Lecture 30/31
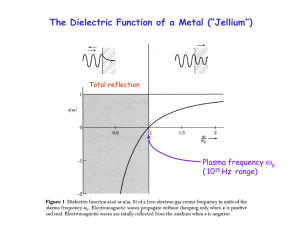
... The imaginary part 2 describes absorption (inelastic, E 0). A bulk plasmon occurs at p= L where 1 = 0 . A surface plasmon occurs at s where 1 = -1 . (More precisely: Im[1/] and Im[1/(+1)] have maxima.) General behavior of the dielectric constant () for a damped oscillator with resonance ...
... The imaginary part 2 describes absorption (inelastic, E 0). A bulk plasmon occurs at p= L where 1 = 0 . A surface plasmon occurs at s where 1 = -1 . (More precisely: Im[1/] and Im[1/(+1)] have maxima.) General behavior of the dielectric constant () for a damped oscillator with resonance ...
Calculating the impact force of a mass on an elastic
... The mass free-falls over a distance d and contacts the structure. It then falls by an additional amount, u, after contact with the structure. The deformation of the structure, through the distance u is determined by the elastic deformation of the structure it falls upon. I presume that, once the el ...
... The mass free-falls over a distance d and contacts the structure. It then falls by an additional amount, u, after contact with the structure. The deformation of the structure, through the distance u is determined by the elastic deformation of the structure it falls upon. I presume that, once the el ...
Materials on an Atomic Level
... and is sometimes also termed allotropy. The prevailing structure depends on both temperature as external pressure. Most materials only have one crystal structure, but are composed of a collection of many small crystals or grains. This means that there are multiple grains inside the specimen, each ha ...
... and is sometimes also termed allotropy. The prevailing structure depends on both temperature as external pressure. Most materials only have one crystal structure, but are composed of a collection of many small crystals or grains. This means that there are multiple grains inside the specimen, each ha ...
Metal
... Secondary, van der Waals, or physical bonds are weak in comparison to the primary or chemical ones; bonding energies are typically on the order of only 10 kJ/mol (0.1 eV/atom). Secondary bonding exists between virtually all atoms or molecules, but its presence may be obscured if any of the three pri ...
... Secondary, van der Waals, or physical bonds are weak in comparison to the primary or chemical ones; bonding energies are typically on the order of only 10 kJ/mol (0.1 eV/atom). Secondary bonding exists between virtually all atoms or molecules, but its presence may be obscured if any of the three pri ...
A lead-free high-TC ferroelectric BaTi2O5 : A first
... group C2/m. The R value of this analysis was about 20%. Tillmanns9 synthesized a single crystal of BaTi2 O5 by rapid solidification from a melt with a composition of BaCO3 :TiO2 540:60 in molar ratio, and the crystal structure was refined using the data collected with a four-cycle x-ray diffractomet ...
... group C2/m. The R value of this analysis was about 20%. Tillmanns9 synthesized a single crystal of BaTi2 O5 by rapid solidification from a melt with a composition of BaCO3 :TiO2 540:60 in molar ratio, and the crystal structure was refined using the data collected with a four-cycle x-ray diffractomet ...
Part V
... • The Atomic Radius of a neutral atom can be crudely thought of as the Mean Quantum Mechanical Radius of the orbital of the outer valence electron for that atom.
• Similarly, the Ionic Radius of an ion can be crudely
thought of as the Mean Quantum Mechanical Radius
of the orbital of the out ...
... • The Atomic Radius of a neutral atom can be crudely thought of as the Mean Quantum Mechanical Radius
+ H 2
... designs, controlled flow of precursors using digital mass flow meters directing precursors to heated single crystal substrate, induction or resistive heater, silicon carbide coated graphite susceptor for mounting substrate • This chemistry creates problems for semiconductor manufacturers wrt safe ha ...
... designs, controlled flow of precursors using digital mass flow meters directing precursors to heated single crystal substrate, induction or resistive heater, silicon carbide coated graphite susceptor for mounting substrate • This chemistry creates problems for semiconductor manufacturers wrt safe ha ...
Prediction of half-metallic properties in TlCrS2 and TlCrSe2 based
... larger than from the d-state of Cr. The contribution from d-state of Cr to spin-down DOS practically absent. Very small spin-down DOS at Fermi level for TlCrSe2 is due to the presence of p-state of Se. The presence of p-states of the Se atom at the Fermi level in the case of spindown channel gives ...
... larger than from the d-state of Cr. The contribution from d-state of Cr to spin-down DOS practically absent. Very small spin-down DOS at Fermi level for TlCrSe2 is due to the presence of p-state of Se. The presence of p-states of the Se atom at the Fermi level in the case of spindown channel gives ...
Chrystal Structures Lab Experiment 1 Professor
... while maintaining the structural makeup of a material. It is effectively a representation of the physical arrangement of atoms in a solid. The unit cell is also defined by its ability to be “stacked” to form larger and larger blocks of material. This model assumes that the atom is akin to a sphere, ...
... while maintaining the structural makeup of a material. It is effectively a representation of the physical arrangement of atoms in a solid. The unit cell is also defined by its ability to be “stacked” to form larger and larger blocks of material. This model assumes that the atom is akin to a sphere, ...
Semiconductor
... Finally, the work of Bohr, Boltzmann, Plank, Einstein and others has developed an understanding of the atomic structure which shows that electrons circle the nucleus in orbits having different associated energies. The electrons also spin on their own axes. The energy of electrons is quantised in tha ...
... Finally, the work of Bohr, Boltzmann, Plank, Einstein and others has developed an understanding of the atomic structure which shows that electrons circle the nucleus in orbits having different associated energies. The electrons also spin on their own axes. The energy of electrons is quantised in tha ...
solid-state materials synthesis methods
... designs, controlled flow of precursors using digital mass flow meters directing precursors to heated single crystal substrate, induction or resistive heater, silicon carbide coated graphite susceptor for mounting substrate • This chemistry creates problems for semiconductor manufacturers wrt safe ha ...
... designs, controlled flow of precursors using digital mass flow meters directing precursors to heated single crystal substrate, induction or resistive heater, silicon carbide coated graphite susceptor for mounting substrate • This chemistry creates problems for semiconductor manufacturers wrt safe ha ...
Unit 51: Electrical Technology - News
... resists the flow of electric charge. In practice, however, perfect insulators do not exist. Dielectric materials with high dielectric constants are considered insulators. In insulating materials valence electrons are tightly bonded to their atoms. ...
... resists the flow of electric charge. In practice, however, perfect insulators do not exist. Dielectric materials with high dielectric constants are considered insulators. In insulating materials valence electrons are tightly bonded to their atoms. ...
Metallic Crystal Structure
... electrons; furthermore, the nature of the bond depends on the electron structures of the constituent atoms. Secondary or physical forces and energies are also found in many solid materials; they are weaker than the primary ones, but nonetheless influence the physical properties of some materials. Me ...
... electrons; furthermore, the nature of the bond depends on the electron structures of the constituent atoms. Secondary or physical forces and energies are also found in many solid materials; they are weaker than the primary ones, but nonetheless influence the physical properties of some materials. Me ...
Steady-state electron transport within InAlN bulk ternary nitride
... band gap and unique electronic characteristics. The InAlN alloy is attracting much attention, due to its lattice matching capability to GaN substrates or buffer layers and its variable band gap energy which can be changed from 1.9 to 6.2 eV [1]; it can potentially be used for the fabrication of adva ...
... band gap and unique electronic characteristics. The InAlN alloy is attracting much attention, due to its lattice matching capability to GaN substrates or buffer layers and its variable band gap energy which can be changed from 1.9 to 6.2 eV [1]; it can potentially be used for the fabrication of adva ...
Correlated Electrons: A Dynamical Mean Field (DMFT) Perspective
... phenomena, that cannot be understood within the standard model of solids. Resistivities that rise without sign of saturation beyond the Mott limit, (e.g. H. Takagi’s work on Vanadates), temperature dependence of the integrated optical weight up to high frequency (e.g. Vandermarel’s work on Silicides ...
... phenomena, that cannot be understood within the standard model of solids. Resistivities that rise without sign of saturation beyond the Mott limit, (e.g. H. Takagi’s work on Vanadates), temperature dependence of the integrated optical weight up to high frequency (e.g. Vandermarel’s work on Silicides ...
ТВ Григорьева МА - Астраханский Государственный
... charge in one direction, or of negative charge in the other direction. By convention, current flow is always considered to be the flow of positive charge, even though that is contrary to the actual flow of (negative) electrons. Hence the current is considered to flow out of the positive terminal of ...
... charge in one direction, or of negative charge in the other direction. By convention, current flow is always considered to be the flow of positive charge, even though that is contrary to the actual flow of (negative) electrons. Hence the current is considered to flow out of the positive terminal of ...
Nanostructure calculation of CoAg core
... Consequently, the blocking temperature of CoAg is higher 共30 K兲 compared to CoNb 共12 K兲. ...
... Consequently, the blocking temperature of CoAg is higher 共30 K兲 compared to CoNb 共12 K兲. ...
Electron Microscopy
... A projector shines a beam of light through (transmits) the slide, as the light passes through it is affected by the structures and objects on the slide. These effects result in only certain parts of the light beam being transmitted through certain parts of the slide. This transmitted beam is then pr ...
... A projector shines a beam of light through (transmits) the slide, as the light passes through it is affected by the structures and objects on the slide. These effects result in only certain parts of the light beam being transmitted through certain parts of the slide. This transmitted beam is then pr ...
Doping and Crystal Growth Techniques
... specifications is the EPD, Etch Pit Density – Dislocations etch more rapidly in acid than crystalline material – Values for EPD can run from essentially zero (FZ grown under microgravity conditions) to 106 cm-2 for some materials that are extremely difficult to grow. Note that EPD of 106 cm-2 mean ...
... specifications is the EPD, Etch Pit Density – Dislocations etch more rapidly in acid than crystalline material – Values for EPD can run from essentially zero (FZ grown under microgravity conditions) to 106 cm-2 for some materials that are extremely difficult to grow. Note that EPD of 106 cm-2 mean ...
Semiconductor Physics
... The conductivity of a semiconductor material can be varied under an external electric field. Devices made from semiconductor materials are the foundation of modern electronics, including ratio, computers , telephones, and may other devices. Semiconductor devices include the transistor, many kinds of ...
... The conductivity of a semiconductor material can be varied under an external electric field. Devices made from semiconductor materials are the foundation of modern electronics, including ratio, computers , telephones, and may other devices. Semiconductor devices include the transistor, many kinds of ...
Formation of a Surface–Sandwich Structure in Pd
... their physical and chemical properties, which are determined by their size, shape, structure and composition. In particular, it is well-known that Pd is a metal with important existing and potential applications as a catalyst in heterogeneous catalysis. The use of Pd as a single active metal compone ...
... their physical and chemical properties, which are determined by their size, shape, structure and composition. In particular, it is well-known that Pd is a metal with important existing and potential applications as a catalyst in heterogeneous catalysis. The use of Pd as a single active metal compone ...
Crystal Defects – Enhancing Silicon Semiconductor Properties by
... Even with the application of thermal energy, only a few covalent bonds are broken, yielding a relatively small current flow. A much more efficient method of increasing current flow in semiconductors is by adding very small amounts of selected additives to them, generally no more than a few parts per ...
... Even with the application of thermal energy, only a few covalent bonds are broken, yielding a relatively small current flow. A much more efficient method of increasing current flow in semiconductors is by adding very small amounts of selected additives to them, generally no more than a few parts per ...
Computational Alchemy @Condensed Matter Theory group
... This effect does not come into play by going from macro to micro dimensions. However, it becomes dominant when the nanometer size range is reached. Small IS Different, and consequently enabling unique applications, for examples: • Opaque substances become transparent (copper); • Inert materials beco ...
... This effect does not come into play by going from macro to micro dimensions. However, it becomes dominant when the nanometer size range is reached. Small IS Different, and consequently enabling unique applications, for examples: • Opaque substances become transparent (copper); • Inert materials beco ...
Homework 1 - Devin Gatherwright IET 307 Portfolio
... interatomic bond that involves the non-directional sharing of valence electrons that are shared mutually between all atoms in the metallic solid;” and is exclusively found in metals and their alloys. Now, in metallic bonding, metallic materials contain 1, 2, or 3 valence electrons at the most. These ...
... interatomic bond that involves the non-directional sharing of valence electrons that are shared mutually between all atoms in the metallic solid;” and is exclusively found in metals and their alloys. Now, in metallic bonding, metallic materials contain 1, 2, or 3 valence electrons at the most. These ...