Aztec*s and spanish
... They were hungry and thirsty, hoping at every turn to see the promised sign: an eagle sitting on a prickly pear cactus, eating a snake. After 200 years of wondering, they found the eagle and a small, swampy island in Lake Texcoco in the Valley of Mexico. ...
... They were hungry and thirsty, hoping at every turn to see the promised sign: an eagle sitting on a prickly pear cactus, eating a snake. After 200 years of wondering, they found the eagle and a small, swampy island in Lake Texcoco in the Valley of Mexico. ...
About the Aztecs Presentation
... They thought that the moon and the sun did battle every night and day. ...
... They thought that the moon and the sun did battle every night and day. ...
one of several migrant groups to arrive in central
... They were also prominent in the marketplace The law subjected women to the strict authority of their fathers or their husbands. With the exception of a few priestesses, ALL Mexica women were married. Society recognized bearing children as equivalent to a warrior capturing an enemy in battle. ...
... They were also prominent in the marketplace The law subjected women to the strict authority of their fathers or their husbands. With the exception of a few priestesses, ALL Mexica women were married. Society recognized bearing children as equivalent to a warrior capturing an enemy in battle. ...
Aztecs - SBAS
... area in and around the Valley of Mexico from 1428 until they were defeated by the Spanish conquistadores and their native allies under Hernán Cortés in 1521. The Aztec Triple Alliance was formed by Itzcoatl of Tenochtitlan, Acolhuacans of Texcoco, and the smaller city-state of Tlacopan in 1428. Desp ...
... area in and around the Valley of Mexico from 1428 until they were defeated by the Spanish conquistadores and their native allies under Hernán Cortés in 1521. The Aztec Triple Alliance was formed by Itzcoatl of Tenochtitlan, Acolhuacans of Texcoco, and the smaller city-state of Tlacopan in 1428. Desp ...
Aztecs Settle in Central Mexico
... • Aztec families lived in land-based communities - men farmed the land; women cooked, raised children - boys formally taught religion, battle skills; girls educated at home • Religion dominated society; Aztecs believed in around 1,000 gods - had public ceremonies; prayed to agricultural gods for goo ...
... • Aztec families lived in land-based communities - men farmed the land; women cooked, raised children - boys formally taught religion, battle skills; girls educated at home • Religion dominated society; Aztecs believed in around 1,000 gods - had public ceremonies; prayed to agricultural gods for goo ...
1. Tenochtitlan The capital of the Aztec empire, now the site of
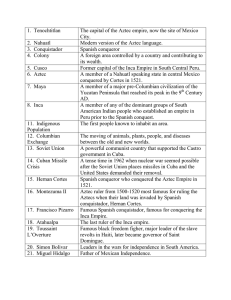
... Modern version of the Aztec language. Spanish conqueror A foreign area controlled by a country and contributing to its wealth. Former capital of the Inca Empire in South Central Peru. A member of a Nahuatl speaking state in central Mexico conquered by Cortes in 1521. A member of a major pre-Columbia ...
... Modern version of the Aztec language. Spanish conqueror A foreign area controlled by a country and contributing to its wealth. Former capital of the Inca Empire in South Central Peru. A member of a Nahuatl speaking state in central Mexico conquered by Cortes in 1521. A member of a major pre-Columbia ...
1. Tenochtitlan The capital of the Aztec empire, now the site of
... Modern version of the Aztec language. Spanish conqueror A foreign area controlled by a country and contributing to its wealth. Former capital of the Inca Empire in South Central Peru. A member of a Nahuatl speaking state in central Mexico conquered by Cortes in 1521. A member of a major pre-Columbia ...
... Modern version of the Aztec language. Spanish conqueror A foreign area controlled by a country and contributing to its wealth. Former capital of the Inca Empire in South Central Peru. A member of a Nahuatl speaking state in central Mexico conquered by Cortes in 1521. A member of a major pre-Columbia ...
Key Terms and People Section Summary
... Cortés marched to the Aztec capital. When he got there Moctezuma welcomed him, but Cortés took the emperor prisoner. Enraged, the Aztecs attacked the Spanish and drove them out of the city. In the confusion Moctezuma was killed. Before long Cortés and his men came back, this time with reinforcements ...
... Cortés marched to the Aztec capital. When he got there Moctezuma welcomed him, but Cortés took the emperor prisoner. Enraged, the Aztecs attacked the Spanish and drove them out of the city. In the confusion Moctezuma was killed. Before long Cortés and his men came back, this time with reinforcements ...
Mesoamerica Conquistadors
... • Cortes was a university law student but dropped out of school to become a New World Conquistador. • Conquistadors were Spanish soldiers and explorers who came to the new world to seek glory and wealth. • 1511 – Participated in the Spanish conquest of Cuba • Known for his bravery and daring. ...
... • Cortes was a university law student but dropped out of school to become a New World Conquistador. • Conquistadors were Spanish soldiers and explorers who came to the new world to seek glory and wealth. • 1511 – Participated in the Spanish conquest of Cuba • Known for his bravery and daring. ...
ComparingAztec Maya IncaNotes
... made of woven reeds & placed them in ________—farmed on soil on these “_________” ...
... made of woven reeds & placed them in ________—farmed on soil on these “_________” ...
the aztecs - Brookings School District
... Xochitl had a difficult time falling asleep. The excitement of tomorrow's festival kept her mind occupied until she finally became drowsy. Tomorrow, she would attend Ochpaniztli, the festival of the eleventh month. This celebration honored Tlazolteotl, the earth mother goddess. Each month of the cal ...
... Xochitl had a difficult time falling asleep. The excitement of tomorrow's festival kept her mind occupied until she finally became drowsy. Tomorrow, she would attend Ochpaniztli, the festival of the eleventh month. This celebration honored Tlazolteotl, the earth mother goddess. Each month of the cal ...
Wld - Maples Elementary School
... 10. What are three advantages of the Valley of Mexico attracting people to settle there? 11. What is obsidian? 12. According to the Aztec, who was the god of the sun and warfare? 13. Aztecs often demanded tribute from their conquered subjects in the form of what products? 14. What are the three clas ...
... 10. What are three advantages of the Valley of Mexico attracting people to settle there? 11. What is obsidian? 12. According to the Aztec, who was the god of the sun and warfare? 13. Aztecs often demanded tribute from their conquered subjects in the form of what products? 14. What are the three clas ...
The Aztecs
... birth to Coyolxanuhqui, goddess of the moon, and to a group of male offspring, who became the stars. Then one day Coatlique found a ball of feathers, which she tucked into her bosom. Whe she looked for it later, it was gone, at which time she realized that she was again pregnant. Her children, the m ...
... birth to Coyolxanuhqui, goddess of the moon, and to a group of male offspring, who became the stars. Then one day Coatlique found a ball of feathers, which she tucked into her bosom. Whe she looked for it later, it was gone, at which time she realized that she was again pregnant. Her children, the m ...
The Aztecs
... The Nahuatl language is often said to include three levels of meaning for its words or expressions: literal, syncretic and connotative. The connotative meaning of Aztlan, due to the plumage of herons, is "Place of Whiteness." The mythical descriptions of Aztlan would have it to be an island. You wou ...
... The Nahuatl language is often said to include three levels of meaning for its words or expressions: literal, syncretic and connotative. The connotative meaning of Aztlan, due to the plumage of herons, is "Place of Whiteness." The mythical descriptions of Aztlan would have it to be an island. You wou ...
Guided Reading Unit 4
... The ancient Aztecs believed in many gods. However, the sun god was most important. The Aztecs believed that the sun god needed human blood and hearts in order to make its journey across the sky each day. As farmers, the sun’s journey meant the difference between life and death. The sun had to rise ...
... The ancient Aztecs believed in many gods. However, the sun god was most important. The Aztecs believed that the sun god needed human blood and hearts in order to make its journey across the sky each day. As farmers, the sun’s journey meant the difference between life and death. The sun had to rise ...
The Conquistadors
... •Incas paid it in gold, but Altahualpa was killed anyway •Despite resistance, Spanish gained control of much of South America including Peru, Ecuador & Chile ...
... •Incas paid it in gold, but Altahualpa was killed anyway •Despite resistance, Spanish gained control of much of South America including Peru, Ecuador & Chile ...
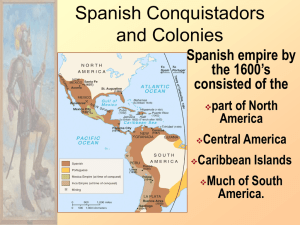
THE LAND OF THE AMERICAS
... • The walls of the ball courts were covered with images of war and sacrifice. • The exact rules of the game that was played are unknown, but we do know that small teams tried to send a ball through a hoop using their hips. ...
... • The walls of the ball courts were covered with images of war and sacrifice. • The exact rules of the game that was played are unknown, but we do know that small teams tried to send a ball through a hoop using their hips. ...
The Aztec Social Hierarchy
... How might this prophecy lead the Aztecs to believe that the gods favored them more than other peoples? How would it affect their attitude towards other people? -Military service was _____________ in Aztec society. -The worst insult was to call someone a _________, as cowardice was a sign of weakness ...
... How might this prophecy lead the Aztecs to believe that the gods favored them more than other peoples? How would it affect their attitude towards other people? -Military service was _____________ in Aztec society. -The worst insult was to call someone a _________, as cowardice was a sign of weakness ...
Assessment: The Aztecs
... 12. The Aztec Empire was based on tribute. This means that the people who lived in the empire A. worshipped Aztec gods. B. had to speak the Aztec language. C. rebelled against the Aztec leaders. D. paid goods to the Aztec government. 13. Which of these facts best shows that war was at the center of ...
... 12. The Aztec Empire was based on tribute. This means that the people who lived in the empire A. worshipped Aztec gods. B. had to speak the Aztec language. C. rebelled against the Aztec leaders. D. paid goods to the Aztec government. 13. Which of these facts best shows that war was at the center of ...
Mesoamerica 2016 Power Point
... have had an important role in their society e. 2 primary Olmec sites (San Lorenzo and La Venta) Evidence suggests that the population at each site was only 1,000 at their peak. 2. Economy – based on agriculture & trade a. farmers of this society practiced what’s known as slash and burn farming - ...
... have had an important role in their society e. 2 primary Olmec sites (San Lorenzo and La Venta) Evidence suggests that the population at each site was only 1,000 at their peak. 2. Economy – based on agriculture & trade a. farmers of this society practiced what’s known as slash and burn farming - ...
Voyages Of Discovery
... 6. The Flowery Wars of the 1450s involved no exchange of territory and were fought by appointment with near-by states because all parties involved believed they needed these. ____________________________________ 7. The last Aztec king had this name bestowed on him by the Spaniards. ________________ ...
... 6. The Flowery Wars of the 1450s involved no exchange of territory and were fought by appointment with near-by states because all parties involved believed they needed these. ____________________________________ 7. The last Aztec king had this name bestowed on him by the Spaniards. ________________ ...
Maya, Aztec, and Inca Civilizations
... Was believed that Quetzalcoatl had traveled east across the sea and would one day return, bringing peace ...
... Was believed that Quetzalcoatl had traveled east across the sea and would one day return, bringing peace ...
Human sacrifice in Aztec culture
.jpg?width=300)
Human sacrifice was a religious practice characteristic of pre-Columbian Aztec civilization, as well as of other Mesoamerican civilizations like the Maya and the Zapotec. The extent of the practice is debated by modern scholars.Spanish explorers, soldiers and clergy who had contact with the Aztecs between 1517, when an expedition from Cuba first explored the Yucatan, and 1521, when Hernán Cortés conquered the Aztec capital of Tenochtitlan, made observations of and wrote reports about the practice of human sacrifice. For example, Bernal Díaz's The Conquest of New Spain includes eyewitness accounts of human sacrifices as well as descriptions of the remains of sacrificial victims. In addition, there are a number of second-hand accounts of human sacrifices written by Spanish friars that relate the testimony of native eyewitnesses. The literary accounts have been supported by archeological research. Since the late 1970s, excavations of the offerings in the Great Pyramid of Tenochtitlan, Teotihuacán's Pyramid of the Moon, and other archaeological sites, have provided physical evidence of human sacrifice among the Mesoamerican peoples.A wide variety of explanations and interpretations of the Aztec practice of human sacrifice have been proposed by modern scholars. Most scholars of Pre-Columbian civilization see human sacrifice among the Aztecs as a part of the long cultural tradition of human sacrifice in Mesoamerica.