
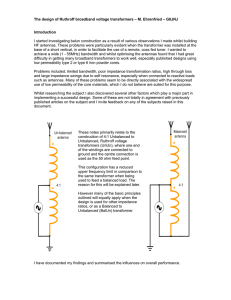
CHAPTER 3: SiGe MONOLITHIC TECHNOLOGIES
... consists of equations for input impedance, input return loss (S11), forward gain (S21) and NF, as well as an approximation of the IIP3 of the LNA. From this model compact design equations were also derived. The above derivations are presented in this chapter. All mathematical modelling for the resea ...
... consists of equations for input impedance, input return loss (S11), forward gain (S21) and NF, as well as an approximation of the IIP3 of the LNA. From this model compact design equations were also derived. The above derivations are presented in this chapter. All mathematical modelling for the resea ...
S F L
... The least common multiple (LCM) of a given set of numbers is the smallest positive number divisible by the numbers in the set. For example, if we list the multiples of 4 and 6, we can see these numbers share common multiples of 12, 24, 36, and 48 to name a few. Multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, ...
... The least common multiple (LCM) of a given set of numbers is the smallest positive number divisible by the numbers in the set. For example, if we list the multiples of 4 and 6, we can see these numbers share common multiples of 12, 24, 36, and 48 to name a few. Multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, ...
1.1 Patterns and Inductive Reasoning
... Conjecture: Every even number greater than 2 can be written as the sum of two primes. This is called Goldbach’s Conjecture. No one has ever proven this conjecture is true or found a counterexample to show that it is false. As of the writing of this text, it is unknown if this conjecture is true or f ...
... Conjecture: Every even number greater than 2 can be written as the sum of two primes. This is called Goldbach’s Conjecture. No one has ever proven this conjecture is true or found a counterexample to show that it is false. As of the writing of this text, it is unknown if this conjecture is true or f ...
1.1 Patterns and Inductive Reasoning
... Conjecture: Every even number greater than 2 can be written as the sum of two primes. This is called Goldbach’s Conjecture. No one has ever proven this conjecture is true or found a counterexample to show that it is false. As of the writing of this text, it is unknown if this conjecture is true or f ...
... Conjecture: Every even number greater than 2 can be written as the sum of two primes. This is called Goldbach’s Conjecture. No one has ever proven this conjecture is true or found a counterexample to show that it is false. As of the writing of this text, it is unknown if this conjecture is true or f ...
x, y
... Test Function ABS • Consider the following function: /* ABS This program function returns the absolute value of the integer passed to the function as a parameter. INPUT: An integer. OUTPUT: The absolute value if the input integer. ...
... Test Function ABS • Consider the following function: /* ABS This program function returns the absolute value of the integer passed to the function as a parameter. INPUT: An integer. OUTPUT: The absolute value if the input integer. ...
R u t c o r Research Metric and ultrametric spaces
... proved that, for every two nodes a, b of the circuit, the effective resistance µa,b is s/r s/r s/r well-defined and for every three nodes a, b, c the inequality µa,b ≤ µa,c + µc,b holds. It obviously implies the standard triangle inequality µa,b ≤ µa,c + µc,b when s ≥ r. For the case s = r = 1, thes ...
... proved that, for every two nodes a, b of the circuit, the effective resistance µa,b is s/r s/r s/r well-defined and for every three nodes a, b, c the inequality µa,b ≤ µa,c + µc,b holds. It obviously implies the standard triangle inequality µa,b ≤ µa,c + µc,b when s ≥ r. For the case s = r = 1, thes ...
Mathematics of radio engineering

The mathematics of radio engineering is the mathematical description by complex analysis of the electromagnetic theory applied to radio. Waves have been studied since ancient times and many different techniques have developed of which the most useful idea is the superposition principle which apply to radio waves. The Huygen's principle, which says that each wavefront creates an infinite number of new wavefronts that can be added, is the base for this analysis.




















![arXiv:math/0511682v1 [math.NT] 28 Nov 2005](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014696627_1-8def914a5ac3ed74bde3727e1309931c-300x300.png)
