ATOMIC THEORY WORKSHEET 1.
... All atoms of a given element have the same number of protons in the nucleus. They may differ in the number of neutrons. Chemically the atoms of a given element are virtually indistinguishable: the types of chemical reactions are the same; the rates may slightly differ for different isotopes. ...
... All atoms of a given element have the same number of protons in the nucleus. They may differ in the number of neutrons. Chemically the atoms of a given element are virtually indistinguishable: the types of chemical reactions are the same; the rates may slightly differ for different isotopes. ...
ATOMIC THEORY WORKSHEET 1. Which of the following
... All atoms of a given element have the same number of protons in the nucleus. They may differ in the number of neutrons. Chemically the atoms of a given element are virtually indistinguishable: the types of chemical reactions are the same; the rates may slightly differ for different isotopes. ...
... All atoms of a given element have the same number of protons in the nucleus. They may differ in the number of neutrons. Chemically the atoms of a given element are virtually indistinguishable: the types of chemical reactions are the same; the rates may slightly differ for different isotopes. ...
CHE 1401 - Fall 2013 - Chapter 7 Homework 7 (Chapter 7: Periodic
... 11) Hydrogen is unique among the elements because __________. 1. It is not really a member of any particular group. 2. Its electron is not at all shielded from its nucleus. 3. It is the lightest element. 4. It is the only element to exist at room temperature as a diatomic gas. 5. It exhibits some c ...
... 11) Hydrogen is unique among the elements because __________. 1. It is not really a member of any particular group. 2. Its electron is not at all shielded from its nucleus. 3. It is the lightest element. 4. It is the only element to exist at room temperature as a diatomic gas. 5. It exhibits some c ...
Protons
... Laura works as a consultant at a software company. The amount of her annual bonus is based upon the number of hours she works. Over summer vacation, Debbie has to read a novel for English class. She has decided to spend the same amount of time reading every day. The number of hours she spends readin ...
... Laura works as a consultant at a software company. The amount of her annual bonus is based upon the number of hours she works. Over summer vacation, Debbie has to read a novel for English class. She has decided to spend the same amount of time reading every day. The number of hours she spends readin ...
Big History Chemistry Study Guide File
... mass and releasing energy in the process. 8. In nuclear _____________, radioactive elements such as ________________ break apart into smaller elements (“decay products”), also releasing energy. 9. The significance of Henry ___________________’s experiment with x-rays and atoms is that it found a num ...
... mass and releasing energy in the process. 8. In nuclear _____________, radioactive elements such as ________________ break apart into smaller elements (“decay products”), also releasing energy. 9. The significance of Henry ___________________’s experiment with x-rays and atoms is that it found a num ...
Ch. 6 Vocabulary
... • atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons ...
... • atoms of the same element that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons ...
Chapter 4.1 and 4.2 - science-b
... In a chemical reaction, one substance changes to another by reorganizing the way the atoms are attached to each other ...
... In a chemical reaction, one substance changes to another by reorganizing the way the atoms are attached to each other ...
Chapter 2: Elements are the building blocks of matter
... May conduct electricity Poor conductors of heat ...
... May conduct electricity Poor conductors of heat ...
The Particle Theory of Matter
... •Naming cations: Use the element name followed by __________________ Some Cations have more than one charged form. •Negatively charged ions: __________________ •Atoms that ___________ electrons to form compounds are called _____________. Anions have a __________________ charge. •Naming Anions: Drop ...
... •Naming cations: Use the element name followed by __________________ Some Cations have more than one charged form. •Negatively charged ions: __________________ •Atoms that ___________ electrons to form compounds are called _____________. Anions have a __________________ charge. •Naming Anions: Drop ...
notes - van Maarseveen
... Information in the periodic table – if you look at the square for each element, you will find two important numbers Number at the top = atomic number Number at the bottom = atomic mass Why are the atomic masses not always whole numbers? Some elements have different forms (known as isotopes) that hav ...
... Information in the periodic table – if you look at the square for each element, you will find two important numbers Number at the top = atomic number Number at the bottom = atomic mass Why are the atomic masses not always whole numbers? Some elements have different forms (known as isotopes) that hav ...
Physical Science EOCT Review Domain 1: Chemistry
... 3) Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds 4) In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged – but never changed into atoms of another element. ...
... 3) Atoms of different elements combine in simple whole-number ratios to form chemical compounds 4) In chemical reactions, atoms are combined, separated, or rearranged – but never changed into atoms of another element. ...
Ch2 lecture outline - OnCourse Systems For Education
... 8. Name the person who developed the periodic table? 9. What was the most important feature of his design? ...
... 8. Name the person who developed the periodic table? 9. What was the most important feature of his design? ...
Isotope Practice Worksheet
... Atoms of a given element which have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. Isotopes have the same position in the periodic table, the same chemical properties and the same atomic charge. ...
... Atoms of a given element which have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons are called isotopes. Isotopes have the same position in the periodic table, the same chemical properties and the same atomic charge. ...
John Dalton`s atomic theories were introduced in 18 hundreds
... however, he made a mistake in thinking atoms of element in a 1:1 ratio, and his system of atomic weights was not correct. He gave oxygen an atomic weight of seven instead of eight. The idea of atoms had been discovered much earlier. The Greeks had talked about atoms, but Dalton's theory was differen ...
... however, he made a mistake in thinking atoms of element in a 1:1 ratio, and his system of atomic weights was not correct. He gave oxygen an atomic weight of seven instead of eight. The idea of atoms had been discovered much earlier. The Greeks had talked about atoms, but Dalton's theory was differen ...
Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules and Ions
... 19th Century) – When two elements form a series of compounds, the ratio of the masses of the second element that combine with 1g of the first element can always be reduced to small whole numbers. The ratio of the masses of oxygen in H2O and H2O2 will be a small whole number (“2”). ...
... 19th Century) – When two elements form a series of compounds, the ratio of the masses of the second element that combine with 1g of the first element can always be reduced to small whole numbers. The ratio of the masses of oxygen in H2O and H2O2 will be a small whole number (“2”). ...
SNC1D- Grade 9- Unit: Chemistry March 03,2009 Periodic Table
... charge. Hydrogen is generally included in this group, because it has a single valence electron. However, it does not have any of the other metallic properties, and generally behaves as a nonmetal when forming compounds. Alkaline Earth metals Group 2 Elements. Shiny, silvery white metals. They are al ...
... charge. Hydrogen is generally included in this group, because it has a single valence electron. However, it does not have any of the other metallic properties, and generally behaves as a nonmetal when forming compounds. Alkaline Earth metals Group 2 Elements. Shiny, silvery white metals. They are al ...
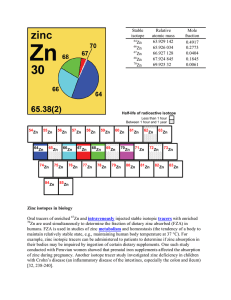
Zinc isotopes in biology Oral tracers of enriched Zn and
... by a radioactive isotope used as a tracer, which emits positrons and which is introduced into the body on a biologically-active molecule. Three-dimensional images of the concentration of the radioactive isotope within the body are then constructed by computer analysis. The imaging often is performed ...
... by a radioactive isotope used as a tracer, which emits positrons and which is introduced into the body on a biologically-active molecule. Three-dimensional images of the concentration of the radioactive isotope within the body are then constructed by computer analysis. The imaging often is performed ...
CHEM 1411 CHAPTER 2
... The prefix “mono” is never used for naming the first element. No prefix is used to indicate the number of H atoms. Naming of Acids An acid is a substance capable of giving H+ ions when dissolved in water (aqueous solution). They contain one or more ‘H’ atoms and an anionic group. Their name starts w ...
... The prefix “mono” is never used for naming the first element. No prefix is used to indicate the number of H atoms. Naming of Acids An acid is a substance capable of giving H+ ions when dissolved in water (aqueous solution). They contain one or more ‘H’ atoms and an anionic group. Their name starts w ...
Ch 1.1 ppt
... • Helium has two protons, so its atomic number is 2. • Atomic mass: the average number of protons and neutrons in an atom. This is the relative mass of the element compared to carbon as a standard. ...
... • Helium has two protons, so its atomic number is 2. • Atomic mass: the average number of protons and neutrons in an atom. This is the relative mass of the element compared to carbon as a standard. ...
Unit1: Matter Review
... • They make very useful compounds such as iodized table salt, chlorine in drinking water, sodium fluoride in toothpaste, etc. • The reactivity of halogens is explained by their structure. These non metals need only 1 electron to fill their outer orbital. They will readily gain this electron to becom ...
... • They make very useful compounds such as iodized table salt, chlorine in drinking water, sodium fluoride in toothpaste, etc. • The reactivity of halogens is explained by their structure. These non metals need only 1 electron to fill their outer orbital. They will readily gain this electron to becom ...
File - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
... Energy level - Energy levels inside an atom are the specific energies that electrons can have when occupying specific orbitals. Group/family – a group (also known as a family) is a column of elements in the periodic table of the chemical elements. There are 18 numbered groups Ion - An atom or molecu ...
... Energy level - Energy levels inside an atom are the specific energies that electrons can have when occupying specific orbitals. Group/family – a group (also known as a family) is a column of elements in the periodic table of the chemical elements. There are 18 numbered groups Ion - An atom or molecu ...
File - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
... Energy level - Energy levels inside an atom are the specific energies that electrons can have when occupying specific orbitals. Group/family – a group (also known as a family) is a column of elements in the periodic table of the chemical elements. There are 18 numbered groups Ion - An atom or molecu ...
... Energy level - Energy levels inside an atom are the specific energies that electrons can have when occupying specific orbitals. Group/family – a group (also known as a family) is a column of elements in the periodic table of the chemical elements. There are 18 numbered groups Ion - An atom or molecu ...
Chapter 3 pages 65
... Rutherford suggested that this bundle was the nucleus. He also suggested that the electrons orbited around the nucleus. This discovery was important because it revealed more about the atoms structure. ...
... Rutherford suggested that this bundle was the nucleus. He also suggested that the electrons orbited around the nucleus. This discovery was important because it revealed more about the atoms structure. ...