Lecture 9: Limiting and Clamping Diode Circuits. Voltage Doubler
... net charge per period so it would never “charge up” to 6 V. Note that here we are looking at the steady state response. It may take a few periods for the capacitor to completely charge. We’re not looking at the transient response. There are two applications of the clamped capacitor circuit discussed ...
... net charge per period so it would never “charge up” to 6 V. Note that here we are looking at the steady state response. It may take a few periods for the capacitor to completely charge. We’re not looking at the transient response. There are two applications of the clamped capacitor circuit discussed ...
Document
... Modular multilevel converter (MMC) is a promising new topology for highvoltage applications. The MMC is made of several identical submodules. For proper operation, each submodule can be considered as a controlled voltage source where capacitor’s voltage should be maintained at a certain level. Besid ...
... Modular multilevel converter (MMC) is a promising new topology for highvoltage applications. The MMC is made of several identical submodules. For proper operation, each submodule can be considered as a controlled voltage source where capacitor’s voltage should be maintained at a certain level. Besid ...
Concepts
... In the mystery box at right, we can put a 2.0 F capacitor, a 4.0 H inductor, or both (in series). Which one will cause the greatest current to flow through the circuit? A) The capacitor B) The inductor C) both D) Insufficient information ...
... In the mystery box at right, we can put a 2.0 F capacitor, a 4.0 H inductor, or both (in series). Which one will cause the greatest current to flow through the circuit? A) The capacitor B) The inductor C) both D) Insufficient information ...
Video Transcript - Rose
... R1’s resistance is the voltage across it by the current through it. This gives R1 = 2 kΩ because V/mA = kΩ. R2’s value is 3 kΩ. For v3 and v4, we know the total voltage across the two is v4 + v3. From the given equation, we know that v4 = 2*v3 because their ratio is 2:1. Set our equation equal to 6 ...
... R1’s resistance is the voltage across it by the current through it. This gives R1 = 2 kΩ because V/mA = kΩ. R2’s value is 3 kΩ. For v3 and v4, we know the total voltage across the two is v4 + v3. From the given equation, we know that v4 = 2*v3 because their ratio is 2:1. Set our equation equal to 6 ...
DN367 - Tiny Versatile Buck Regulators Operate from 3.6V to 36V Input
... LT1936 Produces 3.3V at 1.2A from 4.5V to 36V Figure 1 shows a typical application for the LT1936. This circuit generates 3.3V at 1.2A from an input of 4.5V to 36V. With the same input voltage range, the LT1933 circuit can supply 500mA. The typical output voltage ripple of the Figure 1 circuit is le ...
... LT1936 Produces 3.3V at 1.2A from 4.5V to 36V Figure 1 shows a typical application for the LT1936. This circuit generates 3.3V at 1.2A from an input of 4.5V to 36V. With the same input voltage range, the LT1933 circuit can supply 500mA. The typical output voltage ripple of the Figure 1 circuit is le ...
High-efficiency SMPS using half-bridge resonant topology
... Based on leading edge power supply ICs, ST offers an advanced SMPS architecture designed for high-end LCD and PDP TVs. The architecture is based on an innovative front-end PFC stage, a high efficiency multi-resonant half-bridge converter stage and an auxiliary low consumption flyback converter, all ...
... Based on leading edge power supply ICs, ST offers an advanced SMPS architecture designed for high-end LCD and PDP TVs. The architecture is based on an innovative front-end PFC stage, a high efficiency multi-resonant half-bridge converter stage and an auxiliary low consumption flyback converter, all ...
Inductor Discharging
... • This makes the voltage drop across the resistor drop, so current in the circuit drops. ...
... • This makes the voltage drop across the resistor drop, so current in the circuit drops. ...
little-engineers-09
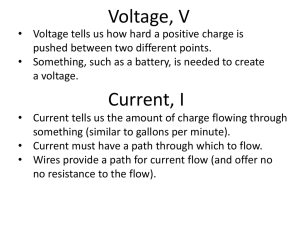
... • Current tells us the amount of charge flowing through something (similar to gallons per minute). • Current must have a path through which to flow. • Wires provide a path for current flow (and offer no no resistance to the flow). ...
... • Current tells us the amount of charge flowing through something (similar to gallons per minute). • Current must have a path through which to flow. • Wires provide a path for current flow (and offer no no resistance to the flow). ...
ad-series-mains-power-supplies
... The AD Series units may be used to supply mobile radios and other appliances from AC mains used in offices, portable site cabins, communication cabins, telephone exchanges, remote antennae sites, ships, oil rigs etc. The units will accept either European 230Vac or US 115Vac inputs and are available ...
... The AD Series units may be used to supply mobile radios and other appliances from AC mains used in offices, portable site cabins, communication cabins, telephone exchanges, remote antennae sites, ships, oil rigs etc. The units will accept either European 230Vac or US 115Vac inputs and are available ...
Product Sheet MKP-C1X-9,5-75
... Creepage between terminals (mm): 16 Clearance (mm): 11 Box qty (pcs): 36 ...
... Creepage between terminals (mm): 16 Clearance (mm): 11 Box qty (pcs): 36 ...
The Flyback Converter
... current is now distributed between the windings differently. The magnetic fields inside the inductor in both cases are identical. Although the two-winding magnetic device is represented using the same symbol as the transformer, a more descriptive name is “twowinding inductor”. This device is someti ...
... current is now distributed between the windings differently. The magnetic fields inside the inductor in both cases are identical. Although the two-winding magnetic device is represented using the same symbol as the transformer, a more descriptive name is “twowinding inductor”. This device is someti ...
Introduction to Power Electronics students version 2
... wider. There are already many power semiconductor devices that are commercially available, however, the development in this direction is continuing. • The power semiconductor devices or power electronic converter fall generally into four categories : -AC to DC Converter (Controlled Rectifier) -DC to ...
... wider. There are already many power semiconductor devices that are commercially available, however, the development in this direction is continuing. • The power semiconductor devices or power electronic converter fall generally into four categories : -AC to DC Converter (Controlled Rectifier) -DC to ...
i C
... if yes - output choke is ready eventualy try with the smaller core if it is to much free room in the window area ...
... if yes - output choke is ready eventualy try with the smaller core if it is to much free room in the window area ...
Buck converter
A buck converter is a voltage step down and current step up converter.The simplest way to reduce the voltage of a DC supply is to use a linear regulator (such as a 7805), but linear regulators waste energy as they operate by dissipating excess power as heat. Buck converters, on the other hand, can be remarkably efficient (95% or higher for integrated circuits), making them useful for tasks such as converting the main voltage in a computer (12V in a desktop, 12-24V in a laptop) down to the 0.8-1.8V needed by the processor.