Chapter 6: Ancient Greece (Notes and Study Guide)
... The Persians Invade 9. The founder of the Persian Empire was ______________________. 10. The Persian invade Greece just north of ___________, where they sat and waited to attack. a. Although the Persians had a lot more people, the _____________ surprisingly attacked them and caught them off guard, e ...
... The Persians Invade 9. The founder of the Persian Empire was ______________________. 10. The Persian invade Greece just north of ___________, where they sat and waited to attack. a. Although the Persians had a lot more people, the _____________ surprisingly attacked them and caught them off guard, e ...
Τίτλος Μαθήματος - E-Course
... be a remnant of a more widespread Arcado-Cypriot-like dialect from the second millennium BC. Somewhat later, in the 8th century BC, a period of massive c__________ began, spreading Greek all over the eastern Mediterranean, with colonists from mainland localities transplanting their dialect abroad, s ...
... be a remnant of a more widespread Arcado-Cypriot-like dialect from the second millennium BC. Somewhat later, in the 8th century BC, a period of massive c__________ began, spreading Greek all over the eastern Mediterranean, with colonists from mainland localities transplanting their dialect abroad, s ...
Sparta vs Athens
... SPARTAN WOMEN Emotionally, physically tough; were taught strength, athletics Family life less important; husbands, wives usually apart More freedom than elsewhere, allowed to own property ...
... SPARTAN WOMEN Emotionally, physically tough; were taught strength, athletics Family life less important; husbands, wives usually apart More freedom than elsewhere, allowed to own property ...
ANCIENT AND CLASSICAL GREECE
... Olive oil, wine, in exchange for grain and other items Trade brought prosperity, population growth, colonization ...
... Olive oil, wine, in exchange for grain and other items Trade brought prosperity, population growth, colonization ...
unit one classical art review
... The Discus Thrower First made by Myron in 460-450 BC. The original Greek bronze is lost but the work is known through numerous Roman copies. This athlete is depicted about to release his throw: "by sheer intelligence" and shows the cultures desire for rhythmos, harmony and balance. (source: Wikiped ...
... The Discus Thrower First made by Myron in 460-450 BC. The original Greek bronze is lost but the work is known through numerous Roman copies. This athlete is depicted about to release his throw: "by sheer intelligence" and shows the cultures desire for rhythmos, harmony and balance. (source: Wikiped ...
The Persian War
... his bravery – as well as the long-haired Persian – who remembers it well.” Epitaph of Aeschylus Where were the Spartans? ...
... his bravery – as well as the long-haired Persian – who remembers it well.” Epitaph of Aeschylus Where were the Spartans? ...
Classical Greece
... Gods and Heroes The gods were powerful, but they were not perfect. They often got jealous or made mistakes. Most Greeks worshipped the same gods, but each polis also claimed one god or goddess as its protector. In addition, all Greeks considered some locations sacred, such as Delphi, where priestes ...
... Gods and Heroes The gods were powerful, but they were not perfect. They often got jealous or made mistakes. Most Greeks worshipped the same gods, but each polis also claimed one god or goddess as its protector. In addition, all Greeks considered some locations sacred, such as Delphi, where priestes ...
WHPP Unit 1 Section 8 Greece
... b/w Mycenae (Greeks) & Troy. • Fought over trade routes. • Homer (700 BCE)—story teller of ancient Greece • Orator • Verbal histories become epics (tall tales with heroes and villains with a lesson) the “Iliad and the Odyssey”. • Odysseus and Achilles – These guys fought at the battle of Troy and re ...
... b/w Mycenae (Greeks) & Troy. • Fought over trade routes. • Homer (700 BCE)—story teller of ancient Greece • Orator • Verbal histories become epics (tall tales with heroes and villains with a lesson) the “Iliad and the Odyssey”. • Odysseus and Achilles – These guys fought at the battle of Troy and re ...
Chapter 6
... of Mycenaean culture Height of power around 1400 BC Earned power through conquest ...
... of Mycenaean culture Height of power around 1400 BC Earned power through conquest ...
THE PERSIAN WARS
... Persian Empire. • Xerxes spent four years planning his attack, building the fleet, and assembling troops. • When news of his massive army spread across Greece, weaker city-states submitted immediately to Persian rule, fearing all out annihilation. • Xerxes had assembled the largest army ever seen. ...
... Persian Empire. • Xerxes spent four years planning his attack, building the fleet, and assembling troops. • When news of his massive army spread across Greece, weaker city-states submitted immediately to Persian rule, fearing all out annihilation. • Xerxes had assembled the largest army ever seen. ...
Ancient Greece
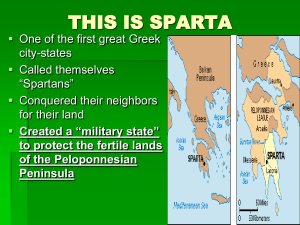
... see if they were fit to live. • Those unfit were left on a mountain side to die. • Taken from mother at the age of 7 and put under control of the state. • Boys lived in military barracks and treated harshly to toughen them and make them mean. • Their education was based on military training and obed ...
... see if they were fit to live. • Those unfit were left on a mountain side to die. • Taken from mother at the age of 7 and put under control of the state. • Boys lived in military barracks and treated harshly to toughen them and make them mean. • Their education was based on military training and obed ...
The Civilization of the Greeks
... • Hired Soldiers to maintain power • Built new marketplaces, temples, and walls ...
... • Hired Soldiers to maintain power • Built new marketplaces, temples, and walls ...
The Persian Wars
... his father’s defeat. • In 480 BC, his army of 360,000 foot soldiers and 800 ships marched over a bridge across the Dardanelles ...
... his father’s defeat. • In 480 BC, his army of 360,000 foot soldiers and 800 ships marched over a bridge across the Dardanelles ...
A short tract on first principles
... 1. How did early Greeks explain phenomena such as a storm at sea or thunder? The early Greeks looked to their gods for explain nations of such natural occurrences, so a storm at sea was caused by the anger of the sea god Poseidon, and a thunderstorm meant the Zeus was throwing his thunderbolt. 2. Wh ...
... 1. How did early Greeks explain phenomena such as a storm at sea or thunder? The early Greeks looked to their gods for explain nations of such natural occurrences, so a storm at sea was caused by the anger of the sea god Poseidon, and a thunderstorm meant the Zeus was throwing his thunderbolt. 2. Wh ...
Reflective Essay
... were willing to look past what he had done to them by changing his allegiance and defecting from Athens to Sparta and then from Sparta to Persia, they were willing to allow him to come back with full honors as if he never left. They did this because he redeemed himself with what he did to the Persia ...
... were willing to look past what he had done to them by changing his allegiance and defecting from Athens to Sparta and then from Sparta to Persia, they were willing to allow him to come back with full honors as if he never left. They did this because he redeemed himself with what he did to the Persia ...
The Trojan, Persian, and Peloponnesian Wars
... The Persian Wars • Who: The Persian Empire, ruled by Darius I and Ancient Greece led by Athens & Sparta • When: 490-479 BCE • Where: Marathon, Thermopylae, Salamis, and Plataea all in Greece. • Why: Bragging rights for conquering Greece, revenge for Greece’s attack on Sardis, & to stop the Greek ba ...
... The Persian Wars • Who: The Persian Empire, ruled by Darius I and Ancient Greece led by Athens & Sparta • When: 490-479 BCE • Where: Marathon, Thermopylae, Salamis, and Plataea all in Greece. • Why: Bragging rights for conquering Greece, revenge for Greece’s attack on Sardis, & to stop the Greek ba ...
Greece and Iran - Willis High School
... • Fear of slave uprising caused Spartans to create a severe and highly militarized society in which all Spartan males trained for the army. ...
... • Fear of slave uprising caused Spartans to create a severe and highly militarized society in which all Spartan males trained for the army. ...
5. CH 5 NOTES
... *Greeks: build a wooden horse o hid soldiers inside *Attack: Troy is destroyed. *Achilles: dies in battle o The Odyssey *The Odyssey: Aftermath of Trojan War *Odysseus: Mycenaean King story of his journey home Travels for 10 years *Gods cause problems Purpose of Greek Religion o Expl ...
... *Greeks: build a wooden horse o hid soldiers inside *Attack: Troy is destroyed. *Achilles: dies in battle o The Odyssey *The Odyssey: Aftermath of Trojan War *Odysseus: Mycenaean King story of his journey home Travels for 10 years *Gods cause problems Purpose of Greek Religion o Expl ...
Focus on Ancient Greek objects
... ‘Painters’; function and shape; black, red figure ware and white ground pottery Themes of decorated pottery: the Trojan war, mythology, daily life Religion: god and goddesses, their roles and significance, worship and sacrifice Explore the roles of different members of society: women, men, children, ...
... ‘Painters’; function and shape; black, red figure ware and white ground pottery Themes of decorated pottery: the Trojan war, mythology, daily life Religion: god and goddesses, their roles and significance, worship and sacrifice Explore the roles of different members of society: women, men, children, ...
The Glory That Was Greece
... The ancient city of Troy, setting for the Trojan War, was located in modern-day __________. ...
... The ancient city of Troy, setting for the Trojan War, was located in modern-day __________. ...
kalokagathia
... There was no single institution; rather, each activity was carried out in a separate place. The young boy of privileged rank would be taken by a kind of chaperon, the paidagogos, who was generally a respected slave within the parents’ household. The elements of literacy were taught by the writing m ...
... There was no single institution; rather, each activity was carried out in a separate place. The young boy of privileged rank would be taken by a kind of chaperon, the paidagogos, who was generally a respected slave within the parents’ household. The elements of literacy were taught by the writing m ...
Greece and Iran, 1000 – 30 BC - The Official Site - Varsity.com
... a middle class led to the emergence in the mid-seventh and sixth centuries b.c.e. of one-man rule by tyrants reduced the power of traditional elites. tyrants were eventually ejected and government developed in one of two directions: oligarchy or democracy. ...
... a middle class led to the emergence in the mid-seventh and sixth centuries b.c.e. of one-man rule by tyrants reduced the power of traditional elites. tyrants were eventually ejected and government developed in one of two directions: oligarchy or democracy. ...
Ancient Greek religion

Ancient Greek religion encompasses the collection of beliefs, rituals, and mythology originating in ancient Greece in the form of both popular public religion and cult practices. These different groups varied enough for it to be possible to speak of Greek religions or ""cults"" in the plural, though most of them shared similarities.Many of the ancient Greek people recognized the major (Olympian) gods and goddesses (Zeus, Poseidon, Hades, Apollo, Artemis, Aphrodite, Ares, Dionysus, Hephaestus, Athena, Hermes, Demeter, Hestia, and Hera), although philosophies such as Stoicism and some forms of Platonism used language that seems to posit a transcendent single deity. Different cities often worshiped the same deities, sometimes with epithets that distinguished them and specified their local nature.The religious practices of the Greeks extended beyond mainland Greece, to the islands and coasts of Ionia in Asia Minor, to Magna Graecia (Sicily and southern Italy), and to scattered Greek colonies in the Western Mediterranean, such as Massalia (Marseille). Greek religion was tempered by Etruscan cult and belief to form much of the later Ancient Roman religion.