Electrical properties
... – This extra electron (donor impurity) is located within the band gap just below the conduction band (see below) – Since the impurity atom donates an electron to the conduction band this type of impurity is referred to as a donor – Note that here no hole is created within the valence band (why?) At ...
... – This extra electron (donor impurity) is located within the band gap just below the conduction band (see below) – Since the impurity atom donates an electron to the conduction band this type of impurity is referred to as a donor – Note that here no hole is created within the valence band (why?) At ...
Theoretical prediction of the nondiffractive propagation of sonic
... The study of the dynamics of waves, even in simple linear media, initiated hundreds of year ago, ever and ever leads to surprisingly new results and insights. One of such “surprises” was the discovery of band gaps in the propagation of light in materials with the refraction index periodically modula ...
... The study of the dynamics of waves, even in simple linear media, initiated hundreds of year ago, ever and ever leads to surprisingly new results and insights. One of such “surprises” was the discovery of band gaps in the propagation of light in materials with the refraction index periodically modula ...
Adsorption energy and spin state of first
... calculated adsorption energies follow the trend of the metal cohesive energies, indicating that the changes in the metal-support and metal-metal interactions along the series are dominated by atomic properties. In all cases, except for Ni at the generalized gradient approximation level, the number o ...
... calculated adsorption energies follow the trend of the metal cohesive energies, indicating that the changes in the metal-support and metal-metal interactions along the series are dominated by atomic properties. In all cases, except for Ni at the generalized gradient approximation level, the number o ...
18 Semiconductors
... σ = 1.6 ×10-19 C × 1.3×1010 cm-3 × 1000 cm2/(V ×s) σ = 2.08 × 10-6 (Ohm × cm)-1 ρ = 4.8 × 105 Ohm × cm R = 4.8 × 105 Ohm × cm ×1 cm /(1cm ×1cm) = 4.8 × 105 Ohm ...
... σ = 1.6 ×10-19 C × 1.3×1010 cm-3 × 1000 cm2/(V ×s) σ = 2.08 × 10-6 (Ohm × cm)-1 ρ = 4.8 × 105 Ohm × cm R = 4.8 × 105 Ohm × cm ×1 cm /(1cm ×1cm) = 4.8 × 105 Ohm ...
Slide 1
... • Lattice: 3D array of regularly spaced points • Crystalline material: atoms situated in a repeating 3D periodic array over large atomic distances • Amorphous material: material with no such order • Hard sphere representation: atoms denoted by hard, touching spheres • Reduced sphere representation • ...
... • Lattice: 3D array of regularly spaced points • Crystalline material: atoms situated in a repeating 3D periodic array over large atomic distances • Amorphous material: material with no such order • Hard sphere representation: atoms denoted by hard, touching spheres • Reduced sphere representation • ...
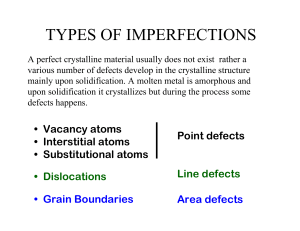
TYPES OF IMPERFECTIONS
... 2. Crystal structure. For appreciable solid solubility the crystal structures for metals of both atom types must be the same. 3. Electronegativity. The more electropositive one element and the more elec- tronegative the other, the greater is the likelihood that they will form an intrmetallic compoun ...
... 2. Crystal structure. For appreciable solid solubility the crystal structures for metals of both atom types must be the same. 3. Electronegativity. The more electropositive one element and the more elec- tronegative the other, the greater is the likelihood that they will form an intrmetallic compoun ...
Chapter 1-Crystal Properties_M A Islam_Lecture 1
... semiconductor in order to change its electrical properties. • The number of dopant atoms needed to create a difference in the ability of a semiconductor to conduct is very small. Where a comparatively small number of dopant atoms are added (of the order of 1 every 100,000,000 atoms) then the doping ...
... semiconductor in order to change its electrical properties. • The number of dopant atoms needed to create a difference in the ability of a semiconductor to conduct is very small. Where a comparatively small number of dopant atoms are added (of the order of 1 every 100,000,000 atoms) then the doping ...
Monte Carlo studies of a novel X-ray tube anode design
... In terms of judging how much of the energy is wasted, ZBE is more important, although higher values of fBE indicate that back-scattered electrons have higher energies and so are more likely to produce additional X-radiation if they can successfully be ‘‘trapped’’ inside the target. Fig. 1 shows resu ...
... In terms of judging how much of the energy is wasted, ZBE is more important, although higher values of fBE indicate that back-scattered electrons have higher energies and so are more likely to produce additional X-radiation if they can successfully be ‘‘trapped’’ inside the target. Fig. 1 shows resu ...
OPTICAL PROPERTIES of Nanomaterials
... Apart from ‘insufficient material’ effects, there are important phenomena which come into play in nanomaterials. These include: dominance of surface plasmons, quantum confinement effects, etc. E.g. in semiconductor quantum dots optical absorption and emission shift to the blue (higher energies ...
... Apart from ‘insufficient material’ effects, there are important phenomena which come into play in nanomaterials. These include: dominance of surface plasmons, quantum confinement effects, etc. E.g. in semiconductor quantum dots optical absorption and emission shift to the blue (higher energies ...
Microscopic Origin of Magnetoelectric Coupling in Noncollinear Multiferroics Jiangping Hu
... the chemical potential at E1 , both bands are fully filled. When the chemical potential at E2 , it is an unconventional band or Mott insulator which can generate ferroelectricity. ...
... the chemical potential at E1 , both bands are fully filled. When the chemical potential at E2 , it is an unconventional band or Mott insulator which can generate ferroelectricity. ...
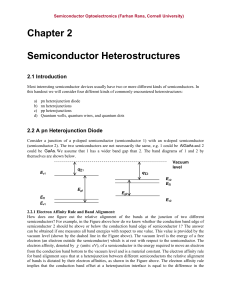
Chapter 2 Semiconductor Heterostructures
... 2.2.1 Electron Affinity Rule and Band Alignment: How does one figure out the relative alignment of the bands at the junction of two different semiconductors? For example, in the Figure above how do we know whether the conduction band edge of semiconductor 2 should be above or below the conduction ba ...
... 2.2.1 Electron Affinity Rule and Band Alignment: How does one figure out the relative alignment of the bands at the junction of two different semiconductors? For example, in the Figure above how do we know whether the conduction band edge of semiconductor 2 should be above or below the conduction ba ...
Chapter 3. The structure of crystalline solids
... Some common silicates are rocks, clays, sand, and a bulk of soils. Silicates are not considered to be ionic because interatomic covalent Si-O bonds are very strong. Silicate structures vary in different arrangements as each oxygen atom requires an extra electron to achieve a stable electronic struct ...
... Some common silicates are rocks, clays, sand, and a bulk of soils. Silicates are not considered to be ionic because interatomic covalent Si-O bonds are very strong. Silicate structures vary in different arrangements as each oxygen atom requires an extra electron to achieve a stable electronic struct ...
High Energy Observational Astrophysics
... http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qkjCe0r5-cw&feature=related ...
... http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qkjCe0r5-cw&feature=related ...
Manufacturing Processes - Philadelphia University Jordan
... (3) HCP: the top and bottom faces of the unit cell consist of six atoms that form regular hexagons and surround a single atom in the center. Another plane that provides three additional atoms to the unit cell is situated between the top and bottom planes. The equivalent of six atoms is contained in ...
... (3) HCP: the top and bottom faces of the unit cell consist of six atoms that form regular hexagons and surround a single atom in the center. Another plane that provides three additional atoms to the unit cell is situated between the top and bottom planes. The equivalent of six atoms is contained in ...
Presentation
... - An electron (or hole) is excited to a higher energy level by absorbing the released energy from an electron-hole recombination - Rate increases with injected free-carrier density & inversely proportional to the bandgap ...
... - An electron (or hole) is excited to a higher energy level by absorbing the released energy from an electron-hole recombination - Rate increases with injected free-carrier density & inversely proportional to the bandgap ...
an introduction to semiconductors
... The hole concentration on the p side of a p–n junction is much greater than that of the n–side, while the electron concentration of the n–side is much greater than that of the p–side. Therefore, the holes diffuse (move from a place where they are in excess to a place where they are lacking) from the ...
... The hole concentration on the p side of a p–n junction is much greater than that of the n–side, while the electron concentration of the n–side is much greater than that of the p–side. Therefore, the holes diffuse (move from a place where they are in excess to a place where they are lacking) from the ...
SOLID-STATE MATERIALS SYNTHESIS METHODS
... • Quantum confined electrons and holes when thickness of quantum well L is comparable to the wavelength of an electron or hole at the Fermi level of the material, band diagram shows confined particle states and quantization effects for electrical and optical properties • Discrete electronic energy s ...
... • Quantum confined electrons and holes when thickness of quantum well L is comparable to the wavelength of an electron or hole at the Fermi level of the material, band diagram shows confined particle states and quantization effects for electrical and optical properties • Discrete electronic energy s ...
2. Prediction of Crystal Structures
... positions per asymmetric unit [15]. The energy is minimized by a special steepestdescent procedure. After the minimization has located an energy minimum, new random values are generated for all free packing parameters. This procedure is repeated, until the best minima are found several times from di ...
... positions per asymmetric unit [15]. The energy is minimized by a special steepestdescent procedure. After the minimization has located an energy minimum, new random values are generated for all free packing parameters. This procedure is repeated, until the best minima are found several times from di ...
Atom
... Fig.1.17(a) is broken to form two single bonds and thus the adjacent mers are connected to each other. Thus a large molecule is formed. Figure 1.17 Addition polymerization of ethylene: (a) Monomers of C2H4 ethylene; (b) Ethylene polymer formed by connection of many ethylene ...
... Fig.1.17(a) is broken to form two single bonds and thus the adjacent mers are connected to each other. Thus a large molecule is formed. Figure 1.17 Addition polymerization of ethylene: (a) Monomers of C2H4 ethylene; (b) Ethylene polymer formed by connection of many ethylene ...
Ceramic Glass
... each other. As the melt cools, thermal vibrational energy decreases and the chains can’t move as easily so the structure becomes more rigid. Silica is the most important constituent of glass, but other oxides are added to change certain physical characteristics or to lower the melting point. Glass i ...
... each other. As the melt cools, thermal vibrational energy decreases and the chains can’t move as easily so the structure becomes more rigid. Silica is the most important constituent of glass, but other oxides are added to change certain physical characteristics or to lower the melting point. Glass i ...
PROJECT CLIL
... classic electric current drift current, the second one happens for the phenomenon of the spread electrical worker. ...
... classic electric current drift current, the second one happens for the phenomenon of the spread electrical worker. ...
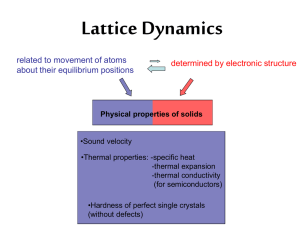
Introduction to Lattice Dynamics
... Lattice Dynamics related to movement of atoms about their equilibrium positions ...
... Lattice Dynamics related to movement of atoms about their equilibrium positions ...
P-type semiconductors
... At 0k Fermi level lies exactly at the middle of the donor level and the bottom of the Conduction band ...
... At 0k Fermi level lies exactly at the middle of the donor level and the bottom of the Conduction band ...
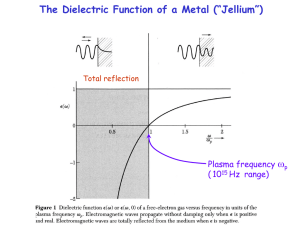
Plasmonics
... Plasmons can be observed by electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS). Electrons with an energy of several keV are reflected from a metal surface and lose energy by exciting 1, 2, 3, … plasmons. Large peaks at multiples of 15.3 eV are from bulk plasmons, and the smaller peaks at multiples of 10.3 eV ...
... Plasmons can be observed by electron energy loss spectroscopy (EELS). Electrons with an energy of several keV are reflected from a metal surface and lose energy by exciting 1, 2, 3, … plasmons. Large peaks at multiples of 15.3 eV are from bulk plasmons, and the smaller peaks at multiples of 10.3 eV ...