BIOS 1710 SI Week 6 Session 1 Tuesday 7:05
... 10. ____% of the water that leaves as filtrate is reabsorbed each day. _____% is absorbed in the proximal tubule. 11. Why are microvilli important to the excretory system? ...
... 10. ____% of the water that leaves as filtrate is reabsorbed each day. _____% is absorbed in the proximal tubule. 11. Why are microvilli important to the excretory system? ...
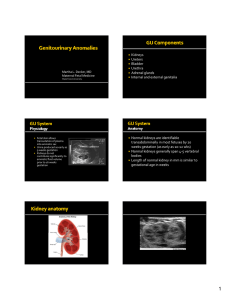
Kidneys Ureters Bladder Urethra Adrenal glands Internal and
... Urine produced as early as 9 weeks gestation Kidneys do not contribute significantly to amniotic fluid volume prior to 16 weeks gestation ...
... Urine produced as early as 9 weeks gestation Kidneys do not contribute significantly to amniotic fluid volume prior to 16 weeks gestation ...
Chronic Kidney Disease: Detection and Evaluation
... represents a loss of at least one-half of normal kidney function; below this level, there is an increased prevalence of CKD complications. Creatinine clearance is used to estimate the GFR. Because creatinine is filtered and secreted by the proximal tubules, the creatinine clearance exceeds the GFR. ...
... represents a loss of at least one-half of normal kidney function; below this level, there is an increased prevalence of CKD complications. Creatinine clearance is used to estimate the GFR. Because creatinine is filtered and secreted by the proximal tubules, the creatinine clearance exceeds the GFR. ...
Urinary System
... Uric Acid- a chemical created when the body breaks down substances called purines which are found in some foods and drinks. Most uric acid dissolves in blood and travels to the kidneys. From there, it passes out in urine. If your body produces too much uric acid or doesn't remove enough if it, you c ...
... Uric Acid- a chemical created when the body breaks down substances called purines which are found in some foods and drinks. Most uric acid dissolves in blood and travels to the kidneys. From there, it passes out in urine. If your body produces too much uric acid or doesn't remove enough if it, you c ...
Chapter Two Line Title Here and Chapter Title Here and Here
... peptide, which allows fine-tuning of final urine concentration. F. Step 3: Tubular Secretion (pp. 972–973; Fig. 25.15) 1. Tubular secretion disposes of unwanted solutes, eliminates unwanted, reabsorbed solutes, rids the body of excess K+, and controls blood pH. 2. Tubular secretion is most active in ...
... peptide, which allows fine-tuning of final urine concentration. F. Step 3: Tubular Secretion (pp. 972–973; Fig. 25.15) 1. Tubular secretion disposes of unwanted solutes, eliminates unwanted, reabsorbed solutes, rids the body of excess K+, and controls blood pH. 2. Tubular secretion is most active in ...
Chapter 15
... – Potential causes: sustained very low blood pressure, infections, transfusion reactions, severe injury, toxin exposure, drug reactions ...
... – Potential causes: sustained very low blood pressure, infections, transfusion reactions, severe injury, toxin exposure, drug reactions ...
UrinarySystem
... RENAL SINUS AT HILUM: BLOOD VESSELS, URETER, NERVES, LYMPHATIC VESSELS RELEASES ERYTHROPOIETIN ? RELEASES RENIN ? ...
... RENAL SINUS AT HILUM: BLOOD VESSELS, URETER, NERVES, LYMPHATIC VESSELS RELEASES ERYTHROPOIETIN ? RELEASES RENIN ? ...
Kidney transplantation

Kidney transplantation or renal transplantation is the organ transplant of a kidney into a patient with end-stage renal disease. Kidney transplantation is typically classified as deceased-donor (formerly known as cadaveric) or living-donor transplantation depending on the source of the donor organ. Living-donor renal transplants are further characterized as genetically related (living-related) or non-related (living-unrelated) transplants, depending on whether a biological relationship exists between the donor and recipient. Exchanges and chains are a novel approach to expand the living donor pool.