Periodic Table and Trends
... The top, right-area of the periodic table has the smallest atomic radius (helium) Which would you assume to have the largest atomic radius: Al, Al+, or AlWhich would you assume to have the smallest atomic radius: C2+, C+, C, C-, C2- ...
... The top, right-area of the periodic table has the smallest atomic radius (helium) Which would you assume to have the largest atomic radius: Al, Al+, or AlWhich would you assume to have the smallest atomic radius: C2+, C+, C, C-, C2- ...
Perioidicty Slide Show 2011
... Highly reactive (only have 1 outer electron to lose)-therefore not found in nature in elemental state; reacts with O2, to form oxide coating and H2O to form basic (alkali) solutions. Increase in reactivity down the group (Fr is most reactive metal). Softest of all metals (can be cut with a knife) an ...
... Highly reactive (only have 1 outer electron to lose)-therefore not found in nature in elemental state; reacts with O2, to form oxide coating and H2O to form basic (alkali) solutions. Increase in reactivity down the group (Fr is most reactive metal). Softest of all metals (can be cut with a knife) an ...
Periodic Table Funsheet
... 16. As you go from left to right across the periodic table, the elements go from (metals / nonmetals) to (metals / nonmetals). 17. The most active element in Group 17 is _______________________________________________________. 18. What sublevels are filling across the Transition Elements? __________ ...
... 16. As you go from left to right across the periodic table, the elements go from (metals / nonmetals) to (metals / nonmetals). 17. The most active element in Group 17 is _______________________________________________________. 18. What sublevels are filling across the Transition Elements? __________ ...
Chapter 6 Review
... Which subatomic particle plays the greatest part in determining the properties of an element? Of the following, which one has the smallest first ionization energy: a) aluminum, or b) silicon? ...
... Which subatomic particle plays the greatest part in determining the properties of an element? Of the following, which one has the smallest first ionization energy: a) aluminum, or b) silicon? ...
Ch. 11.4 Notes (Periodicity) teacher
... tend to __________ e-’s anyway, and this makes them highly ________________ attracted to e-’s when forming a chemical bond. Noble __________ gases – ___________ are not listed in Figure 12.4 since they do not ________ form _____________ compounds ! ...
... tend to __________ e-’s anyway, and this makes them highly ________________ attracted to e-’s when forming a chemical bond. Noble __________ gases – ___________ are not listed in Figure 12.4 since they do not ________ form _____________ compounds ! ...
Unit 3 - The Periodic Table
... Prefer to ________ their two electrons to become ___ ions ___________ reactive never found alone in nature Groups 3-12 TRANSITION METALS Found in the ___________ of the periodic table (the D block) Form ___________________ in solution (ex: Cu is bright blue when dissolved in water) This ...
... Prefer to ________ their two electrons to become ___ ions ___________ reactive never found alone in nature Groups 3-12 TRANSITION METALS Found in the ___________ of the periodic table (the D block) Form ___________________ in solution (ex: Cu is bright blue when dissolved in water) This ...
File - chemistryattweed
... Metals Part 3 As metals and other elements were discovered, scientists recognised that patterns in their physical and chemical properties could be used to organise the elements into a Periodic table. ...
... Metals Part 3 As metals and other elements were discovered, scientists recognised that patterns in their physical and chemical properties could be used to organise the elements into a Periodic table. ...
The Periodical Table and chemical properties
... A metalloid is a chemical element that has properties that are in between those of metals and nonmetals. The six elements commonly recognised as metalloids are boron, aluminium, germanium, arsenic, antimony and tellurium. On a standard periodic table all of these elements can be found in or near a d ...
... A metalloid is a chemical element that has properties that are in between those of metals and nonmetals. The six elements commonly recognised as metalloids are boron, aluminium, germanium, arsenic, antimony and tellurium. On a standard periodic table all of these elements can be found in or near a d ...
Periodic Table Metals, Non
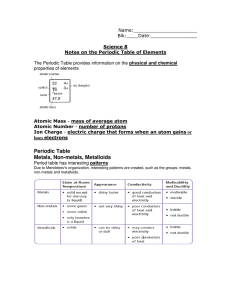
... Science 8 Notes on the Periodic Table of Elements The Periodic Table provides information on the physical and chemical properties of elements ...
... Science 8 Notes on the Periodic Table of Elements The Periodic Table provides information on the physical and chemical properties of elements ...
Chapter 6 Review “The Periodic Table”
... Which subatomic particle plays the greatest part in determining the properties of an element? Of the following, which one has the smallest first ionization energy: a) aluminum, or b) silicon? ...
... Which subatomic particle plays the greatest part in determining the properties of an element? Of the following, which one has the smallest first ionization energy: a) aluminum, or b) silicon? ...
CHM 1032C: Vocabulary Chapter 3
... Proton - A positively charged subatomic particle. s-Block element - A main group element that results from the filling of an s orbital. Shell (electron) - A grouping of electrons in an atom according to energy. Subatomic particle - Three kinds of fundamental particles from which atoms are made: prot ...
... Proton - A positively charged subatomic particle. s-Block element - A main group element that results from the filling of an s orbital. Shell (electron) - A grouping of electrons in an atom according to energy. Subatomic particle - Three kinds of fundamental particles from which atoms are made: prot ...
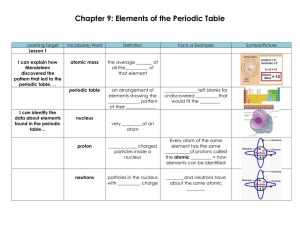
Chapter 9: Elements of the Periodic Table
... In general, most nonmetals are poor _______________________. Solid nonmetals tend to be ___________and ______________. I can describe the families of nonmetals… The families containing nonmetals include the ____________ family, the _____________ family, the _______________ family, the ______________ ...
... In general, most nonmetals are poor _______________________. Solid nonmetals tend to be ___________and ______________. I can describe the families of nonmetals… The families containing nonmetals include the ____________ family, the _____________ family, the _______________ family, the ______________ ...
The Periodic Law Notes (Chapter 5) – Part 2
... Groups 3-12 -are all metals with metallic properties (malleability, luster, good conductors, etc…); are referred to as the Transition Metals -Harder and denser than alkali or alkaline -Less reactive than alkali or alkaline -For the most part their outermost electrons are in a d sublevel -Exceptions ...
... Groups 3-12 -are all metals with metallic properties (malleability, luster, good conductors, etc…); are referred to as the Transition Metals -Harder and denser than alkali or alkaline -Less reactive than alkali or alkaline -For the most part their outermost electrons are in a d sublevel -Exceptions ...
File u1 sec2.2 slide show
... Groups of Elements (p.51) All elements in the periodic table can be classified as ...
... Groups of Elements (p.51) All elements in the periodic table can be classified as ...
PERIODICITY
... – Down a group you have 2 opposite effects: • Nuclear attraction: more protons more positive charge; nucleus pulls electrons in • Shielding effect: increased # of energy levels shields the electrons from the nucleus. ...
... – Down a group you have 2 opposite effects: • Nuclear attraction: more protons more positive charge; nucleus pulls electrons in • Shielding effect: increased # of energy levels shields the electrons from the nucleus. ...
periodic trends worksheet
... Period Group # Family name (if any) # of valence e# protons Metal, nonmetal, or metalloid? Conducts electricity? (yes/no) State at room temperature? Ion Formed? (positive, negative, none, varies) 22. _____________ metal 23. _____________ chlorine 24. _____________ metalloid 25. _____________ transit ...
... Period Group # Family name (if any) # of valence e# protons Metal, nonmetal, or metalloid? Conducts electricity? (yes/no) State at room temperature? Ion Formed? (positive, negative, none, varies) 22. _____________ metal 23. _____________ chlorine 24. _____________ metalloid 25. _____________ transit ...
Periodic Trends Worksheet
... Period Group # Family name (if any) # of valence e# protons Metal, nonmetal, or metalloid? Conducts electricity? (yes/no) State at room temperature? Ion Formed? (positive, negative, none, varies) 22. _____________ metal 23. _____________ chlorine 24. _____________ metalloid 25. _____________ transit ...
... Period Group # Family name (if any) # of valence e# protons Metal, nonmetal, or metalloid? Conducts electricity? (yes/no) State at room temperature? Ion Formed? (positive, negative, none, varies) 22. _____________ metal 23. _____________ chlorine 24. _____________ metalloid 25. _____________ transit ...
Document
... 8. A weighed sample of crystalline sodium carbonate Na2 CO3 and H2O, was heated in a crucible until there was no further change in mass. The mass of the sample reduced by 145%. Calculate the number of moles (n) of the water of crystallization ( Na = 23, O=16, C = 12 H = 1 ) ( 3 Marks ) ...
... 8. A weighed sample of crystalline sodium carbonate Na2 CO3 and H2O, was heated in a crucible until there was no further change in mass. The mass of the sample reduced by 145%. Calculate the number of moles (n) of the water of crystallization ( Na = 23, O=16, C = 12 H = 1 ) ( 3 Marks ) ...
UNIT 4 NOTES: THE PERIODIC TABLE
... 2. They are __________ at reactive as other metals. 3. They form _______________ solutions when dissolved in water. For example Cu+2 is ___________, while Fe3+ is ___________. In other words transition elements have _______________ ions. 4. They have _____________________ positive oxidation states. ...
... 2. They are __________ at reactive as other metals. 3. They form _______________ solutions when dissolved in water. For example Cu+2 is ___________, while Fe3+ is ___________. In other words transition elements have _______________ ions. 4. They have _____________________ positive oxidation states. ...
Atoms, elements and compounds
... Sort the different elements in to groups. Write down each group and the property you grouped the elements by. Write a reason for each of you choices. Look at a copy of the periodic table. Use the table and other sources of information to fill in the missing information on your element data ...
... Sort the different elements in to groups. Write down each group and the property you grouped the elements by. Write a reason for each of you choices. Look at a copy of the periodic table. Use the table and other sources of information to fill in the missing information on your element data ...
Chapter 7 - HCC Learning Web
... • Metals are shiny and lustrous, as well as malleable and ductile. • Metals are solids at room temperature and have very high melting temperatures (exceptions: mercury is liquid at room temperature; gallium and cesium melt just above room temperature). • Metals tend to have low ionization energies a ...
... • Metals are shiny and lustrous, as well as malleable and ductile. • Metals are solids at room temperature and have very high melting temperatures (exceptions: mercury is liquid at room temperature; gallium and cesium melt just above room temperature). • Metals tend to have low ionization energies a ...
File
... • Ionic radii - same as atomic radii, but distance for each atom's common ion • Ionization energy - energy for atom to lose an electron (lower means more likely to lose an electron) • Electron affinity - energy released when an atom gains an electron (higher means more likely to gain electron) • Ele ...
... • Ionic radii - same as atomic radii, but distance for each atom's common ion • Ionization energy - energy for atom to lose an electron (lower means more likely to lose an electron) • Electron affinity - energy released when an atom gains an electron (higher means more likely to gain electron) • Ele ...