* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Aztecs Settle in Central Mexico
Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire wikipedia , lookup
Templo Mayor wikipedia , lookup
National Palace (Mexico) wikipedia , lookup
Tepotzotlán wikipedia , lookup
Fall of Tenochtitlan wikipedia , lookup
Aztec warfare wikipedia , lookup
Aztec Empire wikipedia , lookup
Aztec religion wikipedia , lookup
Human sacrifice in Aztec culture wikipedia , lookup
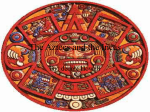
Chapter 12: Later American Civilizations Lesson 1 The Aztecs MAIN IDEAS Geography The Aztecs developed an agricultural society and founded a great empire in the Valley of Mexico. Government The Aztecs had a highly structured society, with authoritarian rulers. Culture The Aztecs made advances in art, architecture, and astronomy. Aztecs Settle in Central Mexico ESSENTIAL QUESTION How did the Aztecs adapt to the Valley of Mexico? Settling in the Valley of Mexico • Aztecs, nomadic hunter-gatherers, lived in what is now northwest Mexico • In 1200s, they moved south into Valley of Mexico, a mountain basin - Toltecs had ruled region, but only small city-states remained • In 1325, Aztecs settled on small island in large lake - built city—Tenochtitlán— “place of the Prickly Pear” - site of Mexico City today • Aztecs began serving as paid warriors for local rulers Adapting to the Land • Aztec land swampy, little farmland; little wood or stone for building • Constructed chinampas on the lake—raised garden beds - grew corn, squash, peppers on chinampas; hunted game near lake • Food supply, population grew; new communities spread around lake • Dug canals, built bridges to enable increased trade in area Chapter 12: Later American Civilizations World History: Medieval and Early Modern Times 1 Building an Empire • Aztecs made alliances with some nearby city-states, conquered others • By 1500s, Aztecs ruled empire of 6 to 12 million people - empire stretched from Gulf to Pacific; from Valley to modern Guatemala • Aztecs demanded tribute—forced payment—from conquered peoples - tribute paid in form of goods such as corn, gold, jade REVIEW QUESTION How did the Aztecs build a powerful empire? Chapter 12: Later American Civilizations World History: Medieval and Early Modern Times 2 Aztec Society and Beliefs ESSENTIAL QUESTION What was the structure of Aztec society? Aztec Class Structure • Three main classes: - nobles (landowners, priests) most powerful; ran government, army - artisans, merchants made up intermediate class - commoners (farmers, craftspeople, soldiers, serfs) majority • Emperor at top of noble class; lived luxuriously, supported by army • Slaves at bottom of commoners • All classes limited womenʼs roles Family Life and Religious Practices • Aztec families lived in land-based communities - men farmed the land; women cooked, raised children - boys formally taught religion, battle skills; girls educated at home • Religion dominated society; Aztecs believed in around 1,000 gods - had public ceremonies; prayed to agricultural gods for good harvests • Priests kept calendars; sometimes war prisoners were sacrificed to gods Aztec Warriors and Warfare • War was sacred duty; boys trained as warriors by age 15 Fall of the Aztec Empire • Emperor Montezuma II demanded more tribute, land, sacrifices (1502) • Hernán Cortés—Spanish explorer—arrived in 1519 seeking gold • Montezuma hoped to avoid war; taken prisoner by Cortés during meeting - Montezuma later killed during fighting with Spanish • Disease, guns defeat Aztecs; Cortés captured Tenochtitlán in 1521 REVIEW QUESTION Why did the Aztec empire fall? Chapter 12: Later American Civilizations World History: Medieval and Early Modern Times 3 The Cultural Legacy of the Aztecs ESSENTIAL QUESTION What cultural advances did the Aztecs make? Art and Architecture • Aztecs built huge, unique temples and palaces in Tenochtitlán - part of Great Temple visible today in Mexico City • Archaeologists have also uncovered everyday objects - gold beads, pottery, headdresses, sculptures, jewelry, gems The Aztec Codices • Aztec used glyphs (colorful pictures, symbols) as their writing system • Codex were deerskin or bark books; reflected details of Aztec life Advances in Astronomy • Aztecs studied stars, planets to predict planting, harvest seasons • Aztecs created two calendars—one for farming, one for religion - religious calendar used to plan ceremonies REVIEW QUESTION What was the Aztec’s cultural legacy? Lesson Summary • The Aztecs adapted to the environment of the Valley of Mexico and built an empire there. • The Aztecsʼ harsh treatment of their subjects weakened their empire and made it easier for the Spanish to conquer them. • The Aztecs made contributions in art, architecture, and astronomy. Why It Matters Now . . . The Aztecs ruled much of what is now Mexico and built their capital where Mexico City, one of the worldʼs largest cities, now stands. Chapter 12: Later American Civilizations World History: Medieval and Early Modern Times 4