Section 4: Islam`s Golden Age
... Non-Muslims were allowed to govern their own communities ○ They paid higher taxes than Muslim subjects ...
... Non-Muslims were allowed to govern their own communities ○ They paid higher taxes than Muslim subjects ...
Ancient World History Guild
... Part I: Identify the following as aspects of the Sunni or Shi’a sect of Islam. 1. Believe that the Caliph may be any righteous Muslim.__________________________________ 2. Were initially followers of Caliph Ali & Muhammad’s daughter Fatima. ____________________ 3. Make up the minority of followers i ...
... Part I: Identify the following as aspects of the Sunni or Shi’a sect of Islam. 1. Believe that the Caliph may be any righteous Muslim.__________________________________ 2. Were initially followers of Caliph Ali & Muhammad’s daughter Fatima. ____________________ 3. Make up the minority of followers i ...
Ancient World History Guild
... Part I: Identify the following as aspects of the Sunni or Shi’a sect of Islam. 1. Believe that the Caliph may be any righteous Muslim.__________________________________ 2. Were initially followers of Caliph Ali & Muhammad’s daughter Fatima. ____________________ 3. Make up the minority of followers i ...
... Part I: Identify the following as aspects of the Sunni or Shi’a sect of Islam. 1. Believe that the Caliph may be any righteous Muslim.__________________________________ 2. Were initially followers of Caliph Ali & Muhammad’s daughter Fatima. ____________________ 3. Make up the minority of followers i ...
Arab Empire and Caliphates PowerPoint
... 1. What was the concern following Muhammad’s death? Muhammad had no son or successor, so who should lead after Muhammad? ...
... 1. What was the concern following Muhammad’s death? Muhammad had no son or successor, so who should lead after Muhammad? ...
World History 9 Chapter 10, Section 2 – “Islam Expands
... Rule of a caliph 2. What is a jihad? Why did Abu-Bakr use it? Striving/struggle against evil/armed struggle against unbelievers To encourage and justify expansion 3. How large was the Muslim empire by 750? 6,000 miles from the Atlantic to the Indus River 4. What were three reasons for the succ ...
... Rule of a caliph 2. What is a jihad? Why did Abu-Bakr use it? Striving/struggle against evil/armed struggle against unbelievers To encourage and justify expansion 3. How large was the Muslim empire by 750? 6,000 miles from the Atlantic to the Indus River 4. What were three reasons for the succ ...
The Muslim World 600-1250
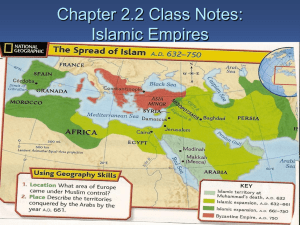
... • By 750, the Muslim empire stretched from the Atlantic Ocean to the Indus River • http://mapsofwar.com/ind/history-of-religion.html ...
... • By 750, the Muslim empire stretched from the Atlantic Ocean to the Indus River • http://mapsofwar.com/ind/history-of-religion.html ...
Islam
... Ka’ba: small cubical shrine in Mecca Umma: community of believers in Medina; developed into core of Islamic state Quran: sacred book; “Word of God” Ulama: Muslim religious scholars Shari’a: Islamic law; held that all Muslims share same morals Sunna: source of law that was the traditions of the Proph ...
... Ka’ba: small cubical shrine in Mecca Umma: community of believers in Medina; developed into core of Islamic state Quran: sacred book; “Word of God” Ulama: Muslim religious scholars Shari’a: Islamic law; held that all Muslims share same morals Sunna: source of law that was the traditions of the Proph ...
Lecture Notes_Islam_Key Concepts
... Unclear of powers Muslim armies fought to confirm the authority of the Caliphate o Led by succession of Caliphs until 1258 o NEED TO KNOW Abbasids See below Muslim Iberia (Al-Andalus) Islamic Spain Last remaining Umayyad from the Abbasid rebellions fled to Spain and developed a princip ...
... Unclear of powers Muslim armies fought to confirm the authority of the Caliphate o Led by succession of Caliphs until 1258 o NEED TO KNOW Abbasids See below Muslim Iberia (Al-Andalus) Islamic Spain Last remaining Umayyad from the Abbasid rebellions fled to Spain and developed a princip ...
Political Islam
... Ali, son in law of Muhammad, saw expansion of Muslim Empire into Persian, Byzantine Empires Each caliph was assassinated by rivals ...
... Ali, son in law of Muhammad, saw expansion of Muslim Empire into Persian, Byzantine Empires Each caliph was assassinated by rivals ...
ABC Book of Islam
... P - Prophet In religion, a prophet is a person who has encountered some divine being, typically an Angel. ...
... P - Prophet In religion, a prophet is a person who has encountered some divine being, typically an Angel. ...
Chapter 11 – 2 Islamic Empires
... • Shiites believed Ali (son in law) should rule and all future caliphs should be descendants • Sunnis believe that the Umayyad caliphs were rightful leaders (two groups = separate customs) ...
... • Shiites believed Ali (son in law) should rule and all future caliphs should be descendants • Sunnis believe that the Umayyad caliphs were rightful leaders (two groups = separate customs) ...
Study Guide #28 The Expansion of Islam
... chose Abu Bakr, Muhammad‟s old friend. Abu Bakr was not a prophet, like Muhammad. He and all those who came after him were known as caliphs, or “successors.” After Abu Bakr became caliph, he used force to bring the desert tribes back into the Muslim fold. Islamic Expansion. Abu Bakr died shortly aft ...
... chose Abu Bakr, Muhammad‟s old friend. Abu Bakr was not a prophet, like Muhammad. He and all those who came after him were known as caliphs, or “successors.” After Abu Bakr became caliph, he used force to bring the desert tribes back into the Muslim fold. Islamic Expansion. Abu Bakr died shortly aft ...
Chapter 6-2: The Arab Empire and Its Successors
... converted to Islam and prospered as soldiers for the Abbasids took over the eastern provinces of the Abbasid dynasty captured Baghdad and most of the Anatolian Peninsula ...
... converted to Islam and prospered as soldiers for the Abbasids took over the eastern provinces of the Abbasid dynasty captured Baghdad and most of the Anatolian Peninsula ...
Byzantine and Sassanid Empire around 600 CE
... • Non-Muslims pay a special head tax, but not forced to convert • Judaism and Christianity tolerated ...
... • Non-Muslims pay a special head tax, but not forced to convert • Judaism and Christianity tolerated ...
The Rise of Spread of Islam
... Caliphate = dynasty of Islamic caliphs Rashidun or Rightly Guided Caliphs (632-661) Abu Bakr; Umar; Uthman; Ali Umayyads (661-750, centered in Damascus) Abbasids (750-1258, centered in Baghdad) Córdobas (756-1031, Iberia) Fatimids (909-1171, North Africa, Shi’a) Almohads (1145-1269, North Africa, Ib ...
... Caliphate = dynasty of Islamic caliphs Rashidun or Rightly Guided Caliphs (632-661) Abu Bakr; Umar; Uthman; Ali Umayyads (661-750, centered in Damascus) Abbasids (750-1258, centered in Baghdad) Córdobas (756-1031, Iberia) Fatimids (909-1171, North Africa, Shi’a) Almohads (1145-1269, North Africa, Ib ...
Expansion of Islam Presentation
... (worldly, secular) leader as well as the spiritual leader – Practically, this dual system died out with the destruction of the Abbasid Caliphate by the Mongols, and temporal and spiritual leadership became decentralized. ...
... (worldly, secular) leader as well as the spiritual leader – Practically, this dual system died out with the destruction of the Abbasid Caliphate by the Mongols, and temporal and spiritual leadership became decentralized. ...
Chapter 11.2 Spread of Islam
... • Crossed into Europe at the Strait of Gibraltar in 711 A.D. • Pushed into France where they were stopped at the Battle of Tours in 732 A.D. • Siege on the capital city of the Byzantine Empire – Constantinople ...
... • Crossed into Europe at the Strait of Gibraltar in 711 A.D. • Pushed into France where they were stopped at the Battle of Tours in 732 A.D. • Siege on the capital city of the Byzantine Empire – Constantinople ...
CHAPTER 9 The Arab Empires
... 6. growing prosperity because of trade 7. Most famous Caliph: Harun al Rashid - known for charity and encouraging artists and writers. "The Golden Age of Abbasid Caliphate" A Council advised the Caliph. It was headed by a Prime Minister known as a Vizier. ...
... 6. growing prosperity because of trade 7. Most famous Caliph: Harun al Rashid - known for charity and encouraging artists and writers. "The Golden Age of Abbasid Caliphate" A Council advised the Caliph. It was headed by a Prime Minister known as a Vizier. ...
Spread of Islam
... Expansion of Islam and Jihad Conquered territory Middle Eastern / North African conquest European conquest Spain in 711 CE Battle of Tours in 732 CE Asian conquest Battle of Talas in 751 CE and into ...
... Expansion of Islam and Jihad Conquered territory Middle Eastern / North African conquest European conquest Spain in 711 CE Battle of Tours in 732 CE Asian conquest Battle of Talas in 751 CE and into ...
The Rise of Islam
... Growth through military activity of autonomous Islamic forces Caliph Harun al-Rashid (786-809 CE) High point of Abbasid dynasty Baghdad center of commerce Great cultural activity Corruption led to Abbasid downfall ...
... Growth through military activity of autonomous Islamic forces Caliph Harun al-Rashid (786-809 CE) High point of Abbasid dynasty Baghdad center of commerce Great cultural activity Corruption led to Abbasid downfall ...
File
... successors organized the Arabs and set in motion a great expansion. i. constant tension over choosing who should rule the empire ii. the lack of a named successor or a male heir created problems of succession. iii. Muhammad had daughters, but in a male-oriented society they would not be ...
... successors organized the Arabs and set in motion a great expansion. i. constant tension over choosing who should rule the empire ii. the lack of a named successor or a male heir created problems of succession. iii. Muhammad had daughters, but in a male-oriented society they would not be ...
Unit 4 - River Mill Academy
... fasting, rituals; pious, miraculous power? Help spread Islam by traveling, preaching, examples Sunni ...
... fasting, rituals; pious, miraculous power? Help spread Islam by traveling, preaching, examples Sunni ...
The Spread of Islam - olsonworldhistory5
... Death of Muhammad Muhammad died in 632 He had not named a successor or instructed how to choose one Using trial custom – Muslims elected Abu Bakr, the first caliph Abu Bakr and next 3 elected caliphs: “rightly-guided” - Umar, Uthman, and Ali ...
... Death of Muhammad Muhammad died in 632 He had not named a successor or instructed how to choose one Using trial custom – Muslims elected Abu Bakr, the first caliph Abu Bakr and next 3 elected caliphs: “rightly-guided” - Umar, Uthman, and Ali ...