Doric style 1. Earliest style 2. Formal, austere 3. Spread from . . . 4. Sty ...
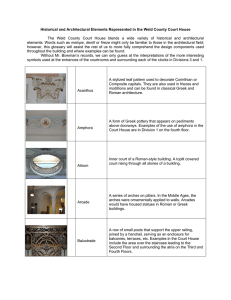
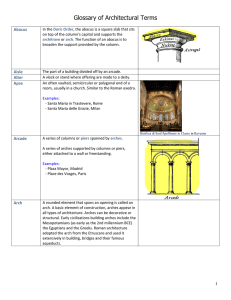
Glossary of Architectural Terms
... The Crystal Palace was a cast-iron and plate-glass building originally erected in Hyde Park, London, England, to house the Great Exhibition of 1851. More than 14,000 exhibitors from around the world gathered in the Palace's 990,000 square feet (92,000 m2) of exhibition space to display examples of t ...
... The Crystal Palace was a cast-iron and plate-glass building originally erected in Hyde Park, London, England, to house the Great Exhibition of 1851. More than 14,000 exhibitors from around the world gathered in the Palace's 990,000 square feet (92,000 m2) of exhibition space to display examples of t ...
greek architecture 2 - Norwell Public Schools
... way would have meant the house would have fallen down. ❖ The Greeks used columns to support their houses. ...
... way would have meant the house would have fallen down. ❖ The Greeks used columns to support their houses. ...
greek architecture
... prehistoric way would have meant the house would have fallen down. The Greeks used columns to support their houses. ...
... prehistoric way would have meant the house would have fallen down. The Greeks used columns to support their houses. ...
Athenian Treasury - Michael C. Carlos Museum
... Here columns were placed across the front of building. At other times they were used on all sides. The top of a Greek column is called a capital. In ancient Greece, capitals came in three different styles; Doric, Ionic and Corinthian. The Athenian Treasury has Doric columns —the simplest of the thre ...
... Here columns were placed across the front of building. At other times they were used on all sides. The top of a Greek column is called a capital. In ancient Greece, capitals came in three different styles; Doric, Ionic and Corinthian. The Athenian Treasury has Doric columns —the simplest of the thre ...
Classical order

""An Order in architecture is a certain assemblage of parts subject to uniform established proportions, regulated by the office that each part has to perform"".The Architectural Orders are the ancient styles of classical architecture, each distinguished by its proportions and characteristic profiles and details, and most readily recognizable by the type of column employed. Three ancient orders of architecture—the Doric, Ionic, and Corinthian—originated in Greece. To these the Romans added the Tuscan, which they made simpler than Doric, and the Composite, which was more ornamental than the Corinthian. The Architectural Order of a classical building is akin to the mode or key of classical music, the grammar or rhetoric of a written composition. It is established by certain modules like the intervals of music, and it raises certain expectations in an audience attuned to its language.