Marine Biology Name: Osmoregulation WebQuest Period: ______
... Organisms in aquatic and terrestrial environments must maintain the right concentration of solutes and amount of water in their body fluids; this involves excretion (getting rid of metabolic wastes and other substances such as hormones that would be toxic if allowed to accumulate in the blood) throu ...
... Organisms in aquatic and terrestrial environments must maintain the right concentration of solutes and amount of water in their body fluids; this involves excretion (getting rid of metabolic wastes and other substances such as hormones that would be toxic if allowed to accumulate in the blood) throu ...
Marine Maldives – medicine cabinet of the 21st century? According
... explored, the oceans offer so much potential for new discoveries including new medicines. In fact, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration in the United States refers to the world's oceans, especially the coral reefs where we find most biodiversity, as the "medicine cabinets of the 21st ...
... explored, the oceans offer so much potential for new discoveries including new medicines. In fact, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration in the United States refers to the world's oceans, especially the coral reefs where we find most biodiversity, as the "medicine cabinets of the 21st ...
Marine Biology Final Exam Review
... What is an emergent plant community? (give examples) Where can mangroves be found in the United States? How have they adapted to the marine environment? Where are salt marshes found in the United States? What important role do they have in juvenile fishes life? What structure helps kelp beds stay af ...
... What is an emergent plant community? (give examples) Where can mangroves be found in the United States? How have they adapted to the marine environment? Where are salt marshes found in the United States? What important role do they have in juvenile fishes life? What structure helps kelp beds stay af ...
PDF: Printable Version
... Bronk’s team is investigating how warmer temperatures, increased runoff, and larger ice-free areas will affect the marine microbial community, and how changes there might ripple up the food web to affect larger organisms and native peoples. They also aim to investigate how climate change will affect ...
... Bronk’s team is investigating how warmer temperatures, increased runoff, and larger ice-free areas will affect the marine microbial community, and how changes there might ripple up the food web to affect larger organisms and native peoples. They also aim to investigate how climate change will affect ...
STUDY GUIDE CHAPTER 3 TEST 2009
... 42) Drifting organisms that may be plant-like or animal-like are called _plankton_. 43) The constant motion of waves can be harnessed to produce _wave _energy. 44) People who live in hot, dry climates often rely on _desalination plants_ for their drinking water. 45) Energy generated from tides is ca ...
... 42) Drifting organisms that may be plant-like or animal-like are called _plankton_. 43) The constant motion of waves can be harnessed to produce _wave _energy. 44) People who live in hot, dry climates often rely on _desalination plants_ for their drinking water. 45) Energy generated from tides is ca ...
M S C
... Hughes has recently published two papers. The first, in American Naturalist, shows that the relatedness of different seagrass genotypes is a better predictor of seagrass biomass than the number of genotypes. The second, in Ecology, discusses how the presence of a neighboring plant species benefits t ...
... Hughes has recently published two papers. The first, in American Naturalist, shows that the relatedness of different seagrass genotypes is a better predictor of seagrass biomass than the number of genotypes. The second, in Ecology, discusses how the presence of a neighboring plant species benefits t ...
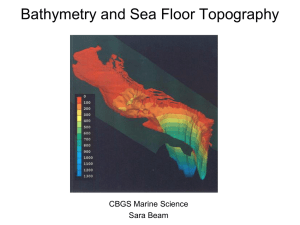
Bathymetry
... mid-ocean ridge cools and becomes increasingly older as it moves away from the ridge crest with seafloor spreading : a. the spreading ridge about 5 million years ago; b. about 2 to 3 million years ago; and c. present-day. Kios and ...
... mid-ocean ridge cools and becomes increasingly older as it moves away from the ridge crest with seafloor spreading : a. the spreading ridge about 5 million years ago; b. about 2 to 3 million years ago; and c. present-day. Kios and ...
Notes Part 2
... two flagella , most are photosynthetic, and some are bioluminescent. Zooxanthellae- symbionts of jellyfish and corals give them their coloration. Plankton is captured with standard sized nets are called net plankton. •Microplankton- cyanoplankton, dinoflagellates, and diatoms. • Nanoplankton- coccol ...
... two flagella , most are photosynthetic, and some are bioluminescent. Zooxanthellae- symbionts of jellyfish and corals give them their coloration. Plankton is captured with standard sized nets are called net plankton. •Microplankton- cyanoplankton, dinoflagellates, and diatoms. • Nanoplankton- coccol ...
MERiFIC partnership: Cornwall Council
... Council long term ambition for marine energy to stimulate innovation, accelerate growth, business development, jobs and skills in our local economy Wave Hub FaBTest Falmouth and Hayle harbour offshore development PRIMaRE MERiFIC SW Marine Energy Park ...
... Council long term ambition for marine energy to stimulate innovation, accelerate growth, business development, jobs and skills in our local economy Wave Hub FaBTest Falmouth and Hayle harbour offshore development PRIMaRE MERiFIC SW Marine Energy Park ...
Six countries team up to conduct research in Northwest Atlantic
... St. John’s, NL (April 25, 2017) – A team of scientists from six countries — with a unique Memorial University connection — will depart from St. John’s, N.L. on April 27 on a trans-Atlantic voyage that’s studying the impact of climate change on the ocean. The research being conducted onboard the Celt ...
... St. John’s, NL (April 25, 2017) – A team of scientists from six countries — with a unique Memorial University connection — will depart from St. John’s, N.L. on April 27 on a trans-Atlantic voyage that’s studying the impact of climate change on the ocean. The research being conducted onboard the Celt ...
Cascadia: The Hidden Fire
... 1. Tell how much of the surface of the Earth is covered in water. What total volume? How much habitat? ...
... 1. Tell how much of the surface of the Earth is covered in water. What total volume? How much habitat? ...
Essential Oceanography
... Look over the available topics & choose a few that you would like to present Your names will be randomized & then, in that order, you will get to pick your topic. Please mark which topic is yours, it is your responsibility to remember the topic. This is due on Friday. ...
... Look over the available topics & choose a few that you would like to present Your names will be randomized & then, in that order, you will get to pick your topic. Please mark which topic is yours, it is your responsibility to remember the topic. This is due on Friday. ...
Chapter 19 Study Notes: The Ocean Basins
... • To see the bottom of the ocean for him or herself while remaining connected to a research ship, a scientist would use a _____________________. – bathysphere. ...
... • To see the bottom of the ocean for him or herself while remaining connected to a research ship, a scientist would use a _____________________. – bathysphere. ...
PDF: Printable Press Release
... chosen for the honor for her leadership in research aimed at understanding the role of biological processes in the ocean’s mid-water “twilight zone” and their influence on carbon and nitrogen cycles in the ocean. “Humans release billions of tons of carbon dioxide to the air each year through the bur ...
... chosen for the honor for her leadership in research aimed at understanding the role of biological processes in the ocean’s mid-water “twilight zone” and their influence on carbon and nitrogen cycles in the ocean. “Humans release billions of tons of carbon dioxide to the air each year through the bur ...
Oceanography
... the food web in these environments 1. phytoplankton – plant plankton – example – diatoms 2. zooplankton – animal-like plankton exampleprotists, crustaceans B. Nekton – organisms that swim in the ocean freely. examples – larger fish, squid, sea turtles, whales C. Benthos – community of organisms that ...
... the food web in these environments 1. phytoplankton – plant plankton – example – diatoms 2. zooplankton – animal-like plankton exampleprotists, crustaceans B. Nekton – organisms that swim in the ocean freely. examples – larger fish, squid, sea turtles, whales C. Benthos – community of organisms that ...
History of Ocean Exploration
... reasons why humans would start exploring the oceans (Think about why we do so today). List all reasons the class comes up with. ...
... reasons why humans would start exploring the oceans (Think about why we do so today). List all reasons the class comes up with. ...
Ocean Topography
... the ocean seafloor that does not reach to the water's surface (sea level). They are also called underwater volcanoes because are typically formed from extinct volcanoes, that rise abruptly. ...
... the ocean seafloor that does not reach to the water's surface (sea level). They are also called underwater volcanoes because are typically formed from extinct volcanoes, that rise abruptly. ...
mitrie_sediment_marine
... Seawater retains heat much better than air, leading to the supposition that most heat related to global warming would be expected to be incorporated into the oceans. Interactions between the atmosphere and the oceans, and thus global climate patterns, are likely to change under the influence of incr ...
... Seawater retains heat much better than air, leading to the supposition that most heat related to global warming would be expected to be incorporated into the oceans. Interactions between the atmosphere and the oceans, and thus global climate patterns, are likely to change under the influence of incr ...
PDF file - Around the Americas
... Center, a Seattle-based not-for-profit science foundation, and renowned ocean sailor Mark Schrader, who has twice before sailed around the world by himself. The Around the Americas sailboat, Ocean Watch, embarked on the expedition from Seattle in May 2009 and has successfully sailed through the Nort ...
... Center, a Seattle-based not-for-profit science foundation, and renowned ocean sailor Mark Schrader, who has twice before sailed around the world by himself. The Around the Americas sailboat, Ocean Watch, embarked on the expedition from Seattle in May 2009 and has successfully sailed through the Nort ...
Marine biology

Marine biology is the scientific study of organisms in the ocean or other marine or brackish bodies of water. Given that in biology many phyla, families and genera have some species that live in the sea and others that live on land, marine biology classifies species based on the environment rather than on taxonomy. Marine biology differs from marine ecology as marine ecology is focused on how organisms interact with each other and the environment, while biology is the study of the organisms themselves.A large proportion of all life on Earth lives in the ocean. Exactly how large the proportion is unknown, since many ocean species are still to be discovered. The ocean is a complex three-dimensional world covering about 71% of the Earth's surface. The habitats studied in marine biology include everything from the tiny layers of surface water in which organisms and abiotic items may be trapped in surface tension between the ocean and atmosphere, to the depths of the oceanic trenches, sometimes 10,000 meters or more beneath the surface of the ocean. Specific habitats include coral reefs, kelp forests, seagrass meadows, the surrounds of seamounts and thermal vents, tidepools, muddy, sandy and rocky bottoms, and the open ocean (pelagic) zone, where solid objects are rare and the surface of the water is the only visible boundary. The organisms studied range from microscopic phytoplankton and zooplankton to huge cetaceans (whales) 30 meters (98 feet) in length.Marine life is a vast resource, providing food, medicine, and raw materials, in addition to helping to support recreation and tourism all over the world. At a fundamental level, marine life helps determine the very nature of our planet. Marine organisms contribute significantly to the oxygen cycle, and are involved in the regulation of the Earth's climate. Shorelines are in part shaped and protected by marine life, and some marine organisms even help create new land.Many species are economically important to humans, including food fish (both finfish and shellfish). It is also becoming understood that the well-being of marine organisms and other organisms are linked in very fundamental ways. The human body of knowledge regarding the relationship between life in the sea and important cycles is rapidly growing, with new discoveries being made nearly every day. These cycles include those of matter (such as the carbon cycle) and of air (such as Earth's respiration, and movement of energy through ecosystems including the ocean). Large areas beneath the ocean surface still remain effectively unexplored.