Ch 5 Part 2 - SchoolRack
... Pericles gave a speech at the funeral of Athenians slain in battle. This speech is considered one of the earliest & greatest expressions of ...
... Pericles gave a speech at the funeral of Athenians slain in battle. This speech is considered one of the earliest & greatest expressions of ...
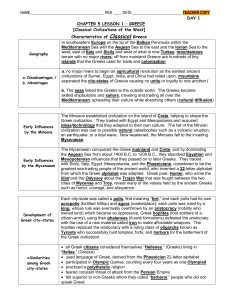
The Early Greeks (p. 117-123) The Geography of Greece What
... Dangers of traveling by land included rocks that could shatter wooden wheels and attack by bandits. Dangers of traveling by sea included attack by pirates, robbery by sailors, and storms that could drive ships into rocks. The Minoans ...
... Dangers of traveling by land included rocks that could shatter wooden wheels and attack by bandits. Dangers of traveling by sea included attack by pirates, robbery by sailors, and storms that could drive ships into rocks. The Minoans ...
What can we learn about the Ancient Greeks L1
... • Ancient Greece was split into many different states, each one was ruled in its own way. Each state had its own laws, government and money but they shared the same language and religion. The two most important city states were Athens and Sparta. ...
... • Ancient Greece was split into many different states, each one was ruled in its own way. Each state had its own laws, government and money but they shared the same language and religion. The two most important city states were Athens and Sparta. ...
on Greek mainland
... ideas/technology that they adapted to their own culture. The fall of the Minoan civilization was due to possible natural catastrophes such as a volcanic eruption, an earthquake, or a tidal wave. Now weakened, the Minoans fell to the invading Mycenaean. The Mycenaean conquered the Greek mainland and ...
... ideas/technology that they adapted to their own culture. The fall of the Minoan civilization was due to possible natural catastrophes such as a volcanic eruption, an earthquake, or a tidal wave. Now weakened, the Minoans fell to the invading Mycenaean. The Mycenaean conquered the Greek mainland and ...
Chapter 4 Ancient Greece Hardcopy Notes
... His first victory was against the Persians, went on to conquer all of Asia Minor, Egypt, and Mesopotamia. ...
... His first victory was against the Persians, went on to conquer all of Asia Minor, Egypt, and Mesopotamia. ...
Ancient Greece 1900 * 133 BC
... • Hellenistic Era – imitate the Greeks • Alexander’s empire fell apart after his death • Greek cities of Hellenistic Era helped expand Greek culture ...
... • Hellenistic Era – imitate the Greeks • Alexander’s empire fell apart after his death • Greek cities of Hellenistic Era helped expand Greek culture ...
Name - Humble ISD
... Courage & mastery of __________________ tactics His example _____________________ men to follow him *Due to his conquests, _______________ language, architecture, literature & art spread throughout Southwest Asia & the near East III. The Hellenistic Kingdoms *Alexander created a new age, the ...
... Courage & mastery of __________________ tactics His example _____________________ men to follow him *Due to his conquests, _______________ language, architecture, literature & art spread throughout Southwest Asia & the near East III. The Hellenistic Kingdoms *Alexander created a new age, the ...
The Renaissance Period
... Much of the inspiration for music in the Renaissance period came from ancient Greek approaches to the arts. ...
... Much of the inspiration for music in the Renaissance period came from ancient Greek approaches to the arts. ...
Greek Civilization Geography of Greece and Crete Greece is located
... d. Drama is the aspect of literature where the Greeks made their greatest literary contribution. They performed plays called tragedies (stories of human suffering) and comedies ( satires that mocked people and customs). The fact that Greek leaders allowed comedies to make fun of or criticize their p ...
... d. Drama is the aspect of literature where the Greeks made their greatest literary contribution. They performed plays called tragedies (stories of human suffering) and comedies ( satires that mocked people and customs). The fact that Greek leaders allowed comedies to make fun of or criticize their p ...
Philip II of Macedonia
... The Greeks objected to equal treatment for Persians and looked down on people who did not speak Greek or follow Greek customs. They called such people barbaroi, from which the word “barbarians” comes. Alexander’s attempt to achieve unity among the people in his empire was not successful. Alexander ...
... The Greeks objected to equal treatment for Persians and looked down on people who did not speak Greek or follow Greek customs. They called such people barbaroi, from which the word “barbarians” comes. Alexander’s attempt to achieve unity among the people in his empire was not successful. Alexander ...
Ancient Greek Theatre
... Most Greek cities had a theatre. They had no ceilings so if it rained (sorry) you had to put up with it the show would go on. ...
... Most Greek cities had a theatre. They had no ceilings so if it rained (sorry) you had to put up with it the show would go on. ...
classical greece
... “Cradle of Western Civilization” Greek civilization would not only dominate the region; it would ultimately extend the influence of Greek culture over most of the Western world. ...
... “Cradle of Western Civilization” Greek civilization would not only dominate the region; it would ultimately extend the influence of Greek culture over most of the Western world. ...
World History Unit 4 – “Empires and Kingdoms: Growth and
... the site of Byzantium was ideally located to serve as a transit and trade point between Europe and Asia Minor In 330 A.D., Roman Emperor Constantine I chose Byzantium as the site of a new Roman capital, Constantinople Five years earlier, at the Council of Nicaea, Constantine had established Christia ...
... the site of Byzantium was ideally located to serve as a transit and trade point between Europe and Asia Minor In 330 A.D., Roman Emperor Constantine I chose Byzantium as the site of a new Roman capital, Constantinople Five years earlier, at the Council of Nicaea, Constantine had established Christia ...
Ancient_Greece - WordPress.com
... Since Greek coastal cities were sandwiched between the ocean and the sea, they developed an awesome navy for trading and ...
... Since Greek coastal cities were sandwiched between the ocean and the sea, they developed an awesome navy for trading and ...
Chapter 2 The Cultural Context of
... • the Golden Age of Greece brought us the statesman Pericles, the philosophers Socrates, Plato and Aristotle • once the Persian threat receded, the Greeks were divided – one lead by Sparta a military state ruled by aristocracy and the other by democratic Athens • a ruinous conflict known as the Pelo ...
... • the Golden Age of Greece brought us the statesman Pericles, the philosophers Socrates, Plato and Aristotle • once the Persian threat receded, the Greeks were divided – one lead by Sparta a military state ruled by aristocracy and the other by democratic Athens • a ruinous conflict known as the Pelo ...
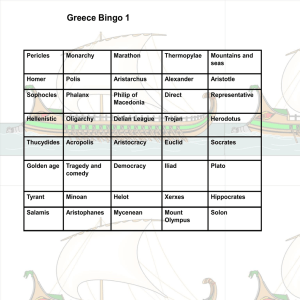
Greece Bingo (Review) - Mr. George Academics
... battle in the Persian wars where the Athenian navy defeated the ...
... battle in the Persian wars where the Athenian navy defeated the ...
The Spread of Greek Culture (p
... river and he returned home in 323B.C. and died at age 33 H. After his death, his generals divided up his empire into smaller dynasties and the empire continued to prosper ...
... river and he returned home in 323B.C. and died at age 33 H. After his death, his generals divided up his empire into smaller dynasties and the empire continued to prosper ...
Introduction Athenaze Introduction Learning Objectives: • the Greek
... Ages (e.g., epsilon and upsilon, which were employed to distinguish ε from the similarly pronounced αι, and υ from οι). • only the capital letters would have been employed in the classical period. The lower-case letters that we now use date to the 9th century AD. • in modern editions of ancient text ...
... Ages (e.g., epsilon and upsilon, which were employed to distinguish ε from the similarly pronounced αι, and υ from οι). • only the capital letters would have been employed in the classical period. The lower-case letters that we now use date to the 9th century AD. • in modern editions of ancient text ...
Greece
... 1. Euclid was an important ______ and a a excellent in _______. 2. _________ and ________ were Greek historians. 3. Athens government had a council of ________. 4. _______ were conquered Messenians that were forced to stay and work for the Spartans. 5.________ was a military state. 6.The Peloponnesi ...
... 1. Euclid was an important ______ and a a excellent in _______. 2. _________ and ________ were Greek historians. 3. Athens government had a council of ________. 4. _______ were conquered Messenians that were forced to stay and work for the Spartans. 5.________ was a military state. 6.The Peloponnesi ...
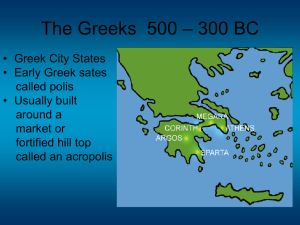
The Greeks 500 – 300 BC
... “Lovers of Wisdom” • Socrates, known through the writings of his student Plato • Plato continued the “Socratic method” of questioning followed by the Academy founded by Socrates • Aristotle, one of Plato’s brightest students, opened his own school the Lyceum and was the teacher of Alexander the Grea ...
... “Lovers of Wisdom” • Socrates, known through the writings of his student Plato • Plato continued the “Socratic method” of questioning followed by the Academy founded by Socrates • Aristotle, one of Plato’s brightest students, opened his own school the Lyceum and was the teacher of Alexander the Grea ...
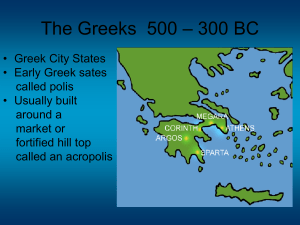
The Greeks 500 – 300 BC
... “Lovers of Wisdom” • Socrates, known through the writings of his student Plato • Plato continued the “Socratic method” of questioning followed by the Academy founded by Socrates • Aristotle, one of Plato’s brightest students, opened his own school the Lyceum and was the teacher of Alexander the Grea ...
... “Lovers of Wisdom” • Socrates, known through the writings of his student Plato • Plato continued the “Socratic method” of questioning followed by the Academy founded by Socrates • Aristotle, one of Plato’s brightest students, opened his own school the Lyceum and was the teacher of Alexander the Grea ...
Jeopardy Bill Patton
... This is a writing system of symbols which was brought from Egypt to ancient Greece. It is easily indentified by the names of the first two Greek characters, alpha and beta. ...
... This is a writing system of symbols which was brought from Egypt to ancient Greece. It is easily indentified by the names of the first two Greek characters, alpha and beta. ...
Greece Study Guide KEY - Warren County Schools
... 6. How was ancient Greek democracy different from democracy in the United States today? citizens voted directly on all issues 7. The word “philosophy” comes from the Greek word for: “love of wisdom” 8. How was ancient Greek democracy different from American democracy? all citizens voted on every iss ...
... 6. How was ancient Greek democracy different from democracy in the United States today? citizens voted directly on all issues 7. The word “philosophy” comes from the Greek word for: “love of wisdom” 8. How was ancient Greek democracy different from American democracy? all citizens voted on every iss ...
Empires and Civilizations in Collision: The Persians and the Greeks
... Hellenistic Era 3. Alexander died in 323 B.C.E.; empire divided into three kingdoms, ruled by Macedonian generals 4. Alexander’s conquests were most important in terms of world history for creation of the Hellenistic era (323–30 B.C.E.) a. dissemination of Greek culture through much of Asia and Egyp ...
... Hellenistic Era 3. Alexander died in 323 B.C.E.; empire divided into three kingdoms, ruled by Macedonian generals 4. Alexander’s conquests were most important in terms of world history for creation of the Hellenistic era (323–30 B.C.E.) a. dissemination of Greek culture through much of Asia and Egyp ...
Greek contributions to Islamic world

Greece played an important role in the transmission of classical knowledge to the Islamic world and to Renaissance Italy, and also in the transmission of medieval Arabic science to Renaissance Italy. Its rich historiographical tradition preserved ancient knowledge upon which art, architecture, literature and technological achievements were built.