Module 13 Hearing - Northside Middle School
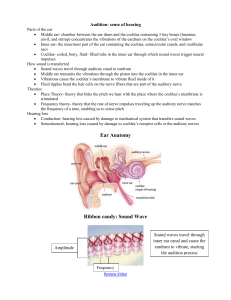
... Fluid ripples bend the hair cells on the nerve fibers that are part of the auditory nerve Theories Place Theory- theory that links the pitch we hear with the place where the cochlea’s membrane is stimulated Frequency theory- theory that the rate of nerve impulses traveling up the auditory nerv ...
... Fluid ripples bend the hair cells on the nerve fibers that are part of the auditory nerve Theories Place Theory- theory that links the pitch we hear with the place where the cochlea’s membrane is stimulated Frequency theory- theory that the rate of nerve impulses traveling up the auditory nerv ...
Do now! - MrSimonPorter
... Learning to listen Sound as vibrations Amplitude and volume Frequency and Pitch Range of human hearing ...
... Learning to listen Sound as vibrations Amplitude and volume Frequency and Pitch Range of human hearing ...
Aim Revision activity notes Revision activity answers
... Show that sound waves travel better in solids than in air by tapping a tuning fork or an unmounted music box and holding it in air, and then so its base touches a solid surface when it is much louder. ...
... Show that sound waves travel better in solids than in air by tapping a tuning fork or an unmounted music box and holding it in air, and then so its base touches a solid surface when it is much louder. ...
Hearing part II
... stapedius ms in response to sounds of high intensity and low frequency (above 80 dB and below 1000 Hz) ...
... stapedius ms in response to sounds of high intensity and low frequency (above 80 dB and below 1000 Hz) ...
The Physics of Sound Wave a disturbance that transfers energy from
... here an echo? • There are often soft materials that absorb the sound waves in a room ...
... here an echo? • There are often soft materials that absorb the sound waves in a room ...
What is sound - Shed The Music
... The ear is made of three parts; the outer ear, middle ear, and the inner ear. When sound comes through the outer ear (the part that you can see on your head) it is channel through the ear canal and comes in contact with the tympanum or eardrum. The tympanum vibrates with the areas of compression and ...
... The ear is made of three parts; the outer ear, middle ear, and the inner ear. When sound comes through the outer ear (the part that you can see on your head) it is channel through the ear canal and comes in contact with the tympanum or eardrum. The tympanum vibrates with the areas of compression and ...
Sound - Safety Executives of New York
... A - Scale (dBA) Attenuation of low frequencies Enhances high frequency perception Human ears attenuate sounds below 1 kHz We perceive high frequency sounds to be louder ...
... A - Scale (dBA) Attenuation of low frequencies Enhances high frequency perception Human ears attenuate sounds below 1 kHz We perceive high frequency sounds to be louder ...
Methodical instructions (indication)
... 2) a medium elastic between the hear and the source of sound; 3) waves are in the frequency range from about 20 to 20000 Hz (this range is called the audible range) 4) the intensity of sound waves is sufficient to obtain human sound perception. 1.Objective characteristics of sound 1) frequency (main ...
... 2) a medium elastic between the hear and the source of sound; 3) waves are in the frequency range from about 20 to 20000 Hz (this range is called the audible range) 4) the intensity of sound waves is sufficient to obtain human sound perception. 1.Objective characteristics of sound 1) frequency (main ...
The Auditory System
... 1.Frequency Theory: basilar membrane vibrates in synchrony with the sound source & causes action potentials to occur at about the same frequency. ( a 100 Hz tone, would have 100 action potentials per second in the auditory nerve) ...
... 1.Frequency Theory: basilar membrane vibrates in synchrony with the sound source & causes action potentials to occur at about the same frequency. ( a 100 Hz tone, would have 100 action potentials per second in the auditory nerve) ...
Slides - Alejandro L. Garcia
... through elastic liquids and solids, such as water and rocks, than through air. This is due to the close proximity of the atoms as they vibrate. ...
... through elastic liquids and solids, such as water and rocks, than through air. This is due to the close proximity of the atoms as they vibrate. ...
sound
... ★ Humans can hear sounds at frequencies from 20Hz to 20,0000 Hz. (we hear best at around 3,000 to 4,000 Hz, where human speech is centered) ...
... ★ Humans can hear sounds at frequencies from 20Hz to 20,0000 Hz. (we hear best at around 3,000 to 4,000 Hz, where human speech is centered) ...
Sounds Waves
... volunteer tell which is higher. Repeat this for 4 different trials. Beat interference: Set box to 440 Hz and listen to sound, change from sound to beats and slowly turn dial down to 430 and record what happens (only one speaker is changing its frequency) Resonance: Tap the tuning fork and listen to ...
... volunteer tell which is higher. Repeat this for 4 different trials. Beat interference: Set box to 440 Hz and listen to sound, change from sound to beats and slowly turn dial down to 430 and record what happens (only one speaker is changing its frequency) Resonance: Tap the tuning fork and listen to ...
Audition
... Place Theory suggests that sound frequencies stimulate the basilar membrane at specific places resulting in perceived pitch. ...
... Place Theory suggests that sound frequencies stimulate the basilar membrane at specific places resulting in perceived pitch. ...
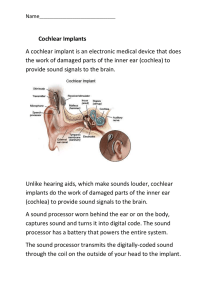
Cochlear Implants
... The implant converts the digitally-coded sound into electrical impulses and sends them along the electrode array placed in the cochlea (the inner ear). The implant's electrodes stimulate the cochlea's hearing nerve, which then sends the impulses to the brain where they are interpreted as sound. 1. T ...
... The implant converts the digitally-coded sound into electrical impulses and sends them along the electrode array placed in the cochlea (the inner ear). The implant's electrodes stimulate the cochlea's hearing nerve, which then sends the impulses to the brain where they are interpreted as sound. 1. T ...
Sound
... Imagine people in a crowded train station with hands in pockets pushing into crowd would send a wave of compression into the crowd in the direction of push (longitudinal) jerking people back and forth (sideways, over several meters) would not spread into the crowd but if everyone held hands (bon ...
... Imagine people in a crowded train station with hands in pockets pushing into crowd would send a wave of compression into the crowd in the direction of push (longitudinal) jerking people back and forth (sideways, over several meters) would not spread into the crowd but if everyone held hands (bon ...
Sound: Properties of sound
... From 20Hz (20 vibrations every second, about the pitch of a tiger’s roar) to 20kHz (20,000 vibrations every second, about the pitch of the ‘mosquito’ noise). If sound is due to vibrations, can we feel sound? Yes. It is easy to touch an instrument and feel it vibrating. When loud music plays in a roo ...
... From 20Hz (20 vibrations every second, about the pitch of a tiger’s roar) to 20kHz (20,000 vibrations every second, about the pitch of the ‘mosquito’ noise). If sound is due to vibrations, can we feel sound? Yes. It is easy to touch an instrument and feel it vibrating. When loud music plays in a roo ...
more information about Misophonia
... A rare and poorly understood condition Misophonia is sometimes called Selective Sound Sensitivity Syndrome, or 4S. It is characterized by a strong negative reaction to particular sounds, called triggers. These are usually, but not always, associated with mouth and body sounds being produced by parti ...
... A rare and poorly understood condition Misophonia is sometimes called Selective Sound Sensitivity Syndrome, or 4S. It is characterized by a strong negative reaction to particular sounds, called triggers. These are usually, but not always, associated with mouth and body sounds being produced by parti ...
chapter-14-2-with
... The sound level of a motorcycle is about 100 dB. The sound level of normal conversation is about 70 dB. How much more intense is the sound from a motorcycle than the sound from a person’s voice ...
... The sound level of a motorcycle is about 100 dB. The sound level of normal conversation is about 70 dB. How much more intense is the sound from a motorcycle than the sound from a person’s voice ...
Chapter 21 Sound
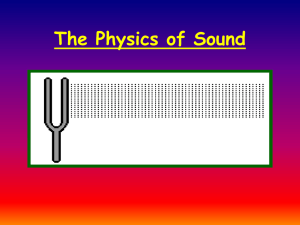
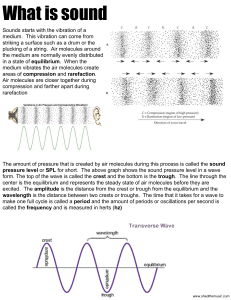
... outward into the air, it pushes the air molecules together • As a result, a region where the air molecules are closer together, or more dense, is created • This region of high density is called a compression • When the tuning fork moves back it causes an area of low density called rarefaction • The ...
... outward into the air, it pushes the air molecules together • As a result, a region where the air molecules are closer together, or more dense, is created • This region of high density is called a compression • When the tuning fork moves back it causes an area of low density called rarefaction • The ...
sensation
... • Lens: A transparent structure behind the pupil in the eye that changes shape to focus images on the retina. • Retina: The light –sensitive surface at the back of the eyeball. • Receptor cells: Specialized cells in every sensory system of the body that can turn other kinds of energy into action po ...
... • Lens: A transparent structure behind the pupil in the eye that changes shape to focus images on the retina. • Retina: The light –sensitive surface at the back of the eyeball. • Receptor cells: Specialized cells in every sensory system of the body that can turn other kinds of energy into action po ...
Sound

In physics, sound is a vibration that propagates as a typically audible mechanical wave of pressure and displacement, through a medium such as air or water. In physiology and psychology, sound is the reception of such waves and their perception by the brain.