PBL Feedback Summary
... When an acute haemolytic reaction occurs, antibodies in the recipient's serum react with antigens on the donor's red blood cells. This results in agglutination (clumping) of cells, which can obstruct capillaries and block blood flow. Haemolysis of the red blood cells releases free haemoglobin into t ...
... When an acute haemolytic reaction occurs, antibodies in the recipient's serum react with antigens on the donor's red blood cells. This results in agglutination (clumping) of cells, which can obstruct capillaries and block blood flow. Haemolysis of the red blood cells releases free haemoglobin into t ...
Perspectives in Fluid Dynamics
... law of viscosity and are known as Newtonian fluid. Other classes of fluids, e.g., paints, polymer solution, blood do not obey the typical linear relationship of stress and strain. They are known as non-Newtonian fluids. Unit of viscosity: Ns/m2 (Pa.s) ...
... law of viscosity and are known as Newtonian fluid. Other classes of fluids, e.g., paints, polymer solution, blood do not obey the typical linear relationship of stress and strain. They are known as non-Newtonian fluids. Unit of viscosity: Ns/m2 (Pa.s) ...
File - Two Bear Midwifery
... body. They also carry carbon dioxide back to the lungs so it can be exhaled. If the RBC count is low (anemia), the body may not be getting the oxygen it needs. If the count is too high (a condition called polycythemia), there is a chance that the red blood cells will clump together and block tiny bl ...
... body. They also carry carbon dioxide back to the lungs so it can be exhaled. If the RBC count is low (anemia), the body may not be getting the oxygen it needs. If the count is too high (a condition called polycythemia), there is a chance that the red blood cells will clump together and block tiny bl ...
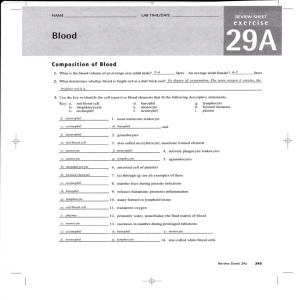
Composition of Blood
... Broadly speaking, why are hematologie studies of blood so important in the diagnosis of disease? Specilic clanges from the normal numhersltJpes of.fotmrd elements andlor plasma constituents are charaderistic of certain ...
... Broadly speaking, why are hematologie studies of blood so important in the diagnosis of disease? Specilic clanges from the normal numhersltJpes of.fotmrd elements andlor plasma constituents are charaderistic of certain ...
WHAT SHOULD I KNOW FOR THE TEST
... Who is considered to be the “Father of Genetics”? What was Gregor Mendel’s contribution to our understanding of genetics? What is the relationship between the P1, F1, and F2 generations? What 2 laws did Mendel propose to explain how traits are inherited? When does segregation and independent assortm ...
... Who is considered to be the “Father of Genetics”? What was Gregor Mendel’s contribution to our understanding of genetics? What is the relationship between the P1, F1, and F2 generations? What 2 laws did Mendel propose to explain how traits are inherited? When does segregation and independent assortm ...
File
... What is blood pressure and what factors affect its level? Pressure of the blood on the arteries Factors affecting blood pressure: 1. Cardiac Output: amount of blood ejected from the heart (weak muscle) 2. Blood volume (5 liters for avg adult): dehydration decreases, water retention (salt intake) inc ...
... What is blood pressure and what factors affect its level? Pressure of the blood on the arteries Factors affecting blood pressure: 1. Cardiac Output: amount of blood ejected from the heart (weak muscle) 2. Blood volume (5 liters for avg adult): dehydration decreases, water retention (salt intake) inc ...
Leukemia - Liberty Hill High School
... (Hemolytic disease of the newborn or Erythroblastosis Fetalis). ...
... (Hemolytic disease of the newborn or Erythroblastosis Fetalis). ...
Blood Typing
... • A Rh negative mom may be exposed to an Rh antigen from the blood of a Rh positive baby during pregnancy or birth. • If Rh + cell enters Rh- mom the mother’s immune system will respond and produce antibodies against the Rh positive blood antigen ...
... • A Rh negative mom may be exposed to an Rh antigen from the blood of a Rh positive baby during pregnancy or birth. • If Rh + cell enters Rh- mom the mother’s immune system will respond and produce antibodies against the Rh positive blood antigen ...
I need to know about D
... There are several tests available which take the patient’s red cells and mix them with antibodies which attach to Rh (D). If there is a strong reaction, the patient is Rh (D) positive. No reaction means negative. Rarely there is a weak reaction. This is called ‘weak D’. ...
... There are several tests available which take the patient’s red cells and mix them with antibodies which attach to Rh (D). If there is a strong reaction, the patient is Rh (D) positive. No reaction means negative. Rarely there is a weak reaction. This is called ‘weak D’. ...
Blood Sample - Lead
... 3 mL of whole blood in a Vacutainer® 3-mL EDTA (lavender top) tube. 2. Refrigerate the whole blood immediately or place in a cooler with ice packs for delivery to the laboratory for processing. Blood tubes should never be placed directly on the ice source because this may cause hemolysis. 3. At the ...
... 3 mL of whole blood in a Vacutainer® 3-mL EDTA (lavender top) tube. 2. Refrigerate the whole blood immediately or place in a cooler with ice packs for delivery to the laboratory for processing. Blood tubes should never be placed directly on the ice source because this may cause hemolysis. 3. At the ...
File
... 4. Positional and directional terms of reference are based on the body being in a/an: Anatomical Position 5. The term that means toward the head is: Superior 35. A combining form for chest is: Pector/o 36. The combining form referring to a swollen, twisted vein is: Varic/o 37. The circulatory distri ...
... 4. Positional and directional terms of reference are based on the body being in a/an: Anatomical Position 5. The term that means toward the head is: Superior 35. A combining form for chest is: Pector/o 36. The combining form referring to a swollen, twisted vein is: Varic/o 37. The circulatory distri ...
Human Blood Typing Lab
... genetically determined classes of human blood which are based on the presence or absence of certain erythrocyte surface antigens (glycoproteins) and are clinically identified by characteristic agglutination reactions; for blood transfusion purposes, the ABO and Rh blood group systems are the most im ...
... genetically determined classes of human blood which are based on the presence or absence of certain erythrocyte surface antigens (glycoproteins) and are clinically identified by characteristic agglutination reactions; for blood transfusion purposes, the ABO and Rh blood group systems are the most im ...
Order Form - AIIMS Jodhpur
... In case of newborn upto 4 months, send another tube with mothers sample also (label “Mother of__________”) For release fill bottom portion and send Insulated box to carry the Component, which will be handed over only to Hospital Staff. ...
... In case of newborn upto 4 months, send another tube with mothers sample also (label “Mother of__________”) For release fill bottom portion and send Insulated box to carry the Component, which will be handed over only to Hospital Staff. ...
File
... 1. Which blood cell is ameboid in shape, granular or agranular? 2. Which veins carry blood into the right atrium? 3. Veins carry (circle one) oxygenated or deoxygenated blood? 4. Which blood cell is biconcave and contains hemoglobin? 5. Arteries carry (circle one) oxygenated or deoxygenated blood? 6 ...
... 1. Which blood cell is ameboid in shape, granular or agranular? 2. Which veins carry blood into the right atrium? 3. Veins carry (circle one) oxygenated or deoxygenated blood? 4. Which blood cell is biconcave and contains hemoglobin? 5. Arteries carry (circle one) oxygenated or deoxygenated blood? 6 ...
Chapter 14: Blood
... bone marrow, where it stimulates the formation of red blood cells. The increases amount of hemoglobin delivers more oxygen to the tissues. Chronic hypoxia, therefore, causes a secondary polycythemia and an increase in hematocrit. There are other clinical conditions that involve erythropoietin. Patie ...
... bone marrow, where it stimulates the formation of red blood cells. The increases amount of hemoglobin delivers more oxygen to the tissues. Chronic hypoxia, therefore, causes a secondary polycythemia and an increase in hematocrit. There are other clinical conditions that involve erythropoietin. Patie ...
Blood Cells
... disposed of. Respiration is there key to working right. In your lungs each red blood cell picks up red oxygen. A red cell contains an ironrich protein called hemoglobin that oxidizes or rusts as it were in your lungs. Blood cells fight to kill germs and infections in the body. Red blood cells can pr ...
... disposed of. Respiration is there key to working right. In your lungs each red blood cell picks up red oxygen. A red cell contains an ironrich protein called hemoglobin that oxidizes or rusts as it were in your lungs. Blood cells fight to kill germs and infections in the body. Red blood cells can pr ...
Explain the mechanisms that prevent blood clotting in intact blood
... 2007a(10)/1999a(2): Explain the mechanisms that prevent blood clotting in intact blood vessels (do not draw the clotting cascade) General: Haemostasis is the physiological mechanism where blood is prevented from being lost from damaged vessels whilst allowing blood to remain fluid in the circulation ...
... 2007a(10)/1999a(2): Explain the mechanisms that prevent blood clotting in intact blood vessels (do not draw the clotting cascade) General: Haemostasis is the physiological mechanism where blood is prevented from being lost from damaged vessels whilst allowing blood to remain fluid in the circulation ...
genetics
... their children will have a Darwin’s Tubercle? Show your work with a Punnet square. 8. Individuals with type O blood are often referred to as “universal donors” with respect to red blood cells (they can donate red blood cells to individuals of any blood type). Are type O individuals also universal do ...
... their children will have a Darwin’s Tubercle? Show your work with a Punnet square. 8. Individuals with type O blood are often referred to as “universal donors” with respect to red blood cells (they can donate red blood cells to individuals of any blood type). Are type O individuals also universal do ...
Motion of red blood cells in a glass microchannel: a global
... In the microcirculation, the flow behavior of RBCs plays a crucial role in many physiological and pathological phenomena. For example, the random-like transverse motion and rotation of RBCs in shear flow is believed to play an important role in thrombogenesis. However, the role of RBCs in the mass t ...
... In the microcirculation, the flow behavior of RBCs plays a crucial role in many physiological and pathological phenomena. For example, the random-like transverse motion and rotation of RBCs in shear flow is believed to play an important role in thrombogenesis. However, the role of RBCs in the mass t ...
Click here for Screening Sign Up
... For employees who do not have TRS Active Care with Aetna, the fees are $85.00 and $105.00 with a PSA for men. Additional testing is available with profile: Vitamin D $30.00 and CRP $20.00. The same fees will apply to spouses and family members without insurance. Health Matters’ technicians are quali ...
... For employees who do not have TRS Active Care with Aetna, the fees are $85.00 and $105.00 with a PSA for men. Additional testing is available with profile: Vitamin D $30.00 and CRP $20.00. The same fees will apply to spouses and family members without insurance. Health Matters’ technicians are quali ...