Stethoscopes: A Potential Source of Nosocomial Infections
... to electronic thermometers,1 blood pressure cuffs2 and latex gloves.3 Stethoscopes have always been part of the physician's basic paraphernalia when examining patients. It has recently been shown to harbor various organisms on their diaphragm surfaces with coagulase negative staphylococci as the pre ...
... to electronic thermometers,1 blood pressure cuffs2 and latex gloves.3 Stethoscopes have always been part of the physician's basic paraphernalia when examining patients. It has recently been shown to harbor various organisms on their diaphragm surfaces with coagulase negative staphylococci as the pre ...
MUKOSA-SISTEM-IMMUN-BAKTERI-VIRUS-CACING
... Degrading toxins Produce vitamin K & short chain fatty acids Maintaining epithelium Compete the pathogens Inhibit pro-inflammatory signals Musketeers Course October 2008 ...
... Degrading toxins Produce vitamin K & short chain fatty acids Maintaining epithelium Compete the pathogens Inhibit pro-inflammatory signals Musketeers Course October 2008 ...
Working Toward Zero Surgical Site Infection Rate
... wash off the dirt! • Wash hands several times a day – especially if you have had gloves on for more than 20 minutes – organisms multiply every 20 minutes 2009 ASHES Annual Conference September 20-24, 2009 Reno, NV ...
... wash off the dirt! • Wash hands several times a day – especially if you have had gloves on for more than 20 minutes – organisms multiply every 20 minutes 2009 ASHES Annual Conference September 20-24, 2009 Reno, NV ...
The comparison of susceptibility patterns of Gram
... P. aeruginosa similarly to the experience of other authors (Fluit et al. 2000; Assadian et al. 2002; Luzzaro et al. 2002; Daxboeck et al. 2004). Overall, our results indicate that MIC values as well as the percentage of susceptibility of non-fermentative microbes such as A. baumannii and P. aerugino ...
... P. aeruginosa similarly to the experience of other authors (Fluit et al. 2000; Assadian et al. 2002; Luzzaro et al. 2002; Daxboeck et al. 2004). Overall, our results indicate that MIC values as well as the percentage of susceptibility of non-fermentative microbes such as A. baumannii and P. aerugino ...
Advanced workshop for treating fungal
... • Pleo Exmykehl drops 10 drops daily or one rectal suppository at bedtime 3X per week ...
... • Pleo Exmykehl drops 10 drops daily or one rectal suppository at bedtime 3X per week ...
Bengt Wretlind
... Wretlind, B; Gezelius, L; Karlsson, I; Hagberg, R. In vitro activity of a new semisynthetic penicillin, PC904, against ampicillin-resistant Gram-negative bacteria. In: Current Chemotherapy, pp. 638-641. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, 1978. ...
... Wretlind, B; Gezelius, L; Karlsson, I; Hagberg, R. In vitro activity of a new semisynthetic penicillin, PC904, against ampicillin-resistant Gram-negative bacteria. In: Current Chemotherapy, pp. 638-641. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC, 1978. ...
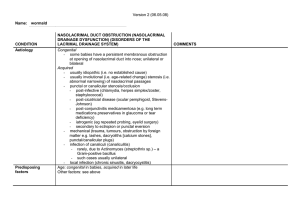
FB sub-tarsal - Vision 2020 UK
... - dilate puncta with progressive diameter punctal dilator - take care not to traumatise tissues - periodic repetition may be required Lacrimal lavage (saline syringing) may be effective in cases of - local (discrete) obstruction - subacute inflammation or infection - less likely to be effective: - i ...
... - dilate puncta with progressive diameter punctal dilator - take care not to traumatise tissues - periodic repetition may be required Lacrimal lavage (saline syringing) may be effective in cases of - local (discrete) obstruction - subacute inflammation or infection - less likely to be effective: - i ...
Clinical pathogenesis of typhoid fever
... burst, are more susceptible to infection with NTS and frequently develop bacteraemia [48]. However, there is no positive correlation between the frequency or severity of typhoid fever and CGD. The induction of an oxidative burst in professional phagocytes depends on TLR signalling, since activation ...
... burst, are more susceptible to infection with NTS and frequently develop bacteraemia [48]. However, there is no positive correlation between the frequency or severity of typhoid fever and CGD. The induction of an oxidative burst in professional phagocytes depends on TLR signalling, since activation ...
Interaction between Salmonella and Schistosomiasis: A Review
... 3.4 million cases and a case fatality rate of 20% [4]. Yet, data specific to the African region are limited. Salmonella serotypes Typhi (S. Typhi) and Paratyphi A, B, and C, are the best described serotypes that cause typhoid fever (TF) and paratyphoid fever, respectively [5]. Both serotypes of the ...
... 3.4 million cases and a case fatality rate of 20% [4]. Yet, data specific to the African region are limited. Salmonella serotypes Typhi (S. Typhi) and Paratyphi A, B, and C, are the best described serotypes that cause typhoid fever (TF) and paratyphoid fever, respectively [5]. Both serotypes of the ...
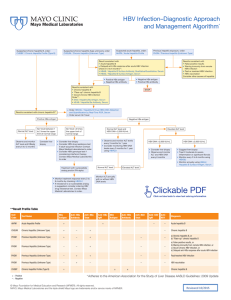
HBV Infection–Diagnostic Approach and Management Algorithm*
... Monitor treatment response every 3 to 6 months by checking HBVQU If resistance to a nucleos(t)ide analog is suggested, consider ordering HBV drug resistance test. Contact Mayo Medical Laboratories to order. ...
... Monitor treatment response every 3 to 6 months by checking HBVQU If resistance to a nucleos(t)ide analog is suggested, consider ordering HBV drug resistance test. Contact Mayo Medical Laboratories to order. ...
FB sub-tarsal - Vision 2020 UK
... - dilate puncta with progressive diameter punctal dilator - take care not to traumatise tissues - periodic repetition may be required Lacrimal lavage (saline syringing) may be effective in cases of - local (discrete) obstruction - subacute inflammation or infection - less likely to be effective: - i ...
... - dilate puncta with progressive diameter punctal dilator - take care not to traumatise tissues - periodic repetition may be required Lacrimal lavage (saline syringing) may be effective in cases of - local (discrete) obstruction - subacute inflammation or infection - less likely to be effective: - i ...
Pathophysiology and Clinical Spectrum of Infections in Systemic
... including generation of autoantibodies in low titers with a transient course, but the progression into an established autoimmune disease is rare.64,65 The most common viral infections in patients who have SLE are parvovirus B19 (there are more than 30 reports of primary B19 infection reported as lup ...
... including generation of autoantibodies in low titers with a transient course, but the progression into an established autoimmune disease is rare.64,65 The most common viral infections in patients who have SLE are parvovirus B19 (there are more than 30 reports of primary B19 infection reported as lup ...
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
... action plan against the rising threat – priority is given to mitigating the development of antibiotic resistance through appropriate use, prevention of infection and developing effective antimicrobials[1]. In a paired surveillance report by the European Centre of Disease P ...
... action plan against the rising threat – priority is given to mitigating the development of antibiotic resistance through appropriate use, prevention of infection and developing effective antimicrobials[1]. In a paired surveillance report by the European Centre of Disease P ...
Research Update from the US Meat Animal
... of anti-OPPV antibody at each sample date were measured. ...
... of anti-OPPV antibody at each sample date were measured. ...
Management of prolapse of the anterior compartment
... denudation of vaginal mucosa for the management of prolapse in 1823 on a cadaver. This was first performed on a living patient in 1830. By 1866 J.M. Simm had performed a series of denudation operations very similar to a modern anterior repair.1 The majority of historical papers describing the aetiol ...
... denudation of vaginal mucosa for the management of prolapse in 1823 on a cadaver. This was first performed on a living patient in 1830. By 1866 J.M. Simm had performed a series of denudation operations very similar to a modern anterior repair.1 The majority of historical papers describing the aetiol ...
review of literature
... the continuous exposure of humans to them – explains the extremely good tolerance of the human organisms to phages. These observations strongly suggest that phage therapy may provide one of the safest as well as most environmentally friendly methods currently available for prophylaxis and treatment ...
... the continuous exposure of humans to them – explains the extremely good tolerance of the human organisms to phages. These observations strongly suggest that phage therapy may provide one of the safest as well as most environmentally friendly methods currently available for prophylaxis and treatment ...
FB sub-tarsal - Vision 2020 UK
... - dilate puncta with progressive diameter punctal dilator - take care not to traumatise tissues - periodic repetition may be required Lacrimal lavage (saline syringing) may be effective in cases of - local (discrete) obstruction - subacute inflammation or infection - less likely to be effective: - i ...
... - dilate puncta with progressive diameter punctal dilator - take care not to traumatise tissues - periodic repetition may be required Lacrimal lavage (saline syringing) may be effective in cases of - local (discrete) obstruction - subacute inflammation or infection - less likely to be effective: - i ...
WATCHING BABY׳S BACK
... If the rash is not treated immediately, it can develop into fungal or bacteria infection of the skin, appearing as very sore red skin sometimes accompanied by pus-filled blisters. In most cases when this happens, fever will be prominent and the baby will be unwell and highly irritable. ...
... If the rash is not treated immediately, it can develop into fungal or bacteria infection of the skin, appearing as very sore red skin sometimes accompanied by pus-filled blisters. In most cases when this happens, fever will be prominent and the baby will be unwell and highly irritable. ...
27. INFECTIONS OF THE UPPER RESPIRATORY TRACT
... • most cases resolve clinically 1 week after the onset of illness • initial observation and aggressive pain management with anti-inflammatory therapy • reserving antibiotics for high-risk patients, patients with complicated disease, or patients who do not improve after 48 to 72 h. • recommend antibi ...
... • most cases resolve clinically 1 week after the onset of illness • initial observation and aggressive pain management with anti-inflammatory therapy • reserving antibiotics for high-risk patients, patients with complicated disease, or patients who do not improve after 48 to 72 h. • recommend antibi ...
27. infections of the upper respiratory tract
... • most cases resolve clinically 1 week after the onset of illness • initial observation and aggressive pain management with anti-inflammatory therapy • reserving antibiotics for high-risk patients, patients with complicated disease, or patients who do not improve after 48 to 72 h. • recommend antibi ...
... • most cases resolve clinically 1 week after the onset of illness • initial observation and aggressive pain management with anti-inflammatory therapy • reserving antibiotics for high-risk patients, patients with complicated disease, or patients who do not improve after 48 to 72 h. • recommend antibi ...
Slide 1
... • Counts of 105 CFU/ml or more indicate significant UTI • (p. 1152, normal count: <104) • Counts as low as 102 CFU/ml in a person with signs/symptoms are indicative of UTI Copyright © 2010, 2007, 2004, 2000, Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. All Rights Reserved. ...
... • Counts of 105 CFU/ml or more indicate significant UTI • (p. 1152, normal count: <104) • Counts as low as 102 CFU/ml in a person with signs/symptoms are indicative of UTI Copyright © 2010, 2007, 2004, 2000, Mosby, Inc., an affiliate of Elsevier Inc. All Rights Reserved. ...
277 ABNORMAL TYROSINE AND PHENYLALANINE METABOLISM
... excretory pattern being of the phenylketonuric type at a low level. After 3 days PPA and PLA had disappeared from the urine. Serum phenylalanine became normal when the intake was decreased to 21 mg phenylalanine/kg. Then the intake was gradually increased up to 53 mg/kg without a significant effect ...
... excretory pattern being of the phenylketonuric type at a low level. After 3 days PPA and PLA had disappeared from the urine. Serum phenylalanine became normal when the intake was decreased to 21 mg phenylalanine/kg. Then the intake was gradually increased up to 53 mg/kg without a significant effect ...
... and beard areas. The inflammation keeps fungal numbers low so that samples of scale and/or tissue may fail to include organisms.16,17 Cultures from the purulent exudate often isolate only colonizing bacteria; infecting fungi usually are not detected because neutrophils kill fungi or at least keep th ...
Urinary tract infection
A urinary tract infection (UTI), also known as acute cystitis or bladder infection, is an infection that affects part of the urinary tract. When it affects the lower urinary tract it is known as a simple cystitis (a bladder infection) and when it affects the upper urinary tract it is known as pyelonephritis (a kidney infection). Symptoms from a lower urinary tract include painful urination and either frequent urination or urge to urinate (or both); while the symptoms of pyelonephritis include fever and flank pain in addition to the symptoms of a lower UTI. In some cases, a painful burning sensation in the urethra may be present even when not urinating. In the elderly and the very young, symptoms may be vague or non-specific. The main causal agent of both types is Escherichia coli, though other bacteria, viruses or fungi may rarely be the cause.Urinary tract infections occur more commonly in women than men, with half of women having at least one infection at some point in their lives. Recurrences are common. Risk factors include female anatomy, sexual intercourse and family history. Pyelonephritis, if it occurs, usually follows a bladder infection but may also result from a blood-borne infection. Diagnosis in young healthy women can be based on symptoms alone. In those with vague symptoms, diagnosis can be difficult because bacteria may be present without there being an infection. In complicated cases or if treatment has failed, a urine culture may be useful. In those with frequent infections, low dose antibiotics may be taken as a preventative measure.In uncomplicated cases, urinary tract infections are easily treated with a short course of antibiotics, although resistance to many of the antibiotics used to treat this condition is increasing. In complicated cases, a longer course or intravenous antibiotics may be needed, and if symptoms have not improved in two or three days, further diagnostic testing is needed. In women, urinary tract infections are the most common form of bacterial infection with 10% developing urinary tract infections yearly. In those who have bacteria or white blood cells in their urine but have no symptoms, antibiotics are generally not needed, although pregnant women are an exception to this recommendation.