A New Variable Star in Perseus
... The secondary minima are shown in Figure 6 and Figure 7. Using this two minima, the duration of the flat part of the secondary minimum is determined as 583 minutes. ...
... The secondary minima are shown in Figure 6 and Figure 7. Using this two minima, the duration of the flat part of the secondary minimum is determined as 583 minutes. ...
Death of the Stars
... To leave the surface of the Sun, you need a speed of 620km/s. When the Sun becomes a white dwarf, you will need 6400km/s. If the Sun became a neutron star, you would need 94,300 km/s. The speed of light is 300,000 km/s, so if we could squeeze even the Sun to about 3 kms radius, even light would not ...
... To leave the surface of the Sun, you need a speed of 620km/s. When the Sun becomes a white dwarf, you will need 6400km/s. If the Sun became a neutron star, you would need 94,300 km/s. The speed of light is 300,000 km/s, so if we could squeeze even the Sun to about 3 kms radius, even light would not ...
Neither Star nor Trigram - 5 Yellow Focus of Attention
... One such example is with the so-called Yang line and Yin Line. When asked ‘how many lines do we see here?’, most would probably say ‘2 lines’. That may be so, but we may also see depiction of any one phenomenon, then the phenomenon one time captured at its momentum of ‘switch on’, another time captu ...
... One such example is with the so-called Yang line and Yin Line. When asked ‘how many lines do we see here?’, most would probably say ‘2 lines’. That may be so, but we may also see depiction of any one phenomenon, then the phenomenon one time captured at its momentum of ‘switch on’, another time captu ...
Lecture 17, PPT version
... Hot, young stars in the spiral arms heat up the gas around them (above) forming H-II regions. Other examples of hot gas that we’ve seen are planetary nebulae and supernova remnants (which can be seen both in the disk and outside the disk). H-II regions are associated with active star formation; plan ...
... Hot, young stars in the spiral arms heat up the gas around them (above) forming H-II regions. Other examples of hot gas that we’ve seen are planetary nebulae and supernova remnants (which can be seen both in the disk and outside the disk). H-II regions are associated with active star formation; plan ...
Milky Way thin disk
... Age and metallicity • Bulge/bar stars are old: of order 10 Gyr • They are also metal-rich; more so than the disk near the Sun • However, so are inner disk stars ...
... Age and metallicity • Bulge/bar stars are old: of order 10 Gyr • They are also metal-rich; more so than the disk near the Sun • However, so are inner disk stars ...
STAR TYPES
... or enhancing one another. This binary star system is tilted (with respect ot us) so that its orbital plane is viewed from its edge. ...
... or enhancing one another. This binary star system is tilted (with respect ot us) so that its orbital plane is viewed from its edge. ...
Exploring the Mystery of Sirius – the Bright Isis and the Dark Nephthys
... Sothis is the ancient name of the star Sirius, attributed by the Greeks. In Egypt it was so significant that the whole calendar was based on its cycle, and the first appearance of the Dog Star on the eastern horizon (its heliacal rising) marked the beginning of a new year. This phenomenon was of an ...
... Sothis is the ancient name of the star Sirius, attributed by the Greeks. In Egypt it was so significant that the whole calendar was based on its cycle, and the first appearance of the Dog Star on the eastern horizon (its heliacal rising) marked the beginning of a new year. This phenomenon was of an ...
General Astronomy - Stockton University
... • RV Tauri stars – Period: 30-100 days; Amplitude of variation: up to 3.0 mag – These are yellow supergiants having a characteristic light variation with alternating deep and shallow minima. Their periods are defined as the interval between two deep minima. Some of these stars show long-term cyclic ...
... • RV Tauri stars – Period: 30-100 days; Amplitude of variation: up to 3.0 mag – These are yellow supergiants having a characteristic light variation with alternating deep and shallow minima. Their periods are defined as the interval between two deep minima. Some of these stars show long-term cyclic ...
chapter8
... intrinsic brightness or luminosity (L) and inversely proportional to the square of the distance (d): L ...
... intrinsic brightness or luminosity (L) and inversely proportional to the square of the distance (d): L ...
Document
... 5. When a star forms, why does it end up with only a fraction of the available matter? 6. What do star clusters tell us about the formation of stars? 7. Where in the Galaxy does star formation take place? 8. How can the death of one star trigger the birth of many other stars? ...
... 5. When a star forms, why does it end up with only a fraction of the available matter? 6. What do star clusters tell us about the formation of stars? 7. Where in the Galaxy does star formation take place? 8. How can the death of one star trigger the birth of many other stars? ...
Nebulae
... 5. When a star forms, why does it end up with only a fraction of the available matter? 6. What do star clusters tell us about the formation of stars? 7. Where in the Galaxy does star formation take place? 8. How can the death of one star trigger the birth of many other stars? ...
... 5. When a star forms, why does it end up with only a fraction of the available matter? 6. What do star clusters tell us about the formation of stars? 7. Where in the Galaxy does star formation take place? 8. How can the death of one star trigger the birth of many other stars? ...
reach for the stars
... ii. Which other DSO is likely to collide with this DSO in about 2.5 million years? ...
... ii. Which other DSO is likely to collide with this DSO in about 2.5 million years? ...
Stars - CBSD.org
... night sky for a long, long time. – We made it Instagram official with the Moon landing. ...
... night sky for a long, long time. – We made it Instagram official with the Moon landing. ...
Astrophysics - Part 2
... Classification by luminosity Relation between brightness and apparent magnitude. Apparent magnitude, m Relation between intensity and apparent magnitude. Measurement of m from photographic plates and distinction between photographic and visual magnitude not required. Absolute magnitude, M Parsec and ...
... Classification by luminosity Relation between brightness and apparent magnitude. Apparent magnitude, m Relation between intensity and apparent magnitude. Measurement of m from photographic plates and distinction between photographic and visual magnitude not required. Absolute magnitude, M Parsec and ...
Pattern recognition of star constellations for spacecraft
... star is below 75% of this limit, one can be sure that the star will not be detected. If the star is between 75% and 125%of the detection limit it might be detected (in this category double stars are included). If a star is above the 125% limit it will positively be detected. Hence there are two cate ...
... star is below 75% of this limit, one can be sure that the star will not be detected. If the star is between 75% and 125%of the detection limit it might be detected (in this category double stars are included). If a star is above the 125% limit it will positively be detected. Hence there are two cate ...
Astronomy 112: The Physics of Stars Class 11 Notes: Stellar
... week, we need to check that our models are stable. What this means is that we need to check not only that we have found solutions to the equations of stellar structure that are steady in time (since we dropped the time derivatives), we need to check that those solutions have the property that small ...
... week, we need to check that our models are stable. What this means is that we need to check not only that we have found solutions to the equations of stellar structure that are steady in time (since we dropped the time derivatives), we need to check that those solutions have the property that small ...
Part 2 of Our Lecture
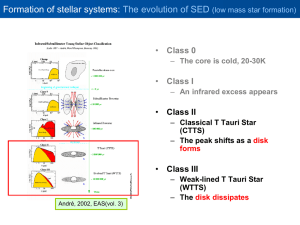
... Formation of stellar systems: CTTS (Class II) • Classical T Tauri Star T Tauri Star with strong Hα emission line - much brighter than other stars of similar T in IR – Dust in disk absorb light from central star and reradiate @ IR – ‘reprocessing’ or ‘irradiated’( or ‘passive’) disk – Disk accretion ...
... Formation of stellar systems: CTTS (Class II) • Classical T Tauri Star T Tauri Star with strong Hα emission line - much brighter than other stars of similar T in IR – Dust in disk absorb light from central star and reradiate @ IR – ‘reprocessing’ or ‘irradiated’( or ‘passive’) disk – Disk accretion ...
The Stars of Namaqualand
... Milky Way as a heavenly Nile. It was the ancient Greeks, who called it Milky Way, because they thought it was created by the Goddess Hera spraying the heavens with her milk. Indeed, the word ‘galaxy’ comes from ‘gala’, the ancient Greek word for milk. ...
... Milky Way as a heavenly Nile. It was the ancient Greeks, who called it Milky Way, because they thought it was created by the Goddess Hera spraying the heavens with her milk. Indeed, the word ‘galaxy’ comes from ‘gala’, the ancient Greek word for milk. ...
Magnetic Accretion onto Neutron Stars A crucial difference between
... such accretion to persist, the radiation cannot escape back up the accretion funnel. Instead, it has to come out the sides. This is a reminder that the Eddington flux is a limit only for spherically symmetric systems, and in this case we have a system that is very aspherical! It also means that the ...
... such accretion to persist, the radiation cannot escape back up the accretion funnel. Instead, it has to come out the sides. This is a reminder that the Eddington flux is a limit only for spherically symmetric systems, and in this case we have a system that is very aspherical! It also means that the ...
Investigating Supernova Remnants - Chandra X
... (Chandra, Hubble) internal pressure and its complete collapse is only prevented by quantum mechanics. Two electrons with the same “spin” are not allowed to occupy the same energy state. Since there are only two ways an electron can spin, only two electrons can occupy any single energy state; this is ...
... (Chandra, Hubble) internal pressure and its complete collapse is only prevented by quantum mechanics. Two electrons with the same “spin” are not allowed to occupy the same energy state. Since there are only two ways an electron can spin, only two electrons can occupy any single energy state; this is ...
Life Cycle of a Star Lesson Plan
... The more massive the star, the shorter its lifespan, primarily because massive stars have greater pressure on their cores, causing them to burn hydrogen more rapidly. The most massive stars last an average of about one million years, while stars of minimum mass (red dwarfs) burn their fuel very slow ...
... The more massive the star, the shorter its lifespan, primarily because massive stars have greater pressure on their cores, causing them to burn hydrogen more rapidly. The most massive stars last an average of about one million years, while stars of minimum mass (red dwarfs) burn their fuel very slow ...
Winter 2014
... mass of our Galaxy may be made up of white dwarfs left behind after lower-mass stars reach their ends. If we follow the arms of the “V” forming Taurus’ head, we will come to the two stars marking the ends of the bull’s horns. In between these two horns is an interesting object that is not visible wi ...
... mass of our Galaxy may be made up of white dwarfs left behind after lower-mass stars reach their ends. If we follow the arms of the “V” forming Taurus’ head, we will come to the two stars marking the ends of the bull’s horns. In between these two horns is an interesting object that is not visible wi ...
Stellar Evolution Chapter 12
... 16. How do star clusters confirm that stars are evolving? a. The H-R diagram of a star cluster is missing the upper part of the main sequence. b. The H-R diagram of a star cluster is missing the lower part of the main sequence. c. The relative motion of stars in a cluster can be estimated by ...
... 16. How do star clusters confirm that stars are evolving? a. The H-R diagram of a star cluster is missing the upper part of the main sequence. b. The H-R diagram of a star cluster is missing the lower part of the main sequence. c. The relative motion of stars in a cluster can be estimated by ...
Star of Bethlehem

In Christian tradition, the Star of Bethlehem, also called the Christmas Star, revealed the birth of Jesus to the Biblical Magi, and later led them to Bethlehem. The star appears only in the nativity story of the Gospel of Matthew, where astrologers from the east are inspired by the star to travel to Jerusalem. There they meet King Herod of Judea, and ask where the king of the Jews had been born. Herod, following a verse from the Book of Micah interpreted as a prophecy, directs them to Bethlehem, to the south of Jerusalem. The star leads them to Jesus' home in the town, where they worship him and give him gifts. The wise men are then given a divine warning not to return to Herod so they return home by a different route.Many Christians see the star as a miraculous sign to mark the birth of the Christ (or messiah). Some theologians claimed that the star fulfilled a prophecy, known as the Star Prophecy. Astronomers have made several attempts to link the star to unusual astronomical events, such as a conjunction of Jupiter and Saturn, a comet or a supernova.Many modern scholars do not consider the story to be describing a historical event but a pious fiction created by the author of the Gospel of Matthew.The subject is a favorite at planetarium shows during the Christmas season, although the Biblical account describes Jesus with a broader Greek word, which can mean either ""infant"" or ""child"" (paidon), rather than the more specific word for infant (brephos), possibly implying that some time has passed since the birth. The visit is traditionally celebrated on Epiphany (January 6) in Western Christianity.