henrichs-sinking particles
... Bottom Line The data indicate that the spring bloom may not be the predominant source of organic matter to the Bering Sea middle shelf. ...
... Bottom Line The data indicate that the spring bloom may not be the predominant source of organic matter to the Bering Sea middle shelf. ...
Chapters 12 and 13
... • The bacteria form the base of the food web • Large, mouthless (and gutless!) tube worms house the bacteria and in return for shelter, obtain nourishment from the bacteria • Large abundances of shrimp feed on the ...
... • The bacteria form the base of the food web • Large, mouthless (and gutless!) tube worms house the bacteria and in return for shelter, obtain nourishment from the bacteria • Large abundances of shrimp feed on the ...
Oceanography Seminar-Oscar Abraham Sosa (PDF)
... the biogeochemistry and ecology of the ocean because it sustains great part of bacterial life in the sea. Bacteria, in the process of consuming and decomposing marine organic matter, return carbon dioxide (through respiration) and inorganic nutrients to the water column making them key regulators of ...
... the biogeochemistry and ecology of the ocean because it sustains great part of bacterial life in the sea. Bacteria, in the process of consuming and decomposing marine organic matter, return carbon dioxide (through respiration) and inorganic nutrients to the water column making them key regulators of ...
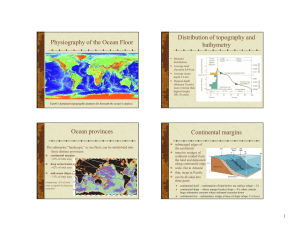
Physiography of the Ocean Floor Distribution of topography and
... continental slope – where margin breaks (slope ~ 4o); often contain huge submarine canyons where sediment cascades down continental rise – sedimentary wedge at base of slope (slope 1o or less) ...
... continental slope – where margin breaks (slope ~ 4o); often contain huge submarine canyons where sediment cascades down continental rise – sedimentary wedge at base of slope (slope 1o or less) ...
Ocean The World Ocean Ocean Floor Features
... 1 recognize how marine organisms can be classified. 2 differentiate between plankton and nekton. 3 describe the area of the ocean in which most benthic organisms live. 4 list the factors used to divide the ocean into marine zones. Ocean Productivity 1 list the factors that influence a region’s photo ...
... 1 recognize how marine organisms can be classified. 2 differentiate between plankton and nekton. 3 describe the area of the ocean in which most benthic organisms live. 4 list the factors used to divide the ocean into marine zones. Ocean Productivity 1 list the factors that influence a region’s photo ...
Marine Sediments
... • Dominant in deep ocean basins in areas where oozes are absent • Especially below CCD in warmer oceans ...
... • Dominant in deep ocean basins in areas where oozes are absent • Especially below CCD in warmer oceans ...
here
... loses heat ~latitude of NY; note cold water descending from the north along Nova ScotiaMaine ...
... loses heat ~latitude of NY; note cold water descending from the north along Nova ScotiaMaine ...
Chemical and Physical Properties of Seawater Chapter 3, p 44
... Fetch - the span of open water over which the wind blows Fetch is important in determining the size of waves Wind starts the wave which eventually settles out into a swell as it gets farther from the source of wind. ...
... Fetch - the span of open water over which the wind blows Fetch is important in determining the size of waves Wind starts the wave which eventually settles out into a swell as it gets farther from the source of wind. ...
Eighth Grade Field Trip Worksheet
... focus on features that are measurable. For example area, mass, volume, density, color, shape and state of matter. The ocean is made up of many physical characteristics including temperature, turbulence, light and salinity (amount of salt). The physical characteristics vary depending on geographic lo ...
... focus on features that are measurable. For example area, mass, volume, density, color, shape and state of matter. The ocean is made up of many physical characteristics including temperature, turbulence, light and salinity (amount of salt). The physical characteristics vary depending on geographic lo ...
Preserving New Caledonia`s Marine Environment
... The benefits of creating a large reserve The waters of New Caledonia are healthy today because of restrictions on international fishing fleets and destructive trawling techniques. But with growing pressures from commercial and industrial fishing, the future health of the marine environment is not g ...
... The benefits of creating a large reserve The waters of New Caledonia are healthy today because of restrictions on international fishing fleets and destructive trawling techniques. But with growing pressures from commercial and industrial fishing, the future health of the marine environment is not g ...
Long term responses of North Atlantic calcifying
... detrimental effect marine organisms or whether other environmental effects such as temperature will play an important role. Why is it important? Ocean acidification is currently a ‘hot topic’ with a lot of worldwide research being carried out on its projected effects. There is much debate in the sci ...
... detrimental effect marine organisms or whether other environmental effects such as temperature will play an important role. Why is it important? Ocean acidification is currently a ‘hot topic’ with a lot of worldwide research being carried out on its projected effects. There is much debate in the sci ...
It Takes a Region: Ecosystem-Based Management in the Gulf of Maine
... more apparent than in the Gulf of Maine, whose fisheries, diverse habitats and cultural resources are key to both the U.S. states and Canadian provinces that call its shores home. To better manage those critical resources in an integrated, ecosystem-based manner, the Northeast Sea Grant Programs est ...
... more apparent than in the Gulf of Maine, whose fisheries, diverse habitats and cultural resources are key to both the U.S. states and Canadian provinces that call its shores home. To better manage those critical resources in an integrated, ecosystem-based manner, the Northeast Sea Grant Programs est ...
Review Question Midterm
... An adaptation that eel grass has is: a. Production and germination of seeds in the water b. production of pollen dispersed by the wind c. Production of organisms that reproduce asexually and then sexually . d. none of the above are correct. ____ 30. Which of the following process is not an adaptatio ...
... An adaptation that eel grass has is: a. Production and germination of seeds in the water b. production of pollen dispersed by the wind c. Production of organisms that reproduce asexually and then sexually . d. none of the above are correct. ____ 30. Which of the following process is not an adaptatio ...
2003 marine ecology event - Florida 4-H
... MARINE HABITATS/ECOSYSTEMS 45. The composition of Florida's beach sand a. varies with location of the beach b. comes from volcanic sources c. is the same on all beaches. d. changes with the season 46. Sand dunes are important to us for geological and ecological reasons. These reasons include: a. The ...
... MARINE HABITATS/ECOSYSTEMS 45. The composition of Florida's beach sand a. varies with location of the beach b. comes from volcanic sources c. is the same on all beaches. d. changes with the season 46. Sand dunes are important to us for geological and ecological reasons. These reasons include: a. The ...
Ocean Circulation Notes
... •Temperature differences cause warmer water near the equator to swell and move toward the poles. •Wind energy is converted to water movements called "currents" by friction between the wind and the water surface. The surface currents resemble the surface winds. Once these surface currents are set in ...
... •Temperature differences cause warmer water near the equator to swell and move toward the poles. •Wind energy is converted to water movements called "currents" by friction between the wind and the water surface. The surface currents resemble the surface winds. Once these surface currents are set in ...
Quiz 4 - Study Guidelines Study Outline
... Does the West Wind Drift have a Northern Hemisphere counterpart? Why or why not? 11. Describe the relationship between the wind, the surface current it creates and the development of equatorial and both types of Coastal Upwelling. 12. How would you change the wind direction in the coastal environmen ...
... Does the West Wind Drift have a Northern Hemisphere counterpart? Why or why not? 11. Describe the relationship between the wind, the surface current it creates and the development of equatorial and both types of Coastal Upwelling. 12. How would you change the wind direction in the coastal environmen ...
Document
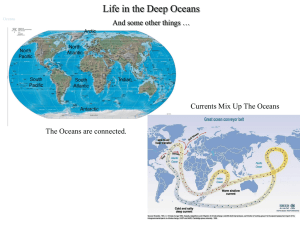
... Why not? Because life needs oxygen or sunlight • No Sunlight below 600 feet! • It's Cold! - Like your Refrigerator • Animals -- even fish -- need Oxygen! But the Answer is … YES - There is Life everywhere in the Oceans! ...
... Why not? Because life needs oxygen or sunlight • No Sunlight below 600 feet! • It's Cold! - Like your Refrigerator • Animals -- even fish -- need Oxygen! But the Answer is … YES - There is Life everywhere in the Oceans! ...
Big Als Big Oceans
... • The majority of sea turtles belong to the family Cheloniidae, however, the leatherback turtle is the only extant member of the family Dermochelyidae. • Leatherback turtles make some of the longest migrations in the natural world. It was recored that one individual swam from Indonesia to the USA. T ...
... • The majority of sea turtles belong to the family Cheloniidae, however, the leatherback turtle is the only extant member of the family Dermochelyidae. • Leatherback turtles make some of the longest migrations in the natural world. It was recored that one individual swam from Indonesia to the USA. T ...
Open File - Earth Science > Home
... temperatures, and low water pressure. These are ideal conditions for marine life. Nekton are common in the neritic zone. These nekton include many fish and other types of seafood that humans eat. The oceanic zone stretches into the deep waters past the continental shelf. The oceanic zone is divided ...
... temperatures, and low water pressure. These are ideal conditions for marine life. Nekton are common in the neritic zone. These nekton include many fish and other types of seafood that humans eat. The oceanic zone stretches into the deep waters past the continental shelf. The oceanic zone is divided ...
Habitat Conservation in the Era of Climate Change
... Upland forests are especially vulnerable to rising temperatures which will impact forest species composition and abundance. Some species that cannot tolerate warmer weather such as sugar maples will migrate northward, reducing the species diversity of the forest. Warmer temperatures will also leave ...
... Upland forests are especially vulnerable to rising temperatures which will impact forest species composition and abundance. Some species that cannot tolerate warmer weather such as sugar maples will migrate northward, reducing the species diversity of the forest. Warmer temperatures will also leave ...
Marine habitats
.jpg?width=300)
The marine environment supplies many kinds of habitats that support marine life. Marine life depends in some way on the saltwater that is in the sea (the term marine comes from the Latin mare, meaning sea or ocean). A habitat is an ecological or environmental area inhabited by one or more living species.Marine habitats can be divided into coastal and open ocean habitats. Coastal habitats are found in the area that extends from as far as the tide comes in on the shoreline out to the edge of the continental shelf. Most marine life is found in coastal habitats, even though the shelf area occupies only seven percent of the total ocean area. Open ocean habitats are found in the deep ocean beyond the edge of the continental shelf.Alternatively, marine habitats can be divided into pelagic and demersal habitats. Pelagic habitats are found near the surface or in the open water column, away from the bottom of the ocean. Demersal habitats are near or on the bottom of the ocean. An organism living in a pelagic habitat is said to be a pelagic organism, as in pelagic fish. Similarly, an organism living in a demersal habitat is said to be a demersal organism, as in demersal fish. Pelagic habitats are intrinsically shifting and ephemeral, depending on what ocean currents are doing.Marine habitats can be modified by their inhabitants. Some marine organisms, like corals, kelp, mangroves and seagrasses, are ecosystem engineers which reshape the marine environment to the point where they create further habitat for other organisms.