are piezoelectric constants
... The superscripted permittivity and compliance s denotes the quantity kept constant under boundary conditions (e.g T is the permittivity under constant stress) "d" and "g" are piezoelectric constants: d = r og r = relative permittivity (or dielectric constant) o = permittivity of free space ( 8. ...
... The superscripted permittivity and compliance s denotes the quantity kept constant under boundary conditions (e.g T is the permittivity under constant stress) "d" and "g" are piezoelectric constants: d = r og r = relative permittivity (or dielectric constant) o = permittivity of free space ( 8. ...
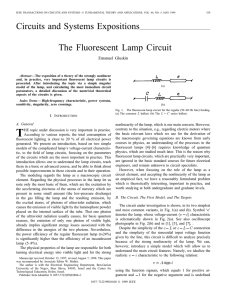
2014 Influence of Discrete Inductance Curves on The Simulation of a Round Rotor Generator Using Coupled Circuit Method
... steady state, it is possible to use analytical models that can represent the damper winding currents. Several works have been done on models based on permeance functions and models using equivalent circuit with different levels of simplification as shown in [1]. The use of permeance functions is a s ...
... steady state, it is possible to use analytical models that can represent the damper winding currents. Several works have been done on models based on permeance functions and models using equivalent circuit with different levels of simplification as shown in [1]. The use of permeance functions is a s ...
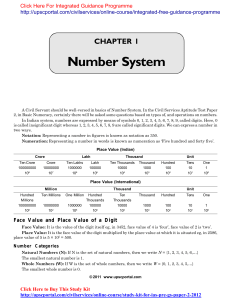
INTERNATIONAL INDIAN SCHOOL, RIYADH CLASS: X SUBJECT
... 26) The perimeter of a right angled triangle is 70units and its hypotenuse is 29 units. Find the lengths of the other sides (20, 21) 27) The length of the sides forming a right angled ∆ is 5x cm and (3x – 4) cm. Area of the triangle is 60 cm2. Find the hypotenuse (17cm) 28) The length of the hypoten ...
... 26) The perimeter of a right angled triangle is 70units and its hypotenuse is 29 units. Find the lengths of the other sides (20, 21) 27) The length of the sides forming a right angled ∆ is 5x cm and (3x – 4) cm. Area of the triangle is 60 cm2. Find the hypotenuse (17cm) 28) The length of the hypoten ...
Mathematics of radio engineering

The mathematics of radio engineering is the mathematical description by complex analysis of the electromagnetic theory applied to radio. Waves have been studied since ancient times and many different techniques have developed of which the most useful idea is the superposition principle which apply to radio waves. The Huygen's principle, which says that each wavefront creates an infinite number of new wavefronts that can be added, is the base for this analysis.