Algebra 2-4 Notes
... Step 2—Count the number of numbers behind the decimal in both numbers. Step 3—Starting at the back of your answer, mover the decimal to the left the number of spaces as the total number of numbers behind the decimal Step 4—Decide whether the answer is positive or negative Find the product. Ex. 3.2(- ...
... Step 2—Count the number of numbers behind the decimal in both numbers. Step 3—Starting at the back of your answer, mover the decimal to the left the number of spaces as the total number of numbers behind the decimal Step 4—Decide whether the answer is positive or negative Find the product. Ex. 3.2(- ...
Section 1.3 - GEOCITIES.ws
... composite number (pg. 77) A composite number is a natural number greater than 1 that has a natural-number factor other than itself and 1. A composite number is composed of the product of 2 or more prime numbers. ...
... composite number (pg. 77) A composite number is a natural number greater than 1 that has a natural-number factor other than itself and 1. A composite number is composed of the product of 2 or more prime numbers. ...
Real Numbers Review WKSH
... Can be written as fractions. Terminating Decimals Repeating Decimals - ½, .222, 1, 2, 2/3, 5/4, 6.1 ...
... Can be written as fractions. Terminating Decimals Repeating Decimals - ½, .222, 1, 2, 2/3, 5/4, 6.1 ...
HEALTH AND SAFETY
... Multiplication In the first 6 matches of the season, a football team scores 4 goals each time. ...
... Multiplication In the first 6 matches of the season, a football team scores 4 goals each time. ...
Sheltonian subtraction
... schools. Ideally, an algorithm should be easy to carry out; fast; accurate; and easy to check. It should also be easy to remember and understand. Here is a new subtraction algorithm, called ‘Sheltonian subtraction’. The algorithm is based on two key ideas. (1) You don’t have to borrow if you aren’t ...
... schools. Ideally, an algorithm should be easy to carry out; fast; accurate; and easy to check. It should also be easy to remember and understand. Here is a new subtraction algorithm, called ‘Sheltonian subtraction’. The algorithm is based on two key ideas. (1) You don’t have to borrow if you aren’t ...
Inequalities and their Graphs
... a is the base and n is the exponent Exponents are NOT factors Means to multiply “a” n times ...
... a is the base and n is the exponent Exponents are NOT factors Means to multiply “a” n times ...
0,1,2,3… - mrmulholland
... Remember: “a number” means a variable. Use trial and error Key words for GCF word problems: largest, biggest, greatest, most, square Key words for LCM word problems: smallest, every, often, at the same time, again, fewest, least, together ...
... Remember: “a number” means a variable. Use trial and error Key words for GCF word problems: largest, biggest, greatest, most, square Key words for LCM word problems: smallest, every, often, at the same time, again, fewest, least, together ...
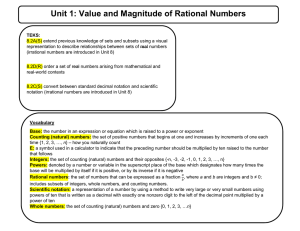
Unit 1: Value and Magnitude of Rational Numbers
... Base: the number in an expression or equation which is raised to a power or exponent Counting (natural) numbers: the set of positive numbers that begins at one and increases by increments of one each time {1, 2, 3, …, n} – how you naturally count E: a symbol used in a calculator to indicate that the ...
... Base: the number in an expression or equation which is raised to a power or exponent Counting (natural) numbers: the set of positive numbers that begins at one and increases by increments of one each time {1, 2, 3, …, n} – how you naturally count E: a symbol used in a calculator to indicate that the ...
Day 29 Presentation - Graphing Linear
... topics. We are going to discuss the methods of graphing functions, the inverses of functions and the arithmetic sequences. ...
... topics. We are going to discuss the methods of graphing functions, the inverses of functions and the arithmetic sequences. ...
Exam 1 Review - jan.ucc.nau.edu
... & 2.4 after the exam. All answers to the Chapter Review Questions will be in the back of your book. Look over all of your old homework problems. Expect a mix of questions from the following types: Short Answer/Explanation Fill in the blank Provide a Model Provide an Example Problem-Solving ...
... & 2.4 after the exam. All answers to the Chapter Review Questions will be in the back of your book. Look over all of your old homework problems. Expect a mix of questions from the following types: Short Answer/Explanation Fill in the blank Provide a Model Provide an Example Problem-Solving ...
Arithmetic

Arithmetic or arithmetics (from the Greek ἀριθμός arithmos, ""number"") is the oldest and most elementary branch of mathematics. It consists of the study of numbers, especially the properties of the traditional operations between them—addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Arithmetic is an elementary part of number theory, and number theory is considered to be one of the top-level divisions of modern mathematics, along with algebra, geometry, and analysis. The terms arithmetic and higher arithmetic were used until the beginning of the 20th century as synonyms for number theory and are sometimes still used to refer to a wider part of number theory.