AP World History Mr. Soff Chapter 11: The Americas on the Eve of
... capital at Tenochtitlan. The Aztecs had a reputation as tough warriors and fanatical followers of their gods. By the time of Moctezuma II, the Aztec state was dominated by a king who represented civil power and served as a representative of the gods on earth. The cult of human sacrifice and conquest ...
... capital at Tenochtitlan. The Aztecs had a reputation as tough warriors and fanatical followers of their gods. By the time of Moctezuma II, the Aztec state was dominated by a king who represented civil power and served as a representative of the gods on earth. The cult of human sacrifice and conquest ...
12 ANCIENT AND CLASSICAL AMERICAS
... Tenuous position of merchants: • Supplied exotic goods and military intelligence • Under suspicion as greedy profiteers ...
... Tenuous position of merchants: • Supplied exotic goods and military intelligence • Under suspicion as greedy profiteers ...
File
... They also could not get bright bird feathers that they adorned themselves with The city also did not have gold or silver deposits To get these things merchants travelled great distances with slaves to carry the goods back ...
... They also could not get bright bird feathers that they adorned themselves with The city also did not have gold or silver deposits To get these things merchants travelled great distances with slaves to carry the goods back ...
Intro: Contrary to the Spanish beliefs that the Aztec
... of religion. One reason why the Aztec people had such a complicated religious life was that they inherited a lot of their practises and rituals from conquered peoples. The Aztec religion also combined elements of polytheism, shamanism and animism. But the element that makes this religion so complica ...
... of religion. One reason why the Aztec people had such a complicated religious life was that they inherited a lot of their practises and rituals from conquered peoples. The Aztec religion also combined elements of polytheism, shamanism and animism. But the element that makes this religion so complica ...
FALL OF THE AZTEC AND INCA EMPIRES Cortes
... Montezuma – emperor of Aztecs; thought Cortes was a god Pizarro- Spanish conquistador who conquered Inca Atahualpa – Inca emperor captured and killed by Pizarro 2. Conquistador – Spanish explorer arriving in Central & South America in search of gold, silver, and new lands to conquer for Spain. 3. Mo ...
... Montezuma – emperor of Aztecs; thought Cortes was a god Pizarro- Spanish conquistador who conquered Inca Atahualpa – Inca emperor captured and killed by Pizarro 2. Conquistador – Spanish explorer arriving in Central & South America in search of gold, silver, and new lands to conquer for Spain. 3. Mo ...
Aztec Empire History
... Capital city-state was Tenochtitlán (Mexico City is now on top of it) Other major city-states were Texcoco and Tlacopan (combined with Tenochtitlán, these were called the “Triple Alliance”) ...
... Capital city-state was Tenochtitlán (Mexico City is now on top of it) Other major city-states were Texcoco and Tlacopan (combined with Tenochtitlán, these were called the “Triple Alliance”) ...
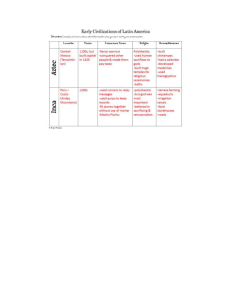
Mesoamerican Civilizations
... from conquered peoples • Polytheistic religion with pyramids/rituals ...
... from conquered peoples • Polytheistic religion with pyramids/rituals ...
Pre-Columbian Americas
... Ritual functions Read omens, advised rulers Occasionally became rulers as well ...
... Ritual functions Read omens, advised rulers Occasionally became rulers as well ...
Aztec PPT notes with answers
... Thousands of natives died in a massive smallpox epidemic because they had never been exposed to the disease and had no immunity built up like the Spanish did ...
... Thousands of natives died in a massive smallpox epidemic because they had never been exposed to the disease and had no immunity built up like the Spanish did ...
Latin American Civilizations
... Cities were religious centers. Pyramid style Temples stood in the middle of the city. Worshiped many gods and performed rituals including human sacrifice to their gods. ...
... Cities were religious centers. Pyramid style Temples stood in the middle of the city. Worshiped many gods and performed rituals including human sacrifice to their gods. ...
Thanks Mrs. Valenti!
... Most men worked in the calpulli fields Women cooked, wove cloth, & cared for the young Around ages 10-14, boys were sent to school to learn about Aztec religion, history, and other things ...
... Most men worked in the calpulli fields Women cooked, wove cloth, & cared for the young Around ages 10-14, boys were sent to school to learn about Aztec religion, history, and other things ...
Aztec Empire
... under the leader Monteczuma they expanded to 1/3 of Mexico- Mostly in South Population of 25 million at peak Grew stronger through war, tribute, and trade. Tribute– The Aztecs made neighboring tribes pay them in order to not be attacked. Neighboring tribes “paid tribute” but, with good reason they d ...
... under the leader Monteczuma they expanded to 1/3 of Mexico- Mostly in South Population of 25 million at peak Grew stronger through war, tribute, and trade. Tribute– The Aztecs made neighboring tribes pay them in order to not be attacked. Neighboring tribes “paid tribute” but, with good reason they d ...
The Aztecs
... The Aztecs rarely kept their art. It all went to the nobility or they traded it to other nations. Unlike Mayan and Olmec Art, Aztec Art was very lifelike. You can tell dif ferent ages, and expressions on ...
... The Aztecs rarely kept their art. It all went to the nobility or they traded it to other nations. Unlike Mayan and Olmec Art, Aztec Art was very lifelike. You can tell dif ferent ages, and expressions on ...
Name____________________________
... day they began to sing again, but without warning they were all put to death. The dancers and singers were completely unarmed. They brought only their embroidered cloaks, their turquoises, their lip plugs, their necklaces, their clusters of heron feathers, their trinkets made of deer hooves. ...
... day they began to sing again, but without warning they were all put to death. The dancers and singers were completely unarmed. They brought only their embroidered cloaks, their turquoises, their lip plugs, their necklaces, their clusters of heron feathers, their trinkets made of deer hooves. ...
mesoamerica - WordPress.com
... Ruled through conquest Military empire Had one emperor and conquered rules paid tribute Some conquered people became slaves Stole crops, clothing, and anything else they could ...
... Ruled through conquest Military empire Had one emperor and conquered rules paid tribute Some conquered people became slaves Stole crops, clothing, and anything else they could ...
Act 8.5 Key Aztec Culture Reflects its Worldview pages 283
... The Importance of Time to the Aztec The Aztec used two calendars: xiuhtlapohualli, the main 365 solar day calendar and a ritual calendar base on a 260 day cycle called tonalpohualli. The xiuhtlapohualli corresponded to seasons and was used to determine when to plant and harvest groups as well as whe ...
... The Importance of Time to the Aztec The Aztec used two calendars: xiuhtlapohualli, the main 365 solar day calendar and a ritual calendar base on a 260 day cycle called tonalpohualli. The xiuhtlapohualli corresponded to seasons and was used to determine when to plant and harvest groups as well as whe ...
Name___________________________________________
... 1325CE, they founded their city, which they named Tenochtitlan. Over the years, the Aztecs gradually increased in strength and number. In 1428, they joined with two other city-states – Texcoco and Tlacopan – to form the Triple Alliance. This alliance became the leading power in the Valley of Mexico ...
... 1325CE, they founded their city, which they named Tenochtitlan. Over the years, the Aztecs gradually increased in strength and number. In 1428, they joined with two other city-states – Texcoco and Tlacopan – to form the Triple Alliance. This alliance became the leading power in the Valley of Mexico ...
AZTECS
... - # of dots represented months - glyphs represented days - year started with the alligator - each of the 20 days had its own name - Solar calendar – similar to our calendar - used 52 year time periods to divide history like our 100 years (century) - believed they lived in the 5th time period - time ...
... - # of dots represented months - glyphs represented days - year started with the alligator - each of the 20 days had its own name - Solar calendar – similar to our calendar - used 52 year time periods to divide history like our 100 years (century) - believed they lived in the 5th time period - time ...
Pre-AP World History.11
... 1. Religion serves as integrating force of unification and oppression A. Polytheistic: gods of rain, water, fire, food, sun, etc. B. Atleast 128 religious deities in Aztec religion; each with female counterpart 1. Served as patrons of cities, tribes, occupations, etc. 2. Honored through yearly festi ...
... 1. Religion serves as integrating force of unification and oppression A. Polytheistic: gods of rain, water, fire, food, sun, etc. B. Atleast 128 religious deities in Aztec religion; each with female counterpart 1. Served as patrons of cities, tribes, occupations, etc. 2. Honored through yearly festi ...
APWH Ch 11 Notes Pre-Columbian America
... – Environmental degradation caused by overpopulation – Epidemic disease ...
... – Environmental degradation caused by overpopulation – Epidemic disease ...
Maya Aztec Inca notes and facts
... o Many people believe it was environmental- drought or food shortage Aztec • Settled on Lake Texcoco (present day Mexico City is built on top Aztec ruins) • Main city was Tenochtitlan which means place of the nopal and was an artificial island o It was a very sophisticated city with aqueducts to sto ...
... o Many people believe it was environmental- drought or food shortage Aztec • Settled on Lake Texcoco (present day Mexico City is built on top Aztec ruins) • Main city was Tenochtitlan which means place of the nopal and was an artificial island o It was a very sophisticated city with aqueducts to sto ...
The Aztecs
... birth to Coyolxanuhqui, goddess of the moon, and to a group of male offspring, who became the stars. Then one day Coatlique found a ball of feathers, which she tucked into her bosom. Whe she looked for it later, it was gone, at which time she realized that she was again pregnant. Her children, the m ...
... birth to Coyolxanuhqui, goddess of the moon, and to a group of male offspring, who became the stars. Then one day Coatlique found a ball of feathers, which she tucked into her bosom. Whe she looked for it later, it was gone, at which time she realized that she was again pregnant. Her children, the m ...
File
... • The Aztec were finally led by their chieftain, Tenoch, to a swampy island in the middle of Lake Texcoco sometime in the 12th or 13th century. • This area was said to have been their destined land as foretold by their patron god, Huitzilopochtli. • The Aztec called the land Tenochtitlan and over t ...
... • The Aztec were finally led by their chieftain, Tenoch, to a swampy island in the middle of Lake Texcoco sometime in the 12th or 13th century. • This area was said to have been their destined land as foretold by their patron god, Huitzilopochtli. • The Aztec called the land Tenochtitlan and over t ...
Aztec`s - Plain Local Schools
... Punishments carried out the next day Steal - pay 3x the price poorly made goods - goods taken away No jail, you were caged, death by drowning None sacrificed as it might upset the gods ...
... Punishments carried out the next day Steal - pay 3x the price poorly made goods - goods taken away No jail, you were caged, death by drowning None sacrificed as it might upset the gods ...
Aztec religion

The Aztec religion is the Mesoamerican religion of the Aztecs. Like other Mesoamerican religions, it had elements of human sacrifice in connection with a large number of religious festivals which were held according to patterns of the Aztec calendar. It had a large and ever increasing pantheon; the Aztecs would often adopt deities of other geographic regions or peoples into their own religious practice. Aztec cosmology divided the world into upper and nether worlds, each associated with a specific set of deities and astronomical objects. Important in Aztec religion were the sun, moon and the planet Venus—all of which held different symbolic and religious meanings and were connected to deities and geographical places.Large parts of the Aztec pantheon were inherited from previous Mesoamerican civilizations and others, such as Tlaloc, Quetzalcoatl and Tezcatlipoca, were venerated by different names in most cultures throughout the history of Mesoamerica. For the Aztecs especially important deities were Tlaloc the god of rain, Huitzilopochtli the patron god of the Mexica tribe, Quetzalcoatl the culture hero and god of civilization and order, and Tezcatlipoca the god of destiny and fortune, connected with war and sorcery. Each of these gods had their own temples within the Aztec capital Tenochtitlan—Tlaloc and Huitzilopochtli were both worshipped at the Templo Mayor, and a third monument in the plaza before the Templo Mayor is thought to have been a shrine devoted to the wind god Ehecatl, known to be an aspect of Quetzalcoatl. A common Aztec religious practice was the recreation of the divine: Mythological events would be ritually recreated and living persons would impersonate specific deities and be revered as a god—and often ritually sacrificed.