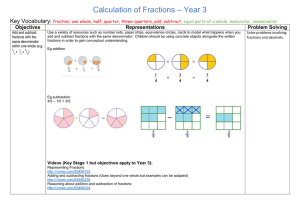
Calculation of Fractions – Year 3
... A similar model can be used for repeated addition for multiplication of fractions and mixed numbers by whole numbers. ...
... A similar model can be used for repeated addition for multiplication of fractions and mixed numbers by whole numbers. ...
Sc. and fU. Scheme
... from 1981 admission onwards, for M.A /M.Sc.iM.Com. courses and for the new unified scheme and syliabi being introduced in the University departments and affiliated colleges. 2 The Academic Council at its meeting held on 27-6-81 had approved the new scheme and syllabi, for science subjects at P.G. le ...
... from 1981 admission onwards, for M.A /M.Sc.iM.Com. courses and for the new unified scheme and syliabi being introduced in the University departments and affiliated colleges. 2 The Academic Council at its meeting held on 27-6-81 had approved the new scheme and syllabi, for science subjects at P.G. le ...
algebra i notes - Walden University ePortfolio for Mike Dillon
... FACTORING OUT THE GCF (Greatest Common Factor) **To factor a polynomial, take out the GCF of each of the terms. **The GCF of the terms includes: 1) The GCF of the coefficients (the biggest number that goes into them) 2) The most of each of the variables in common **Find the GCF of the following term ...
... FACTORING OUT THE GCF (Greatest Common Factor) **To factor a polynomial, take out the GCF of each of the terms. **The GCF of the terms includes: 1) The GCF of the coefficients (the biggest number that goes into them) 2) The most of each of the variables in common **Find the GCF of the following term ...
High Frequency Harmonics Emission in Smart Grids
... The term ‘smart grid‘, is nowadays very often used in many publications and so far has not been explicitly defined, however it refers mainly to such an operation of electricity delivery process that allows to optimize energy efficiency by flexible interconnection of central and distributed generator ...
... The term ‘smart grid‘, is nowadays very often used in many publications and so far has not been explicitly defined, however it refers mainly to such an operation of electricity delivery process that allows to optimize energy efficiency by flexible interconnection of central and distributed generator ...
2010-2011 Catalog Name: ____________________________ ID # ______________________ Date: _________
... 2010-2011 Catalog Name: ____________________________ ID # ______________________ Date: _________ ...
... 2010-2011 Catalog Name: ____________________________ ID # ______________________ Date: _________ ...
2011-2012 Catalog Mathematics 44 units
... 2011-2012 Catalog Name: ____________________________ ID # ______________________ Date: _________ ...
... 2011-2012 Catalog Name: ____________________________ ID # ______________________ Date: _________ ...
PreCalculus
... Difference of perfect squares: Your answer is the product of two binomials. Take the square root of each term. One binomial is Plus and the other binomial is Subtract. Ex: 4x2 – 25y4 = (2x + 5y2)(2x – 5y2) Sum or Difference of a perfect cube: Your answer is a binomial times a trinomial. Binomial par ...
... Difference of perfect squares: Your answer is the product of two binomials. Take the square root of each term. One binomial is Plus and the other binomial is Subtract. Ex: 4x2 – 25y4 = (2x + 5y2)(2x – 5y2) Sum or Difference of a perfect cube: Your answer is a binomial times a trinomial. Binomial par ...
ppt
... Sorting Arrays using Bubble Sort • Core of sorting: an if structure. • This is nested inside a for loop to look at each pair of values in the array. • This loop in nested inside another loop to make multiple passes through the array. • Look at SortThem & its source code. ...
... Sorting Arrays using Bubble Sort • Core of sorting: an if structure. • This is nested inside a for loop to look at each pair of values in the array. • This loop in nested inside another loop to make multiple passes through the array. • Look at SortThem & its source code. ...
Mathematics of radio engineering

The mathematics of radio engineering is the mathematical description by complex analysis of the electromagnetic theory applied to radio. Waves have been studied since ancient times and many different techniques have developed of which the most useful idea is the superposition principle which apply to radio waves. The Huygen's principle, which says that each wavefront creates an infinite number of new wavefronts that can be added, is the base for this analysis.