File
... that the types of living organisms on Earth have changed over the course of time. Fossils reveal organisms that no longer exist, fossils that are similar to present day organisms, and fossils that look the same as some present day organisms. New fossils are constantly being found. ...
... that the types of living organisms on Earth have changed over the course of time. Fossils reveal organisms that no longer exist, fossils that are similar to present day organisms, and fossils that look the same as some present day organisms. New fossils are constantly being found. ...
The Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection
... that the types of living organisms on Earth have changed over the course of time. ● Fossils reveal organisms that no longer exist, fossils that are similar to present day organisms, and fossils that look the same as some present day organisms. ● New fossils are constantly being found. ...
... that the types of living organisms on Earth have changed over the course of time. ● Fossils reveal organisms that no longer exist, fossils that are similar to present day organisms, and fossils that look the same as some present day organisms. ● New fossils are constantly being found. ...
Darwin`s Theory of Evolution
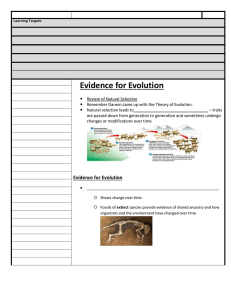
... Evidence for Evolution 1. Biogeography – Patterns of species distribution – Closely related but different = variations among populations that resulted in the development of different species – Distantly related but similar = species that are similar and live in similar environments but in different ...
... Evidence for Evolution 1. Biogeography – Patterns of species distribution – Closely related but different = variations among populations that resulted in the development of different species – Distantly related but similar = species that are similar and live in similar environments but in different ...
2015 EARTH`S HISTORY/ EVOLUTION STUDY GUIDE NAME
... 16. Give two examples of a trace fossil? A MARK LEFT BY A DINOSAUR’S TAIL, A PRESERVED FOOTPRINT 17. The phrase “younger over older” could be used to remember the principle of SUPERPOSITION 18. How do geologists use the geologic time scale? TO DIVIDE EARTH’S HISTORY INTO MANAGEABLE PARTS 19. Which k ...
... 16. Give two examples of a trace fossil? A MARK LEFT BY A DINOSAUR’S TAIL, A PRESERVED FOOTPRINT 17. The phrase “younger over older” could be used to remember the principle of SUPERPOSITION 18. How do geologists use the geologic time scale? TO DIVIDE EARTH’S HISTORY INTO MANAGEABLE PARTS 19. Which k ...
Evidence of the Past
... structures that had a useful role at one time but no longer do. The presence of these structures suggests that the organism evolved from another life form where that structure played a more important role. examples: remnants of hind-limb bones in whales and some snakes ______________________________ ...
... structures that had a useful role at one time but no longer do. The presence of these structures suggests that the organism evolved from another life form where that structure played a more important role. examples: remnants of hind-limb bones in whales and some snakes ______________________________ ...
Evolution QUESTIONS
... 1. What was Charles Darwin’s job on the British ship (HMS Beagle), and what did his observations lead him to develop? ...
... 1. What was Charles Darwin’s job on the British ship (HMS Beagle), and what did his observations lead him to develop? ...
adaptation A characteristic that helps an organism survive in its
... The remnant of a once-useful anatomical structure. ...
... The remnant of a once-useful anatomical structure. ...
Biology
... 5. Back in Britain, what did Darwin learn about the birds he collected? ____________________________ 6. How many different species were there? __________________________________________________ 7. Darwin thought humans were descended from what animal? __________________________________ 8. What helpe ...
... 5. Back in Britain, what did Darwin learn about the birds he collected? ____________________________ 6. How many different species were there? __________________________________________________ 7. Darwin thought humans were descended from what animal? __________________________________ 8. What helpe ...
Chapter 16
... • Darwin noticed similarities between species seen on mainland and island chains • Thought similarities could be explained by ...
... • Darwin noticed similarities between species seen on mainland and island chains • Thought similarities could be explained by ...
Life ch 6 Review - Evolution What was Lamark`s theory of evolution
... 98% of our DNA with chimpanzees. 3. vestigial structure – body parts that our ancestors used before but they no longer serve a purpose, evolving to not have them, appendix. Pelvis bone in whales and manatees. 4. embryo(logy) – similarities between humans and fish and chickens when developing suggest ...
... 98% of our DNA with chimpanzees. 3. vestigial structure – body parts that our ancestors used before but they no longer serve a purpose, evolving to not have them, appendix. Pelvis bone in whales and manatees. 4. embryo(logy) – similarities between humans and fish and chickens when developing suggest ...
Review for Chapter 6 Test - Changes Over time word document
... 8. Darwin thought that species evolved rapidly. _________________________ ...
... 8. Darwin thought that species evolved rapidly. _________________________ ...
2. What can be learned from the fossil record?
... 32. Which part of the name Homo erectus identifies the genus? ______________ 33. List in order from smallest to largest the seven categories in Linnaeus’s system of classification. _______________________________________________________________________________________________ 34. Give an example of ...
... 32. Which part of the name Homo erectus identifies the genus? ______________ 33. List in order from smallest to largest the seven categories in Linnaeus’s system of classification. _______________________________________________________________________________________________ 34. Give an example of ...
EVOLUTION NOTEScomplete2010 - Fredericksburg City Public
... ____________________________are scientists who study the lives and cultures of human through fossils and artifacts ...
... ____________________________are scientists who study the lives and cultures of human through fossils and artifacts ...
Ch 7 - Evolution Review Jeopardy Game
... What trait of the finches did Charles Darwin study? What did he conclude was the reason for the differences in this trait? ...
... What trait of the finches did Charles Darwin study? What did he conclude was the reason for the differences in this trait? ...
jcib ap biology
... from the mainlaind that organisms on islands further out. And all organisms had more in common with mainland animals than with eachother. 4. Changes were also reflected in the fossil record (traveled with Lyell’s Principles of Geology) 5. These changes must have happened of over 100s or 1000s of gen ...
... from the mainlaind that organisms on islands further out. And all organisms had more in common with mainland animals than with eachother. 4. Changes were also reflected in the fossil record (traveled with Lyell’s Principles of Geology) 5. These changes must have happened of over 100s or 1000s of gen ...
EVOLUTION-CHAPTER 1-3
... Relative Dating- younger fossils are closer to the surface and older fossils are found deeper. ...
... Relative Dating- younger fossils are closer to the surface and older fossils are found deeper. ...
AP Biology Ch 19 notes
... homologous structures - anatomical signs of evolution vestigial organs - structures of little, if any, importance to an organism - remnants of structures that had important functions in ancestors - example: vestiges of pelvis and leg bones in whales ...
... homologous structures - anatomical signs of evolution vestigial organs - structures of little, if any, importance to an organism - remnants of structures that had important functions in ancestors - example: vestiges of pelvis and leg bones in whales ...
Theory of Evolution Notes - Effingham County Schools
... o Galápagos finches that live in areas with hard-shelled nuts have ...
... o Galápagos finches that live in areas with hard-shelled nuts have ...
Evidence for Evolution
... comparing protein & DNA sequences. The greater the similarities in DNA and protein sequences, the more likely two organisms share a common ancestor. ...
... comparing protein & DNA sequences. The greater the similarities in DNA and protein sequences, the more likely two organisms share a common ancestor. ...
Theory of Evolution Notes Outline
... II. Charles Darwin: Naturalist & Theologist. 1. Sailed on the ship named ____________ as a naturalist in the early 1800s. 2. Observed species diversity and unity in the ________________ ________________ off the coast of South America. 3. Most famous species:________________ 4. Explained that the fi ...
... II. Charles Darwin: Naturalist & Theologist. 1. Sailed on the ship named ____________ as a naturalist in the early 1800s. 2. Observed species diversity and unity in the ________________ ________________ off the coast of South America. 3. Most famous species:________________ 4. Explained that the fi ...
You Light Up My Life
... Challenges to Early Beliefs • Biogeography - discovery of species in isolated ...
... Challenges to Early Beliefs • Biogeography - discovery of species in isolated ...
Evolution - Richard Dawkins Foundation
... 1.The scientific theory of evolution is the organizing principle of life science. 2. The scientific theory or evolution is supported by multiple forms of evidence. 3.Natural selection is the primary mechanism leading to change over time in organisms. ...
... 1.The scientific theory of evolution is the organizing principle of life science. 2. The scientific theory or evolution is supported by multiple forms of evidence. 3.Natural selection is the primary mechanism leading to change over time in organisms. ...
Water Test 1 Review Sheet
... What is the difference between radioactive dating and the law of superposition and what does each tell us? ...
... What is the difference between radioactive dating and the law of superposition and what does each tell us? ...
Chapter 15: Evolution
... Section 1: Darwin’s Theory of Natural Selection Darwin on the HMS Beagle: ...
... Section 1: Darwin’s Theory of Natural Selection Darwin on the HMS Beagle: ...
Transitional fossil

A transitional fossil is any fossilized remains of a life form that exhibits traits common to both an ancestral group and its derived descendant group. This is especially important where the descendant group is sharply differentiated by gross anatomy and mode of living from the ancestral group. These fossils serve as a reminder that taxonomic divisions are human constructs that have been imposed in hindsight on a continuum of variation. Because of the incompleteness of the fossil record, there is usually no way to know exactly how close a transitional fossil is to the point of divergence. Therefore, it cannot be assumed that transitional fossils are direct ancestors of more recent groups, though they are frequently used as models for such ancestors.In 1859, when Charles Darwin's On the Origin of Species was first published, the fossil record was poorly known. Darwin described the perceived lack of transitional fossils as, ""...the most obvious and gravest objection which can be urged against my theory,"" but explained it by relating it to the extreme imperfection of the geological record. He noted the limited collections available at that time, but described the available information as showing patterns that followed from his theory of descent with modification through natural selection. Indeed, Archaeopteryx was discovered just two years later, in 1861, and represents a classic transitional form between dinosaurs and birds. Many more transitional fossils have been discovered since then, and there is now abundant evidence of how all classes of vertebrates are related, much of it in the form of transitional fossils. Specific examples include humans and other primates, tetrapods and fish, and birds and dinosaurs.The term ""missing link"" has been used extensively in popular writings on human evolution to refer to a perceived gap in the hominid evolutionary record. It is most commonly used to refer to any new transitional fossil finds. Scientists, however, do not use the term, as it refers to a pre-evolutionary view of nature.