European Exploration GRQ
... 3. What had disrupted Western Europe’s trade routes with Asia? • Ottoman Empire controlled Eastern Mediterranean and blocked the land routes ...
... 3. What had disrupted Western Europe’s trade routes with Asia? • Ottoman Empire controlled Eastern Mediterranean and blocked the land routes ...
Discovery and Expansion
... A. Prince Henry the Navigator founded school for exploration; led expeditions down western coast of Africa B. Portugal established trading posts in N Africa coasts on Mediterranean; controlled gold trade between Africa and Europe C. Bartholomew Diaz (1487)-rounded Cape of Good Hope to reach southern ...
... A. Prince Henry the Navigator founded school for exploration; led expeditions down western coast of Africa B. Portugal established trading posts in N Africa coasts on Mediterranean; controlled gold trade between Africa and Europe C. Bartholomew Diaz (1487)-rounded Cape of Good Hope to reach southern ...
Spain`s Empire
... natives as slaves, shipped hundreds to Spain – most died in the process, the rest after arriving. They used the natives as torture toys, sex slaves, and as dog food. ...
... natives as slaves, shipped hundreds to Spain – most died in the process, the rest after arriving. They used the natives as torture toys, sex slaves, and as dog food. ...
The Age of Exploration - Hackettstown School District
... • Competed with Portugal for direct route to Asia • 1492 – Ferdinand and Isabella hired Christopher Columbus to find a route to Asia by sailing west – Big reason – F&I purged the Jews and lost many intellectuals & influential people, so they needed help! – Genoese captain ...
... • Competed with Portugal for direct route to Asia • 1492 – Ferdinand and Isabella hired Christopher Columbus to find a route to Asia by sailing west – Big reason – F&I purged the Jews and lost many intellectuals & influential people, so they needed help! – Genoese captain ...
Page C (Section II): Portugal Leads the Way
... The Arabs didn’t like that and decided to attack, but the Portuguese had better ships and beat the Arabs. Only 15 years after da Gama’s trip, the Portuguese controlled all the Indian Ocean. They next started trade and posts all the way to eastern China and Japan. ...
... The Arabs didn’t like that and decided to attack, but the Portuguese had better ships and beat the Arabs. Only 15 years after da Gama’s trip, the Portuguese controlled all the Indian Ocean. They next started trade and posts all the way to eastern China and Japan. ...
Exploration Unit- Study Guide Answers
... astrolabe • 6. Portugal • 7. Prince Henry mapmakers, astronomers, and ship builders ...
... astrolabe • 6. Portugal • 7. Prince Henry mapmakers, astronomers, and ship builders ...
File
... 5. Which group of Europeans was the first to arrive in the New World? Vikings 6. What is a caravel? Sails system used on ships 7. What is an astrolabe? Device that allowed sailors to determine their positions on the globe by using the stars and the horizon. 8. Who was Prince Henry “The Navigator”? A ...
... 5. Which group of Europeans was the first to arrive in the New World? Vikings 6. What is a caravel? Sails system used on ships 7. What is an astrolabe? Device that allowed sailors to determine their positions on the globe by using the stars and the horizon. 8. Who was Prince Henry “The Navigator”? A ...
1. Population and Settlement
... 3. Traders used overland routes to travel to India and China. These traders brought back precious metals, silks and spices to Europe. The overland routes were dangerous and difficult, but the traders risked the journey ...
... 3. Traders used overland routes to travel to India and China. These traders brought back precious metals, silks and spices to Europe. The overland routes were dangerous and difficult, but the traders risked the journey ...
age of exploration (1450-1750)
... • 1487: Bartholomeu Dias sailed around tip of Africa • 1498: Vasco Da Gama sailed around Africa into the Indian Ocean to India and brought back spices to Portugal. • This event causes trade with Italy and the Mediterranean sea to decline. ...
... • 1487: Bartholomeu Dias sailed around tip of Africa • 1498: Vasco Da Gama sailed around Africa into the Indian Ocean to India and brought back spices to Portugal. • This event causes trade with Italy and the Mediterranean sea to decline. ...
Age of Exploration1
... The first was its geographical position along the west coast of the Iberian Peninsula, which allowed for the natural development of a seafaring tradition. The second was the evolution of a complex maritime economy in which the port cities of Lisbon and Oporto became the commercial centers of the ...
... The first was its geographical position along the west coast of the Iberian Peninsula, which allowed for the natural development of a seafaring tradition. The second was the evolution of a complex maritime economy in which the port cities of Lisbon and Oporto became the commercial centers of the ...
Lecture Notes European Exploration and Expansion
... consider the sea as a possible route to Asia. B. Overseas voyages would end Europe's isolation and prepare the way for the rise of the world's first global age. C. Innovations in the construction of ships-including multiple masts and the shifting of the rudder from side to stern made ships more mane ...
... consider the sea as a possible route to Asia. B. Overseas voyages would end Europe's isolation and prepare the way for the rise of the world's first global age. C. Innovations in the construction of ships-including multiple masts and the shifting of the rudder from side to stern made ships more mane ...
EuropeanExplorationandColonizationEmpires
... --This was successful & was later copied in the New World --Encouraged a slave trade that lasted another 400 years… ...
... --This was successful & was later copied in the New World --Encouraged a slave trade that lasted another 400 years… ...
European Exploration - mrs
... control of the Strait of Malacca. • Seizing this waterway gave them control of the Moluccas. • These were islands so rich in spices that they later became known as the Spice Islands. ...
... control of the Strait of Malacca. • Seizing this waterway gave them control of the Moluccas. • These were islands so rich in spices that they later became known as the Spice Islands. ...
Lesson 6 – Arab-Israeli Issues
... Used force to take over islands in the Caribbean, as well as places in Central America, South America, and ...
... Used force to take over islands in the Caribbean, as well as places in Central America, South America, and ...
The Age of Exploration
... Good Hope at southern tip of Africa. • Found route to Indian Ocean • Trade can go from Europe to Asia by sea. ...
... Good Hope at southern tip of Africa. • Found route to Indian Ocean • Trade can go from Europe to Asia by sea. ...
myth 2.2 “The Search for New Trade Routes”
... • Asia– silk, spices • Trade Routes • most were overland routes like Silk Road ...
... • Asia– silk, spices • Trade Routes • most were overland routes like Silk Road ...
Unit 4 Study guide- Age of Exploration
... Explain how the spice trade worked before the Age of Exploration and how this system of trade helped spark exploration. Be able to explain the trading policy of China, Korea or Japan. Explain the impact of the Crusades had on the Age of Exploration. Explain the major motivations people had to explor ...
... Explain how the spice trade worked before the Age of Exploration and how this system of trade helped spark exploration. Be able to explain the trading policy of China, Korea or Japan. Explain the impact of the Crusades had on the Age of Exploration. Explain the major motivations people had to explor ...
Chapter 21: Reaching Out: Expanding Horizons of Cross
... which guarded the Strait of Gibraltar and Atlantic entry to the Mediterranean Sea. Colonization of the Atlantic Islands 72. Portuguese mariners soon colonized Atlantic islands off of Africa and the southern tier of Europe (including the Madeiras, Azores and Cape Verde islands), planting sugarcane ...
... which guarded the Strait of Gibraltar and Atlantic entry to the Mediterranean Sea. Colonization of the Atlantic Islands 72. Portuguese mariners soon colonized Atlantic islands off of Africa and the southern tier of Europe (including the Madeiras, Azores and Cape Verde islands), planting sugarcane ...
Concerto Around the World in Not Quite Eighty Days
... would later fall in the same fashion. As the Guanche perished, African slaves took their place. Small numbers of African slaves had been part of the Mediterranean labor force since the early Roman Empire, but now their numbers increased. In the last decades of the 15th century, about 1,300 African s ...
... would later fall in the same fashion. As the Guanche perished, African slaves took their place. Small numbers of African slaves had been part of the Mediterranean labor force since the early Roman Empire, but now their numbers increased. In the last decades of the 15th century, about 1,300 African s ...
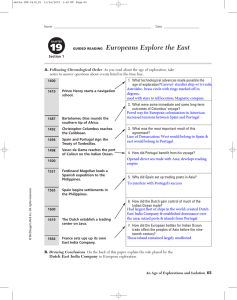
Europeans explore the east
... outcomes of Columbus’ voyage? Paved way for European colonization in Americas; increased tensions between Spain and Portugal ...
... outcomes of Columbus’ voyage? Paved way for European colonization in Americas; increased tensions between Spain and Portugal ...
Dutch East India Company
... The Dutch East India Company was a joint stock company who monopolized the spice trade of the 17th century. They established trading ports all over Asia. The Dutch East India Company sought a way to bypass the Portuguese stronghold on the spice trade with the Far East. With the formation of the Dutc ...
... The Dutch East India Company was a joint stock company who monopolized the spice trade of the 17th century. They established trading ports all over Asia. The Dutch East India Company sought a way to bypass the Portuguese stronghold on the spice trade with the Far East. With the formation of the Dutc ...
Chapter 2 – Age of Exploration Lesson 1 – Technology Shapes
... together to improve sea travel and invent new tools. Explored African coast to gain wealth by trading for gold and ivory; also to spread religion around Africa Trading posts – stores and small settlements where goods could be bought and sold Slave trade – slave traders bought and sold humans a ...
... together to improve sea travel and invent new tools. Explored African coast to gain wealth by trading for gold and ivory; also to spread religion around Africa Trading posts – stores and small settlements where goods could be bought and sold Slave trade – slave traders bought and sold humans a ...
Spice trade

The spice trade refers to the trade between historical civilizations in Asia, Northeast Africa and Europe. Spices such as cinnamon, cassia, cardamom, ginger, pepper, and turmeric were known, and used for commerce, in the Eastern World well into antiquity. Opium was also imported. These spices found their way into the Middle East before the beginning of the Christian Era, where the true sources of these spices was withheld by the traders, and associated with fantastic tales. Prehistoric writings and stone age carvings of neolithic age obtained indicates that India's South West Coast path, especially Kerala had established itself as a major spice trade centre from as early as 3000 B.C, which marks the beginning of Spice Trade (History of Kerala) and is still referred to as the land of spices or as the Spice Garden of India.The Greco-Roman world followed by trading along the Incense route and the Roman-India routes. During the first millennium, the sea routes to India and Sri Lanka (the Roman - Taprobane) were controlled by the Indians and Ethiopians that became the maritime trading power of the Red Sea. The Kingdom of Axum (ca 5th-century BC–AD 11th century) had pioneered the Red Sea route before the 1st century AD. By mid-7th century AD the rise of Islam closed off the overland caravan routes through Egypt and the Suez, and sundered the European trade community from Axum and India.Arab traders eventually took over conveying goods via the Levant and Venetian merchants to Europe until the rise of the Ottoman Turks cut the route again by 1453. Overland routes helped the spice trade initially, but maritime trade routes led to tremendous growth in commercial activities. During the high and late medieval periods Muslim traders dominated maritime spice trading routes throughout the Indian Ocean, tapping source regions in the Far East and shipping spices from trading emporiums in India westward to the Persian Gulf and the Red Sea, from which overland routes led to Europe.The trade was changed by the European Age of Discovery, during which the spice trade, particularly in black pepper, became an influential activity for European traders. The route from Europe to the Indian Ocean via the Cape of Good Hope was pioneered by the Portuguese explorer navigator Vasco da Gama in 1498, resulting in new maritime routes for trade.This trade — driving the world economy from the end of the Middle Ages well into the modern times — ushered in an age of European domination in the East. Channels, such as the Bay of Bengal, served as bridges for cultural and commercial exchanges between diverse cultures as nations struggled to gain control of the trade along the many spice routes. European dominance was slow to develop. The Portuguese trade routes were mainly restricted and limited by the use of ancient routes, ports, and nations that were difficult to dominate. The Dutch were later able to bypass many of these problems by pioneering a direct ocean route from the Cape of Good Hope to the Sunda Strait in Indonesia.