Ch 15 - FCUSD.org
... Marine organisms can be classified according to where they live and how they move. Plankton all organisms—algae(Phytoplankton), animals(Zooplankton), and bacteria—that drift with ocean currents. ...
... Marine organisms can be classified according to where they live and how they move. Plankton all organisms—algae(Phytoplankton), animals(Zooplankton), and bacteria—that drift with ocean currents. ...
Open Ocean Notes
... Where is algae (phytoplankton) found in the open ocean? The surface zone Algae is the base of the open ocean food web Many open ocean animals stay in deep water during the day and surface at night to feed. ...
... Where is algae (phytoplankton) found in the open ocean? The surface zone Algae is the base of the open ocean food web Many open ocean animals stay in deep water during the day and surface at night to feed. ...
Oceanography Chapter 15: Marine Animals
... Oceanography Chapter 15: Marine Animals Heterotrophic – cannot synthesize their own food Eat autotrophs or lower level heterotrophs True multicellular critters arose 700-900 MYA (Proterozoic Eon) >about 2 BY after cyanobacteria put out enough free oxygen into the atmosphere ¾ O2 Revolution - 1% to 2 ...
... Oceanography Chapter 15: Marine Animals Heterotrophic – cannot synthesize their own food Eat autotrophs or lower level heterotrophs True multicellular critters arose 700-900 MYA (Proterozoic Eon) >about 2 BY after cyanobacteria put out enough free oxygen into the atmosphere ¾ O2 Revolution - 1% to 2 ...
March 27th Scientist`s Walk on the Wildside: Campers take a
... will experience how blubber is used to keep animals warm, how echolocation helps toothed whales to hunt for food, how baleen whales feed on tiny prey and get an up close look at various replica marine mammal skeletons. Sea otter skulls, a polar bear’s claw, and even a walrus’ tusk are a few of the r ...
... will experience how blubber is used to keep animals warm, how echolocation helps toothed whales to hunt for food, how baleen whales feed on tiny prey and get an up close look at various replica marine mammal skeletons. Sea otter skulls, a polar bear’s claw, and even a walrus’ tusk are a few of the r ...
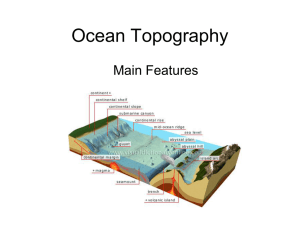
Ocean Topography
... Continental shelf • The continental shelf is the extended perimeter of each continent and associated coastal plain, and was part of the continent during the glacial periods, but is undersea during interglacial periods. ...
... Continental shelf • The continental shelf is the extended perimeter of each continent and associated coastal plain, and was part of the continent during the glacial periods, but is undersea during interglacial periods. ...
Research on marine resources in East Africa
... Research on marine resources in East Africa Many of the world’s most productive ecosystems are found along the coastlines of the tropics and in the adjacent sea, systems which are vital to the lives of many poor people. However, population growth and urbanisation has lead to an overexploitation of c ...
... Research on marine resources in East Africa Many of the world’s most productive ecosystems are found along the coastlines of the tropics and in the adjacent sea, systems which are vital to the lives of many poor people. However, population growth and urbanisation has lead to an overexploitation of c ...
The Law of the Sea
... ocean-bottom plain that lies immediately offshore the continents. It averages between 200-500 feet in depth, and is separated from the “abyssal plain” (deep-ocean bottom averaging about 15,000 feet in depth) by a steep drop-off called the “continental slope.” C ti Continental t l shelf h lf is i the ...
... ocean-bottom plain that lies immediately offshore the continents. It averages between 200-500 feet in depth, and is separated from the “abyssal plain” (deep-ocean bottom averaging about 15,000 feet in depth) by a steep drop-off called the “continental slope.” C ti Continental t l shelf h lf is i the ...
Chapter 8 Review
... affected 41% of the world oceans and no parts of the oceans have been left untouched. People who live near the coast are destroying and degrading the aquatic biodiversity. Forty-five percent of the US lives near the coast and that number is rapidly increasing. • Major threats to marine systems from ...
... affected 41% of the world oceans and no parts of the oceans have been left untouched. People who live near the coast are destroying and degrading the aquatic biodiversity. Forty-five percent of the US lives near the coast and that number is rapidly increasing. • Major threats to marine systems from ...
Marine Biology - El Camino College
... Or you may reference any legitimate Marine Biology journal. Several magazines and journals are available in the ECC library, but you are also encouraged to try at Cal State Long Beach Library which has a far larger selection, or various city libraries. Please bring the article title and source to me ...
... Or you may reference any legitimate Marine Biology journal. Several magazines and journals are available in the ECC library, but you are also encouraged to try at Cal State Long Beach Library which has a far larger selection, or various city libraries. Please bring the article title and source to me ...
INFO - Andalusian Stories
... SUMMARY: This research is being conducted by researchers from the Andalusian Centre for Marine Science and Technology and has been financially supported by the Andalusian Government and the European Union. Drugs get to marine environments through waste water because the human body excretes drug part ...
... SUMMARY: This research is being conducted by researchers from the Andalusian Centre for Marine Science and Technology and has been financially supported by the Andalusian Government and the European Union. Drugs get to marine environments through waste water because the human body excretes drug part ...
Upwelling and Hydrothermal Vents
... ocean is bacteria. There are animals that have the bacteria live inside them to provide them with food. These include tube worms, clams, and mussels There are scavengers, including shrimp, crabs, and anemones that feed on the bacteria and other zooplankton that live at the vent Lastly, there a ...
... ocean is bacteria. There are animals that have the bacteria live inside them to provide them with food. These include tube worms, clams, and mussels There are scavengers, including shrimp, crabs, and anemones that feed on the bacteria and other zooplankton that live at the vent Lastly, there a ...
Lesson 5: Coral Reefs and the Open Ocean - Florida 4-H
... contain some of the most diverse organisms and least known habitats of our planet. The ecological aspects of oceanography (the field of science that studies oceans) study the distribution and interdependency of marine communities and ways they are influenced by the environment. Let’s begin by lookin ...
... contain some of the most diverse organisms and least known habitats of our planet. The ecological aspects of oceanography (the field of science that studies oceans) study the distribution and interdependency of marine communities and ways they are influenced by the environment. Let’s begin by lookin ...
Lesson 5 - Florida 4-H
... contain some of the most diverse organisms and least known habitats of our planet. The ecological aspects of oceanography (the field of science that studies oceans) study the distribution and interdependency of marine communities and ways they are influenced by the environment. Let’s begin by lookin ...
... contain some of the most diverse organisms and least known habitats of our planet. The ecological aspects of oceanography (the field of science that studies oceans) study the distribution and interdependency of marine communities and ways they are influenced by the environment. Let’s begin by lookin ...
Preserving New Caledonia`s Marine Environment
... Many iconic and threatened species can be found in New Caledonia’s waters. These include humpback whales, dugongs, large sharks, sea turtles, manta rays, Napoleon wrasse, sea snakes, and seabirds. These species depend on healthy habitats for feeding, nesting, reproducing, and migrating. ...
... Many iconic and threatened species can be found in New Caledonia’s waters. These include humpback whales, dugongs, large sharks, sea turtles, manta rays, Napoleon wrasse, sea snakes, and seabirds. These species depend on healthy habitats for feeding, nesting, reproducing, and migrating. ...
6H2O + 6CO2 + energy + nutrients = C6H12O6 + 6O2 Focus on left
... caused by the height of water. Function of water height and water density Pressure generally increases at a rate of 1 atm per 10 m of water. ...
... caused by the height of water. Function of water height and water density Pressure generally increases at a rate of 1 atm per 10 m of water. ...
Chapter 16
... Marine and Coastal Ecosystems 1. Regions of ocean water differ greatly, and some zones support more life than others. a. The uppermost 10 m (33 ft) of water absorbs 80% of solar energy, so nearly all of the oceans’ primary productivity occurs in the top layer, or photic zone. b. Habitats and ecosyst ...
... Marine and Coastal Ecosystems 1. Regions of ocean water differ greatly, and some zones support more life than others. a. The uppermost 10 m (33 ft) of water absorbs 80% of solar energy, so nearly all of the oceans’ primary productivity occurs in the top layer, or photic zone. b. Habitats and ecosyst ...
PPT
... caused by the height of water. Function of water height and water density Pressure generally increases at a rate of 1 atm per 10 m of water. ...
... caused by the height of water. Function of water height and water density Pressure generally increases at a rate of 1 atm per 10 m of water. ...
The State of the Oceans
... Within their vast expanse, oceans support tremendous biodiversity. Scientists to date have catalogued nearly a quarter-million species in the ocean (O’Dor, 2003), but they estimate that up to 10 million more have yet to be discovered (Sala & Knowlton, 2006). Oceans also play an essential role in reg ...
... Within their vast expanse, oceans support tremendous biodiversity. Scientists to date have catalogued nearly a quarter-million species in the ocean (O’Dor, 2003), but they estimate that up to 10 million more have yet to be discovered (Sala & Knowlton, 2006). Oceans also play an essential role in reg ...
Marine Science / Study Guide for the Final!!! If there is a statement
... What is the photic zone? How deep is it? Does sound travel faster or slower in water? What is the average salinity of the ocean? The most abundant salt ions in the ocean are ____. Define salinity. What process produces oxygen in water? Does cold or hot water hold more oxygen? How do refractometers m ...
... What is the photic zone? How deep is it? Does sound travel faster or slower in water? What is the average salinity of the ocean? The most abundant salt ions in the ocean are ____. Define salinity. What process produces oxygen in water? Does cold or hot water hold more oxygen? How do refractometers m ...
Marine Invertebrates
... • Marine hermit crabs are found worldwide. There are about five hundred known species of hermit crabs in the world, most of which are aquatic and live in saltwater at depths ranging from shallow coral reefs and shorelines to deep sea bottoms. Hermit crabs require empty shells as they grow; having va ...
... • Marine hermit crabs are found worldwide. There are about five hundred known species of hermit crabs in the world, most of which are aquatic and live in saltwater at depths ranging from shallow coral reefs and shorelines to deep sea bottoms. Hermit crabs require empty shells as they grow; having va ...
Test #2 Results by Next Week Chapter 10: Biological Productivity
... benthos includes organisms attached to or living on or in the sea bed. This group includes plants and animals. – Epiflora or epifauna live on the sea bottom. – Infauna live in the sea bottom. Benthic plants are restricted to shallow waters because of their requirement for light. Benthic animals ...
... benthos includes organisms attached to or living on or in the sea bed. This group includes plants and animals. – Epiflora or epifauna live on the sea bottom. – Infauna live in the sea bottom. Benthic plants are restricted to shallow waters because of their requirement for light. Benthic animals ...
Hodgson_ETC coastal report
... UBA-D and REC • The purpose of the Technical Paper is to review evidence of the impacts of climate change, adaptation policies, measures and actions across Europe’s coasts – it seeks to capture key points/issues/messages and does not aim to be comprehensive • The review will contribute to EEA’s coas ...
... UBA-D and REC • The purpose of the Technical Paper is to review evidence of the impacts of climate change, adaptation policies, measures and actions across Europe’s coasts – it seeks to capture key points/issues/messages and does not aim to be comprehensive • The review will contribute to EEA’s coas ...
PRESS RELEASE 9th May 2012 NEW DIRECTOR OF THE SIR
... pleased to announce the appointment of Professor Nicholas Owens as Director of the Foundation with effect from the 1st August. During a distinguished career spanning over 30 years in the field of marine science Professor Owens has served as the Director of British Antarctic Survey, the Chief Executi ...
... pleased to announce the appointment of Professor Nicholas Owens as Director of the Foundation with effect from the 1st August. During a distinguished career spanning over 30 years in the field of marine science Professor Owens has served as the Director of British Antarctic Survey, the Chief Executi ...
Marine biology

Marine biology is the scientific study of organisms in the ocean or other marine or brackish bodies of water. Given that in biology many phyla, families and genera have some species that live in the sea and others that live on land, marine biology classifies species based on the environment rather than on taxonomy. Marine biology differs from marine ecology as marine ecology is focused on how organisms interact with each other and the environment, while biology is the study of the organisms themselves.A large proportion of all life on Earth lives in the ocean. Exactly how large the proportion is unknown, since many ocean species are still to be discovered. The ocean is a complex three-dimensional world covering about 71% of the Earth's surface. The habitats studied in marine biology include everything from the tiny layers of surface water in which organisms and abiotic items may be trapped in surface tension between the ocean and atmosphere, to the depths of the oceanic trenches, sometimes 10,000 meters or more beneath the surface of the ocean. Specific habitats include coral reefs, kelp forests, seagrass meadows, the surrounds of seamounts and thermal vents, tidepools, muddy, sandy and rocky bottoms, and the open ocean (pelagic) zone, where solid objects are rare and the surface of the water is the only visible boundary. The organisms studied range from microscopic phytoplankton and zooplankton to huge cetaceans (whales) 30 meters (98 feet) in length.Marine life is a vast resource, providing food, medicine, and raw materials, in addition to helping to support recreation and tourism all over the world. At a fundamental level, marine life helps determine the very nature of our planet. Marine organisms contribute significantly to the oxygen cycle, and are involved in the regulation of the Earth's climate. Shorelines are in part shaped and protected by marine life, and some marine organisms even help create new land.Many species are economically important to humans, including food fish (both finfish and shellfish). It is also becoming understood that the well-being of marine organisms and other organisms are linked in very fundamental ways. The human body of knowledge regarding the relationship between life in the sea and important cycles is rapidly growing, with new discoveries being made nearly every day. These cycles include those of matter (such as the carbon cycle) and of air (such as Earth's respiration, and movement of energy through ecosystems including the ocean). Large areas beneath the ocean surface still remain effectively unexplored.