Module 53: The Psychological Therapies, Summary Notes
... (a). Person-Centered Therapy- It was developed by Carl Rogers; therapist uses techniques such as active listening within a genuine, accepting, empathic environment to facilitate clients growth. It is called nondirectivetherapy and the therapist refrains from directing the client toward certain insig ...
... (a). Person-Centered Therapy- It was developed by Carl Rogers; therapist uses techniques such as active listening within a genuine, accepting, empathic environment to facilitate clients growth. It is called nondirectivetherapy and the therapist refrains from directing the client toward certain insig ...
13 Treatment of Abnormal Behavior
... • Interpersonal psychotherapy – digs for the cause, but with a more specific goalimprove relationships (12 – 16 weeks) ...
... • Interpersonal psychotherapy – digs for the cause, but with a more specific goalimprove relationships (12 – 16 weeks) ...
Chapter 9 Learning Objectives
... After reading this chapter, the learner should be able to: Module 9.1 Understand the essential aspects of psychotherapy. Describe traditional Freudian analysis. Discuss the major aspects of traditional psychoanalysis (such as free association and transference) Identify how modern psychodynamic appro ...
... After reading this chapter, the learner should be able to: Module 9.1 Understand the essential aspects of psychotherapy. Describe traditional Freudian analysis. Discuss the major aspects of traditional psychoanalysis (such as free association and transference) Identify how modern psychodynamic appro ...
Treatment of Disorders
... – Clients enter in crisis (temporary) – Want to believe it was worth the effort – Placebo effect (expect to get better) – Regression toward the mean (the usual state is better than rock bottom, which is where most patients start) ...
... – Clients enter in crisis (temporary) – Want to believe it was worth the effort – Placebo effect (expect to get better) – Regression toward the mean (the usual state is better than rock bottom, which is where most patients start) ...
Chapter 15 Jeopardy: Psychological Therapies
... What are authenticity: the genuine, open, and honest response of the therapist to the client unconditional positive regard: the warmth, respect, and accepting atmosphere created by the therapist for the client in person-centered therapy empathy: the ability of the therapist to understand the feeling ...
... What are authenticity: the genuine, open, and honest response of the therapist to the client unconditional positive regard: the warmth, respect, and accepting atmosphere created by the therapist for the client in person-centered therapy empathy: the ability of the therapist to understand the feeling ...
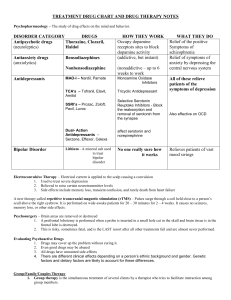
DrugTreatmentNotes
... Advantages to group therapy 1) therapist can see how client interacts 2) client feels less alone 3) group members can raise each others’ self-confidence, selfacceptance, and expectations for improvement 4) clients can learn from each other 5) group members may become more sensitive and more willing ...
... Advantages to group therapy 1) therapist can see how client interacts 2) client feels less alone 3) group members can raise each others’ self-confidence, selfacceptance, and expectations for improvement 4) clients can learn from each other 5) group members may become more sensitive and more willing ...
Chapter 17
... to facilitate clients’ growth. _____________________: technique in which therapist is non-directive towards client and empathizes with them by _____________________________________________. Client Centered Therapy Promotes Self-Awareness When given __________________________ clients start to accept ...
... to facilitate clients’ growth. _____________________: technique in which therapist is non-directive towards client and empathizes with them by _____________________________________________. Client Centered Therapy Promotes Self-Awareness When given __________________________ clients start to accept ...
therapy synopsis
... This process is assisted by the phenomenon of of transference—the projection of repressed feelings for important people in one’s life onto the analyst and then believing that those feelings are feelings toward the analyst. Even though the patient may think these feelings are genuine, they are not, t ...
... This process is assisted by the phenomenon of of transference—the projection of repressed feelings for important people in one’s life onto the analyst and then believing that those feelings are feelings toward the analyst. Even though the patient may think these feelings are genuine, they are not, t ...
17.Psychological Therapies
... •Freud used free association, hypnosis and dream interpretation to gain insight into the client’s unconscious. ...
... •Freud used free association, hypnosis and dream interpretation to gain insight into the client’s unconscious. ...
Quiz Therapy (30 points total) Multiple Choice 20
... 4) Systematicdesensitizationwas developed around the principle that A) people's thinking processesdetermine their behaviors. B) people cannot be both afraid and relaxed at the same time. C) people will not repeat behaviors that are followed by punishment. D) time out is not effective becauseit is im ...
... 4) Systematicdesensitizationwas developed around the principle that A) people's thinking processesdetermine their behaviors. B) people cannot be both afraid and relaxed at the same time. C) people will not repeat behaviors that are followed by punishment. D) time out is not effective becauseit is im ...
Notesch13therapy
... Modern psychoanalysis-not as long or expensive, lots of neo-Freudians focus on conscious motives now ...
... Modern psychoanalysis-not as long or expensive, lots of neo-Freudians focus on conscious motives now ...
Treatments For Psychological Disorders
... Manifest content Latent content Analysis of resistance An unwillingness or inability to talk about certain thoughts, motives or experiences Analysis of transference Transference- the process whereby clients project onto the therapist attitudes and feelings they had in a past relationship ...
... Manifest content Latent content Analysis of resistance An unwillingness or inability to talk about certain thoughts, motives or experiences Analysis of transference Transference- the process whereby clients project onto the therapist attitudes and feelings they had in a past relationship ...
February 9, Psych Cont`d
... PSYCHOTHERAPY • USE LANGUAGE (TALK) TO HEAL SUFFERING • FOCUS ON BIOGRAPHY • INVOLVE INTERPERSONAL RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN PATIENT AND THERAPIST ...
... PSYCHOTHERAPY • USE LANGUAGE (TALK) TO HEAL SUFFERING • FOCUS ON BIOGRAPHY • INVOLVE INTERPERSONAL RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN PATIENT AND THERAPIST ...
Insight TherapiesPsychoanalysis – designed to Free association
... Alternative forms of treatment (many) Half-way houses Family-crisis interventions Day-care Prevention ...
... Alternative forms of treatment (many) Half-way houses Family-crisis interventions Day-care Prevention ...
Module 70 notes - Bremerton School District
... An eclectic approach - uses techniques from various forms of therapy. ...
... An eclectic approach - uses techniques from various forms of therapy. ...
Therapies guide - Counselling Rooms
... such as focused breathing and meditation as a vehicle for developing awareness of thought processes and their effects on emotions and behaviour, whilst also acknowledging that we exist independently of our thoughts and therefore do not have to respond to them. Person-Centred Counselling has develope ...
... such as focused breathing and meditation as a vehicle for developing awareness of thought processes and their effects on emotions and behaviour, whilst also acknowledging that we exist independently of our thoughts and therefore do not have to respond to them. Person-Centred Counselling has develope ...
Psychotherapy - Barrington 220
... Directing your hidden feelings and wishes towards your therapist ...
... Directing your hidden feelings and wishes towards your therapist ...
(MAD) with the Three Letter Acronym (TLA)
... Behavior Therapy (DBT), Interpersonal Therapy (IPT), Family Focused Therapy (FFT), and Emotionally Focused Therapy (EFT). This is the order in which they are listed, and they are then described, adequately enough, but in the tone one might use to describe a list of the five antibiotics best used to ...
... Behavior Therapy (DBT), Interpersonal Therapy (IPT), Family Focused Therapy (FFT), and Emotionally Focused Therapy (EFT). This is the order in which they are listed, and they are then described, adequately enough, but in the tone one might use to describe a list of the five antibiotics best used to ...
File
... - All emotions have three parts: physical, behavioural and cognitive - Emotional Intelligence ...
... - All emotions have three parts: physical, behavioural and cognitive - Emotional Intelligence ...
Slide 1
... between therapists and clients. The aim is to help clients understand the nature of their problems and the meaning of their behaviors, thoughts, and feelings. Insight therapists may use a variety of approaches, including psychodynamic, cognitive, or humanistic. Behavior therapies also involve conver ...
... between therapists and clients. The aim is to help clients understand the nature of their problems and the meaning of their behaviors, thoughts, and feelings. Insight therapists may use a variety of approaches, including psychodynamic, cognitive, or humanistic. Behavior therapies also involve conver ...
Behavior Therapies
... much shorter session and also aims to to help patients gain insight into the roots of their difficulties. However instead of focusing on past, this approach focuses on current relationships and how to deal with problems….looking for symptom relief instead of personality change. ...
... much shorter session and also aims to to help patients gain insight into the roots of their difficulties. However instead of focusing on past, this approach focuses on current relationships and how to deal with problems….looking for symptom relief instead of personality change. ...
Treatment of Abnormal Behavior
... • EVALUATE EVIDENCE THE CLIENT HAS FOR AND AGAINST AUTOMATIC THOUGHTS • REASSIGN THE BLAME TO SITUATIONAL FACTORS • DISCUSS ALTERNATIVE SOLUTIONS ...
... • EVALUATE EVIDENCE THE CLIENT HAS FOR AND AGAINST AUTOMATIC THOUGHTS • REASSIGN THE BLAME TO SITUATIONAL FACTORS • DISCUSS ALTERNATIVE SOLUTIONS ...