MAT 001 Developmental Mathematics Skills
... 7. Acquire a clear understanding of the concepts of perimeter, area, and volume when applied to simple geometric figures; 8. Evaluate expressions with variables using signed numbers; 9. Develop the ability to analyze appropriate verbal problems. PROCEDURE: Students are responsible for all material t ...
... 7. Acquire a clear understanding of the concepts of perimeter, area, and volume when applied to simple geometric figures; 8. Evaluate expressions with variables using signed numbers; 9. Develop the ability to analyze appropriate verbal problems. PROCEDURE: Students are responsible for all material t ...
Math40Lesson5
... A prime number is a whole number, greater, greater then 1, that has only 1 and itself as factors. Whole numbers greater than 1 that are not prime are called composite numbers. Whole numbers Divisible by 2 are EVEN numbers. Whole numbers not divisible by 2 are ODD numbers. The prime factorization of ...
... A prime number is a whole number, greater, greater then 1, that has only 1 and itself as factors. Whole numbers greater than 1 that are not prime are called composite numbers. Whole numbers Divisible by 2 are EVEN numbers. Whole numbers not divisible by 2 are ODD numbers. The prime factorization of ...
Warm Up
... sign, the outcome is positive – Multiplying or dividing integers with different signs, the outcome is negative ...
... sign, the outcome is positive – Multiplying or dividing integers with different signs, the outcome is negative ...
Lesson 2, Section 1
... 2. If the two numbers have the ‘same’ sign, the answer is positive. 3. If the two numbers have ‘different’ signs, the answer is negative. 4. If there are more than two numbers, count the number of negatives. If odd, the answer is negative; if even, the answer is positive. a a a ...
... 2. If the two numbers have the ‘same’ sign, the answer is positive. 3. If the two numbers have ‘different’ signs, the answer is negative. 4. If there are more than two numbers, count the number of negatives. If odd, the answer is negative; if even, the answer is positive. a a a ...
Integers and Rationals
... Need new numbers to find answer to the last one. Often called fractions. We also use the term rational numbers. A rational number is a number in the form a/b with a and b integers and b0. a is called the numerator and be is called the denominator. ...
... Need new numbers to find answer to the last one. Often called fractions. We also use the term rational numbers. A rational number is a number in the form a/b with a and b integers and b0. a is called the numerator and be is called the denominator. ...
Trust Calculation Policy Final Version July 14
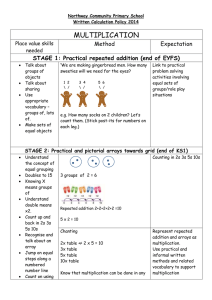
... Teachers should show how groups of three are repeatedly subtracted. They should then show that the result is no different if we count up in threes to if we count down (subtract) in threes. It should be explained that it is much easier to count up and they can use their times table knowledge to help ...
... Teachers should show how groups of three are repeatedly subtracted. They should then show that the result is no different if we count up in threes to if we count down (subtract) in threes. It should be explained that it is much easier to count up and they can use their times table knowledge to help ...
Rational Numbers
... keeps it’s identity Place Value – Holds a place when there isn’t a quantity for that value ...
... keeps it’s identity Place Value – Holds a place when there isn’t a quantity for that value ...
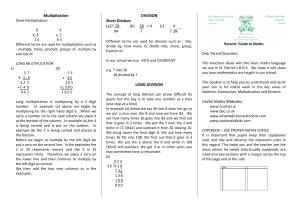
Multiplication DIVISION Short Division (a)7 28 (b) 28 = 4 (c) 4 04 7 7
... 2 in 26 represents twenty and the 3 in 35 represents thirty. Therefore we place a zero on the lower line and then continue to multiply by the left digit as normal. We then add the two new columns as in the examples. ...
... 2 in 26 represents twenty and the 3 in 35 represents thirty. Therefore we place a zero on the lower line and then continue to multiply by the left digit as normal. We then add the two new columns as in the examples. ...
Name_______________________________
... It is an order to how we calculate answers. First we simplify grouping symbols, then exponents, then multiplying and dividing. Finally adding and subtracting. Why do we have an order (of operations)? We have an order so that everyone--all across the world--arrives at the same answer for the same giv ...
... It is an order to how we calculate answers. First we simplify grouping symbols, then exponents, then multiplying and dividing. Finally adding and subtracting. Why do we have an order (of operations)? We have an order so that everyone--all across the world--arrives at the same answer for the same giv ...
Sequence and Series
... Arithmetic Series The first amphitheaters were built for contests between gladiators. Modern amphitheaters are usually used for the performing arts. Amphitheaters generally get wider as the distance from the stage increases. Suppose a small amphitheater can seat 18 people in the first row and each r ...
... Arithmetic Series The first amphitheaters were built for contests between gladiators. Modern amphitheaters are usually used for the performing arts. Amphitheaters generally get wider as the distance from the stage increases. Suppose a small amphitheater can seat 18 people in the first row and each r ...
Document
... – Perform these as they occur from left to right. Do not first do all multiplication and then come back for division. They are equal-level operations ...
... – Perform these as they occur from left to right. Do not first do all multiplication and then come back for division. They are equal-level operations ...
2-9-1 Integer Arithmetic Review
... 2-9-1 Integer Arithmetic Review Simplify the following. a) |4| ...
... 2-9-1 Integer Arithmetic Review Simplify the following. a) |4| ...
Arithmetic

Arithmetic or arithmetics (from the Greek ἀριθμός arithmos, ""number"") is the oldest and most elementary branch of mathematics. It consists of the study of numbers, especially the properties of the traditional operations between them—addition, subtraction, multiplication and division. Arithmetic is an elementary part of number theory, and number theory is considered to be one of the top-level divisions of modern mathematics, along with algebra, geometry, and analysis. The terms arithmetic and higher arithmetic were used until the beginning of the 20th century as synonyms for number theory and are sometimes still used to refer to a wider part of number theory.