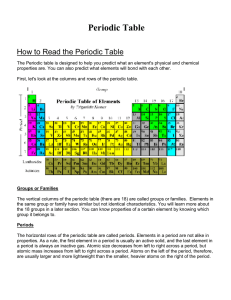
How to Read the Periodic Table
... How to Read the Periodic Table: 1. What are the vertical columns of the Periodic Table called? 2. What are the horizontal rows of the Periodic Table called? 3. How many groups/families are there on the Periodic Table? 4. How many periods are there on the Periodic Table? 5. Describe a trend in the Pe ...
... How to Read the Periodic Table: 1. What are the vertical columns of the Periodic Table called? 2. What are the horizontal rows of the Periodic Table called? 3. How many groups/families are there on the Periodic Table? 4. How many periods are there on the Periodic Table? 5. Describe a trend in the Pe ...
In modern periodic table, elements in the same column have similar
... • As you move down a group, reactivity of metals increases – Atoms are bigger and e-’s are held less tightly ...
... • As you move down a group, reactivity of metals increases – Atoms are bigger and e-’s are held less tightly ...
Summer Assignment for AP Chemistry: I hope you are all ready for a
... combustion), predict the products, and then write the balanced reaction. Remember to use the solubility rules for double replacement reactions and the activity series for single replacement reactions. Hint: when writing these reactions, ignore all of the information about heat, or bubbling, or mixin ...
... combustion), predict the products, and then write the balanced reaction. Remember to use the solubility rules for double replacement reactions and the activity series for single replacement reactions. Hint: when writing these reactions, ignore all of the information about heat, or bubbling, or mixin ...
Chemistry Summative Exam Part 2 Study Guide Answer Key
... What elements are the most reactive and where are they located on the periodic table? The most reactive elements are the alkali metals located in the first family of the periodic table of elements. The column all the way to the left of the periodic table. 18. What elements are the least reactive and ...
... What elements are the most reactive and where are they located on the periodic table? The most reactive elements are the alkali metals located in the first family of the periodic table of elements. The column all the way to the left of the periodic table. 18. What elements are the least reactive and ...
Atoms in the Periodic Table
... They are never found uncombined in nature. They have two valence electrons. Alkaline earth metals include magnesium and calcium, among others. ...
... They are never found uncombined in nature. They have two valence electrons. Alkaline earth metals include magnesium and calcium, among others. ...
Unit 8 Packet - Page 1 of 18 Honors Chemistry
... 8. Octane, C8H18, is a component of gasoline. Write the balanced equation for the complete combustion of octane. (extra credit) 9. The poisonous gas, hydrogen sulfide, can be neutralized with a base such as NaOH producing water and sodium sulfide. A student asked to write a balanced equation for the ...
... 8. Octane, C8H18, is a component of gasoline. Write the balanced equation for the complete combustion of octane. (extra credit) 9. The poisonous gas, hydrogen sulfide, can be neutralized with a base such as NaOH producing water and sodium sulfide. A student asked to write a balanced equation for the ...
Periodic Table How did Dmitri Mendeleev arrange the periodic table?
... • As you go from left to right, atomic number increases by 1 – number of protons increases by 1 – number of electrons also increases by 1 in the same valence shell ...
... • As you go from left to right, atomic number increases by 1 – number of protons increases by 1 – number of electrons also increases by 1 in the same valence shell ...
groups - Orangefield ISD
... ◦ Has metallic and nonmetallic properties, so is not considered part of any group ...
... ◦ Has metallic and nonmetallic properties, so is not considered part of any group ...
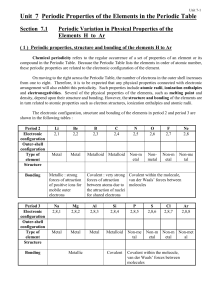
Unit 7 Periodic Properties of the Elements in the Periodic Table
... All the non-metals in periods 2 and 3 (except diamond) form molecular structure. Each of these elements consists of separate, small molecules, i.e. N2 , O2 , F2 , Ne , P4 , S8 , Cl2 , Ar . There are only very weak intermolecular forces (van der Waals forces) between the separate molecules. Consequen ...
... All the non-metals in periods 2 and 3 (except diamond) form molecular structure. Each of these elements consists of separate, small molecules, i.e. N2 , O2 , F2 , Ne , P4 , S8 , Cl2 , Ar . There are only very weak intermolecular forces (van der Waals forces) between the separate molecules. Consequen ...
Formula Equation - Chemistry Teaching Resources
... the correct valency number and then balancing the two halves of the compound. This is easier if you use Valency Pictures. For example, to work out the formula for potassium oxide. ...
... the correct valency number and then balancing the two halves of the compound. This is easier if you use Valency Pictures. For example, to work out the formula for potassium oxide. ...
The Periodic Table
... The modern periodic table is arranged in order of increasing atomic number. The atomic number is the total number of protons in the nucleus. The electron mostly determines the properties of an element. ...
... The modern periodic table is arranged in order of increasing atomic number. The atomic number is the total number of protons in the nucleus. The electron mostly determines the properties of an element. ...
Formula Notes `Completed` - Chemistry Teaching Resources
... the correct valency number and then balancing the two halves of the compound. This is easier if you use Valency Pictures. For example, to work out the formula for potassium oxide. ...
... the correct valency number and then balancing the two halves of the compound. This is easier if you use Valency Pictures. For example, to work out the formula for potassium oxide. ...
6.6 – Periodic Table
... Group or Family – Vertical column on the periodic table. These elements in groups or families usually share similar chemical properties. Period – Horizontal row on the periodic table. These elements have the same number of occupied energy levels. Valence Electrons – Electrons found in the outermost ...
... Group or Family – Vertical column on the periodic table. These elements in groups or families usually share similar chemical properties. Period – Horizontal row on the periodic table. These elements have the same number of occupied energy levels. Valence Electrons – Electrons found in the outermost ...
C2 revision slides V3 + questions + MS – F
... increases number of collisions and increases rate Temperature: Particles have more energy and move faster and collide more often. More particles have energy greater than the activation energy so more successful collisions Catalyst: Catalysts change the rate of chemical reactions but are not used up ...
... increases number of collisions and increases rate Temperature: Particles have more energy and move faster and collide more often. More particles have energy greater than the activation energy so more successful collisions Catalyst: Catalysts change the rate of chemical reactions but are not used up ...
Ionic bonding
... increases number of collisions and increases rate Temperature: Particles have more energy and move faster and collide more often. More particles have energy greater than the activation energy so more successful collisions Catalyst: Catalysts change the rate of chemical reactions but are not used up ...
... increases number of collisions and increases rate Temperature: Particles have more energy and move faster and collide more often. More particles have energy greater than the activation energy so more successful collisions Catalyst: Catalysts change the rate of chemical reactions but are not used up ...
C2 Revision Quick Questions FT
... increases number of collisions and increases rate Temperature: Particles have more energy and move faster and collide more often. More particles have energy greater than the activation energy so more successful collisions Catalyst: Catalysts change the rate of chemical reactions but are not used up ...
... increases number of collisions and increases rate Temperature: Particles have more energy and move faster and collide more often. More particles have energy greater than the activation energy so more successful collisions Catalyst: Catalysts change the rate of chemical reactions but are not used up ...
C2 Revision Quick Questions FT
... increases number of collisions and increases rate Temperature: Particles have more energy and move faster and collide more often. More particles have energy greater than the activation energy so more successful collisions Catalyst: Catalysts change the rate of chemical reactions but are not used up ...
... increases number of collisions and increases rate Temperature: Particles have more energy and move faster and collide more often. More particles have energy greater than the activation energy so more successful collisions Catalyst: Catalysts change the rate of chemical reactions but are not used up ...
Honors Chapter 11 Reactions
... iron sulfide and hydrochloric acid FeS (aq) + HCl (aq) FeCl2 (aq) + H2S (g) hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide HCl (aq) + NaOH (aq) NaCl (aq) + H2O (l) potassium iodide and lead (II) nitrate ...
... iron sulfide and hydrochloric acid FeS (aq) + HCl (aq) FeCl2 (aq) + H2S (g) hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide HCl (aq) + NaOH (aq) NaCl (aq) + H2O (l) potassium iodide and lead (II) nitrate ...
Atomic Structure and Periodic Table Worksheet
... Anything that takes up space is called ___________________ . There are three states of matter; ___________________, ___________________ and ___________________. For example, water exists in ___________________ form as rivers, lakes and streams. Water in a solid form is called ___________________. Wh ...
... Anything that takes up space is called ___________________ . There are three states of matter; ___________________, ___________________ and ___________________. For example, water exists in ___________________ form as rivers, lakes and streams. Water in a solid form is called ___________________. Wh ...
Notes - RCSD
... Electrons move very quickly around the nucleus in an electron cloud The charges on protons (+) and electrons (-) cause them to be attracted to each other. This attraction is what holds an atom together (similar to a magnet). Atoms are mostly empty space The protons and neutrons are heavy particles a ...
... Electrons move very quickly around the nucleus in an electron cloud The charges on protons (+) and electrons (-) cause them to be attracted to each other. This attraction is what holds an atom together (similar to a magnet). Atoms are mostly empty space The protons and neutrons are heavy particles a ...
1 - contentextra
... electrons in its outer energy level. Boron is in Period 2, as it has two occupied energy levels and in Group 3 as there are three electrons in its outer energy level. The chemical and physical properties of elements arranged in order of increasing atomic numbers vary periodically. Periodicity is the ...
... electrons in its outer energy level. Boron is in Period 2, as it has two occupied energy levels and in Group 3 as there are three electrons in its outer energy level. The chemical and physical properties of elements arranged in order of increasing atomic numbers vary periodically. Periodicity is the ...
reviewTWO
... 6) Potassium bromide added to lithium iodide makes lithium bromide and potassium iodide. 7) When silver(I) nitrate is added to calcium chloride, calcium nitrate and silver(I) chloride are produced. 8) Potassium sulphate plus magnesium chloride forms magnesium sulphate and potassium chloride. 9) When ...
... 6) Potassium bromide added to lithium iodide makes lithium bromide and potassium iodide. 7) When silver(I) nitrate is added to calcium chloride, calcium nitrate and silver(I) chloride are produced. 8) Potassium sulphate plus magnesium chloride forms magnesium sulphate and potassium chloride. 9) When ...
Structure of Atoms/Periodic Table Review 1. Shade in location of the
... 2. How is the modern periodic table organized? 3. Who created the first periodic table? 4. What can you predict about an element based on where it is on the periodic table? ...
... 2. How is the modern periodic table organized? 3. Who created the first periodic table? 4. What can you predict about an element based on where it is on the periodic table? ...
pp04
... examples: very reactive; one valence e not found as pure elements soft, shiny (on a fresh surface), good conductors of electricity ...
... examples: very reactive; one valence e not found as pure elements soft, shiny (on a fresh surface), good conductors of electricity ...
Lecture 3 – The Periodic Table
... (a) We refer to the building-up principle (the Aufbau principle) discussed in Section 7.9 and start writing the electron configuration with principal quantum number n = 1 and continuing upward until all the electrons are accounted for. (b) What are the electron configuration characteristics of repre ...
... (a) We refer to the building-up principle (the Aufbau principle) discussed in Section 7.9 and start writing the electron configuration with principal quantum number n = 1 and continuing upward until all the electrons are accounted for. (b) What are the electron configuration characteristics of repre ...