Vocabulary
... 7) Place Theory: in hearing, the theory that links the pitch we hear with the place where the cochlea’s membrane is stimulated 8) Frequency Theory: in hearing, the theory that the rate of nerve impulses traveling up the auditory nerve matches the frequency of a tone, thus enabling us to sense its pi ...
... 7) Place Theory: in hearing, the theory that links the pitch we hear with the place where the cochlea’s membrane is stimulated 8) Frequency Theory: in hearing, the theory that the rate of nerve impulses traveling up the auditory nerve matches the frequency of a tone, thus enabling us to sense its pi ...
Hearing
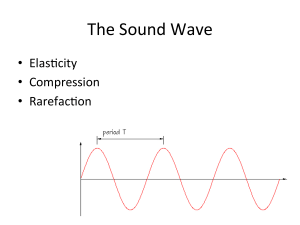
... apart. This movement produces variations in pres sure that radiate in all directions. The transmitting substance is usually air, but sound waves can also travel through water and solids, as you know if you have ever put your ear to the wall to hear voices in the next room . As with vision, physical ...
... apart. This movement produces variations in pres sure that radiate in all directions. The transmitting substance is usually air, but sound waves can also travel through water and solids, as you know if you have ever put your ear to the wall to hear voices in the next room . As with vision, physical ...
Unit 2. Lesson 5. Noise Pollution
... impact that results in declined hearing ability in marine mammals. Sudden and long or repeated exposure to high frequency sounds can cause permanent hearing loss. Sudden onset of intense sounds can also induce trauma. One of these sounds would be the sudden revving of a boat engine from idle to full ...
... impact that results in declined hearing ability in marine mammals. Sudden and long or repeated exposure to high frequency sounds can cause permanent hearing loss. Sudden onset of intense sounds can also induce trauma. One of these sounds would be the sudden revving of a boat engine from idle to full ...
What are sound waves? - Peoria Public Schools
... particles. The particles in matter make up the medium through which waves can travel. • The particles of a medium only vibrate back and forth along the path of the sound waves. • Most sounds travel through air, but some travel through other materials, such as water, glass, and metal. • In a vacuum t ...
... particles. The particles in matter make up the medium through which waves can travel. • The particles of a medium only vibrate back and forth along the path of the sound waves. • Most sounds travel through air, but some travel through other materials, such as water, glass, and metal. • In a vacuum t ...
The Auditory System
... Acoustic input typically comes from many different sources; they have different combinations of frequencies, their amplitudes change independently and they have different locations. But the sound waves coming into the ears are just the sum of all these different acoustic signals. The auditory system ...
... Acoustic input typically comes from many different sources; they have different combinations of frequencies, their amplitudes change independently and they have different locations. But the sound waves coming into the ears are just the sum of all these different acoustic signals. The auditory system ...
Sensation & Perception
... have three different types of photoreceptors, each most sensitive to a different range of wavelengths ...
... have three different types of photoreceptors, each most sensitive to a different range of wavelengths ...
Hearing
... How might the placement of our ears alongside our head make it difficult to hear sounds coming from certain locations? Explain. ...
... How might the placement of our ears alongside our head make it difficult to hear sounds coming from certain locations? Explain. ...
PS CH 8 practice
... a. appears to decrease. b. appears to increase. c. stays the same. d. goes up and down repeatedly. ____ 23. A fundamental tone is a sound wave of only one a. frequency. b. pitch. c. timbre. d. intensity. ____ 24. What is a set of tones combined in a way that is pleasing to the ear? a. noise b. sound ...
... a. appears to decrease. b. appears to increase. c. stays the same. d. goes up and down repeatedly. ____ 23. A fundamental tone is a sound wave of only one a. frequency. b. pitch. c. timbre. d. intensity. ____ 24. What is a set of tones combined in a way that is pleasing to the ear? a. noise b. sound ...
Scientific American, February 23, 2017 - Brainvolts
... demonstrated in research on lab animals. So you might pass a hearing test, because the hair cells are still working, and some of the connections are still intact. Some of the connections that carry important information like speech, however, are missing But we have available protections. Ear protect ...
... demonstrated in research on lab animals. So you might pass a hearing test, because the hair cells are still working, and some of the connections are still intact. Some of the connections that carry important information like speech, however, are missing But we have available protections. Ear protect ...
What are some practical ways we use sound energy?
... respond to sound The receptors are tiny hair cells that shake back and forth in response to sound waves When they shake, the hair cells create nerve impulses which go to the brain along the auditory nerve ...
... respond to sound The receptors are tiny hair cells that shake back and forth in response to sound waves When they shake, the hair cells create nerve impulses which go to the brain along the auditory nerve ...
Light Energy Sound Energy Fill out the Venn Diagram
... • Humans hear sound waves in a limited frequency range. • The human ear can hear sounds from 20-‐20,000 Hz. • Any sound below that frequency range is called infrasound. • Any sound above tha ...
... • Humans hear sound waves in a limited frequency range. • The human ear can hear sounds from 20-‐20,000 Hz. • Any sound below that frequency range is called infrasound. • Any sound above tha ...
PPT
... Sound Pressure is measured in units called Pascals 1 Pascal (Pa) = 1 Newton of force/m2 1 atmosphere = 100,000 Pa Human absolute hearing threshold = 0.00002 Pa = 20 microPa (i.e., 2 ten billionths of an atmosphere) Frequency measured in cycles/sec = Hertz (Hz) Nominal range of sensitivity: 20 – 20,0 ...
... Sound Pressure is measured in units called Pascals 1 Pascal (Pa) = 1 Newton of force/m2 1 atmosphere = 100,000 Pa Human absolute hearing threshold = 0.00002 Pa = 20 microPa (i.e., 2 ten billionths of an atmosphere) Frequency measured in cycles/sec = Hertz (Hz) Nominal range of sensitivity: 20 – 20,0 ...
Hearing and the environment
... Binaural cues - location cues based on the comparison of the signals received by the left and right ears Interaural time difference (ITD)- difference between the times sounds reach the two ears When distance to each ear is the same, there are no differences in time. When the source is to the side ...
... Binaural cues - location cues based on the comparison of the signals received by the left and right ears Interaural time difference (ITD)- difference between the times sounds reach the two ears When distance to each ear is the same, there are no differences in time. When the source is to the side ...
Hearing Sultan
... Fibres end in the auditory area, where it is heard, then interpretation occurs in the auditory association areas (wernikes area) ...
... Fibres end in the auditory area, where it is heard, then interpretation occurs in the auditory association areas (wernikes area) ...
Groups of Musical Instruments
... sound quality of music depends on the instruments making the music. The sound quality of musical instruments results from blending a fundamental tone with its overtones. Fundamental Tones and Overtones – As a guitar string vibrates, waves travel along the string and reflect back, setting up a standi ...
... sound quality of music depends on the instruments making the music. The sound quality of musical instruments results from blending a fundamental tone with its overtones. Fundamental Tones and Overtones – As a guitar string vibrates, waves travel along the string and reflect back, setting up a standi ...
Sounds Around
... Our ears are constantly being bombarded with sound – so much that we automatically “tune out” a lot of it. Some sounds are “music to our ears” while others can annoy us and even damage the delicate structures in our ears. This activity helps students “tune in” to the sounds in their environment and ...
... Our ears are constantly being bombarded with sound – so much that we automatically “tune out” a lot of it. Some sounds are “music to our ears” while others can annoy us and even damage the delicate structures in our ears. This activity helps students “tune in” to the sounds in their environment and ...
What is an audiogram?
... rate of vibration, the higher the frequency of the sound. Sound frequency is usually measured in Hertz (Hz). A 250 Hertz (250Hz) tone sounds like a deep, low-pitched horn. A small, tinkling bell has a high-pitch sound, probably measuring around 3,000 to 4,000 Hz. Normal, healthy, young human ears ca ...
... rate of vibration, the higher the frequency of the sound. Sound frequency is usually measured in Hertz (Hz). A 250 Hertz (250Hz) tone sounds like a deep, low-pitched horn. A small, tinkling bell has a high-pitch sound, probably measuring around 3,000 to 4,000 Hz. Normal, healthy, young human ears ca ...
Lecture 20: The Auditory System: Aniruddha Das
... The auditory system is optimally designed to pick out the most salient features of sound. Sound is a longitudinal pressure wave, causing tiny vibrations of local air pressure. The ear has to be sensitive enough to pick these up: barely audible sounds have an amplitude of ~ 1 / 1010 of atmospheric ...
... The auditory system is optimally designed to pick out the most salient features of sound. Sound is a longitudinal pressure wave, causing tiny vibrations of local air pressure. The ear has to be sensitive enough to pick these up: barely audible sounds have an amplitude of ~ 1 / 1010 of atmospheric ...
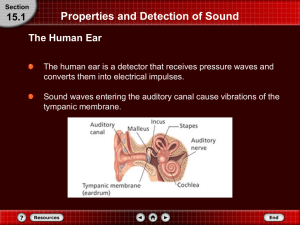
Properties and Detection of Sound
... Most people perceive a 10-dB increase in sound level as about twice as loud as the original level. In addition to pressure variations, power and intensity of sound waves can be described by decibel scales. ...
... Most people perceive a 10-dB increase in sound level as about twice as loud as the original level. In addition to pressure variations, power and intensity of sound waves can be described by decibel scales. ...
File
... • Includes 3 semicircular canals which are set at different angles filled with fluid • In the canals there are sensors (Hair Cells) that respond to the movement of the fluid • The function of the vestibular system include sensing the position of the head, keeping the head upright, and ...
... • Includes 3 semicircular canals which are set at different angles filled with fluid • In the canals there are sensors (Hair Cells) that respond to the movement of the fluid • The function of the vestibular system include sensing the position of the head, keeping the head upright, and ...
Sound and Hearing
... Sound Pressure is measured in units called Pascals 1 Pascal (Pa) = 1 Newton of force/m2 1 atmosphere = 100,000 Pa Human absolute hearing threshold = 0.00002 Pa = 20 microPa (i.e., 2 ten billionths of an atmosphere) Frequency measured in cycles/sec = Hertz (Hz) Nominal range of sensitivity: 20 – 20,0 ...
... Sound Pressure is measured in units called Pascals 1 Pascal (Pa) = 1 Newton of force/m2 1 atmosphere = 100,000 Pa Human absolute hearing threshold = 0.00002 Pa = 20 microPa (i.e., 2 ten billionths of an atmosphere) Frequency measured in cycles/sec = Hertz (Hz) Nominal range of sensitivity: 20 – 20,0 ...
hearing - My Haiku
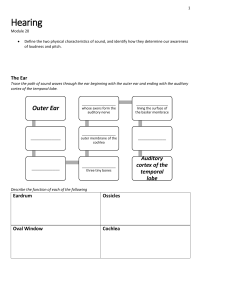
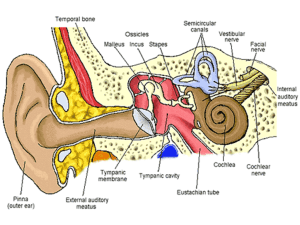
... Oval window --> Point on the surface of the cochlea which receives the sound vibration from the ossicles; as the oval window vibrates, the fluid in the cochlea vibrates, moving hair cells along the basilar membrane Cochlea --> A hearing organ where sound waves are changed into neural impulses Hair c ...
... Oval window --> Point on the surface of the cochlea which receives the sound vibration from the ossicles; as the oval window vibrates, the fluid in the cochlea vibrates, moving hair cells along the basilar membrane Cochlea --> A hearing organ where sound waves are changed into neural impulses Hair c ...
Sound

In physics, sound is a vibration that propagates as a typically audible mechanical wave of pressure and displacement, through a medium such as air or water. In physiology and psychology, sound is the reception of such waves and their perception by the brain.