7.2 ISLAM EXPANDS
... was invented during this time. (from “sakks”) Huge Muslim cities and trade gave birth to achievements in the arts and sciences (Sec. ...
... was invented during this time. (from “sakks”) Huge Muslim cities and trade gave birth to achievements in the arts and sciences (Sec. ...
Islamic expansion and culture
... • The leaders after Muhammad’s death are known as caliphs • The caliph Abu-Bakr used jihad to justify Islamic expansion • Armed struggle against non-believers • One of the “rightly guided” caliphs ...
... • The leaders after Muhammad’s death are known as caliphs • The caliph Abu-Bakr used jihad to justify Islamic expansion • Armed struggle against non-believers • One of the “rightly guided” caliphs ...
The Arab Empire and its Successors
... – his father-in-law over Ali his cousin and son-in-law – caliph (would cause conflict later) ...
... – his father-in-law over Ali his cousin and son-in-law – caliph (would cause conflict later) ...
The Arab Empire and its Successors
... – his father-in-law over Ali his cousin and son-in-law – caliph (would cause conflict later) ...
... – his father-in-law over Ali his cousin and son-in-law – caliph (would cause conflict later) ...
Chapter 5, Lesson 2 The Spread of Islam
... • When Muhammad died in 632, Muslims knew a strong leader would be required to keep the Islamic state united • Chose new leader called a caliph, or “successor” ...
... • When Muhammad died in 632, Muslims knew a strong leader would be required to keep the Islamic state united • Chose new leader called a caliph, or “successor” ...
Muslim Civilizations 10.2-10.3
... River Valley in the east. • Many different peoples were under their rule and non-Muslims were charged a tax. All religions could worship freely. ...
... River Valley in the east. • Many different peoples were under their rule and non-Muslims were charged a tax. All religions could worship freely. ...
10.2 The Spread of Islam
... Treatment of Conquered Peoples Many people attracted by Islam’s message and accept Islam. Qur’an forbids forced conversion so, many retain their own religions, but had to pay a poll tax so they don’t have to serve in the army. Christians and Jews can practice, but not spread their religions. ...
... Treatment of Conquered Peoples Many people attracted by Islam’s message and accept Islam. Qur’an forbids forced conversion so, many retain their own religions, but had to pay a poll tax so they don’t have to serve in the army. Christians and Jews can practice, but not spread their religions. ...
Islam Test Study Guide
... 19.) According to the Shiites, who could be caliph? 20.) The Sunni Muslims followed the teaching of Muhammad. According to the Sunni Muslims, who could be caliph? 21.) What was the name of the battle in France that halted (stopped) the Muslim advance into Europe? 22.) What major accomplishments were ...
... 19.) According to the Shiites, who could be caliph? 20.) The Sunni Muslims followed the teaching of Muhammad. According to the Sunni Muslims, who could be caliph? 21.) What was the name of the battle in France that halted (stopped) the Muslim advance into Europe? 22.) What major accomplishments were ...
Chapter 9 Section2 The Spread of Islam
... Abu Bakr: (c. 573–634) First Muslim caliph; as a close companion and successor to Muhammad, he unified the restive Bedouin tribes of central Arabia into a strong fighting force that he led into Iraq and Syria. Caliph:"successor to the Prophet"; title given to the political and religious leader o ...
... Abu Bakr: (c. 573–634) First Muslim caliph; as a close companion and successor to Muhammad, he unified the restive Bedouin tribes of central Arabia into a strong fighting force that he led into Iraq and Syria. Caliph:"successor to the Prophet"; title given to the political and religious leader o ...
The Arab Empire
... Empire’s capital moved from Medina to Roman/Byzantine city of Damascus in Syria Ruling class = Arab military aristocracy ...
... Empire’s capital moved from Medina to Roman/Byzantine city of Damascus in Syria Ruling class = Arab military aristocracy ...
Chapter 6
... God,” or jihad. • In 661 general Mu’awiyah became caliph. • He was a rival of Ali (Muhammad’s son in law) and was known for one major virtue: – He used force only if necessary. ...
... God,” or jihad. • In 661 general Mu’awiyah became caliph. • He was a rival of Ali (Muhammad’s son in law) and was known for one major virtue: – He used force only if necessary. ...
Islam Expands - Wando High School
... Willing to fight to extend and defend Islam. Well disciplined armies with good commanders. Surrounding empires were weak. People who had suffered from religious persecution welcomed the more tolerant invaders. • Attracted to Islam’s offer of equality and hope • Attracted by the economic benefit ...
... Willing to fight to extend and defend Islam. Well disciplined armies with good commanders. Surrounding empires were weak. People who had suffered from religious persecution welcomed the more tolerant invaders. • Attracted to Islam’s offer of equality and hope • Attracted by the economic benefit ...
The Spread of Islam
... won control of Baghdad They then became the dominant force in the Islamic world Eventually the Turkish Muslims seized Syria, Mesopotamia and much of Asia minor They attacked the Byzantines and won some battles against them The Turkish Muslims raided northern India and because they were good at fight ...
... won control of Baghdad They then became the dominant force in the Islamic world Eventually the Turkish Muslims seized Syria, Mesopotamia and much of Asia minor They attacked the Byzantines and won some battles against them The Turkish Muslims raided northern India and because they were good at fight ...
Name - Long Branch Public Schools
... Byzantines (1071 CE) taking all of Anatolia. -Seljuks feud over claims to who is sultan (caliph), thus for years ignoring irrigation, city maintenance, etc. -Major pop. decline, cities shrink, drying up of Mesopotamia region The Crusades - 1099 CE – 1187 CE -Muslims lose Jerusalem to Christian knigh ...
... Byzantines (1071 CE) taking all of Anatolia. -Seljuks feud over claims to who is sultan (caliph), thus for years ignoring irrigation, city maintenance, etc. -Major pop. decline, cities shrink, drying up of Mesopotamia region The Crusades - 1099 CE – 1187 CE -Muslims lose Jerusalem to Christian knigh ...
Growth of Islamic Society
... 679 Hasan led a great suicide charge. His head was sent to the capital. This would result in the Sunni-Shi’ite split ...
... 679 Hasan led a great suicide charge. His head was sent to the capital. This would result in the Sunni-Shi’ite split ...
After Muhammad`s death in 632, his father-in
... After Muhammad’s death in 632, his father-in-law Abu Bakr succeeded him. This was the beginning of the Rashidun Caliphate which lasted until 661. Following Abu’s death in 634, no clear line of succession had been established. The first two caliphs succeeding Abu were assassinated. Muhammad’s son-in- ...
... After Muhammad’s death in 632, his father-in-law Abu Bakr succeeded him. This was the beginning of the Rashidun Caliphate which lasted until 661. Following Abu’s death in 634, no clear line of succession had been established. The first two caliphs succeeding Abu were assassinated. Muhammad’s son-in- ...
Islam after Muhammad Arabian Caliphate
... Ottomans: powerful army; began in Turkey in 1200. Ottoman Empire a. Conquered Byzantine Empire, pushed north into Constantinople, capital city b. Then in Syria, Palestine, Egypt, and parts of Arabia c. Sultan Suleiman Ottoman Gov’t lasted until WWI in 1916 a. Laws for Muslims, Christians, and Jews i ...
... Ottomans: powerful army; began in Turkey in 1200. Ottoman Empire a. Conquered Byzantine Empire, pushed north into Constantinople, capital city b. Then in Syria, Palestine, Egypt, and parts of Arabia c. Sultan Suleiman Ottoman Gov’t lasted until WWI in 1916 a. Laws for Muslims, Christians, and Jews i ...
The Rise and Fall of the Caliphates
... Spread Islam Muslims allowed conquered people to worship their own religion Christians & Jews received special treatment Still had to pay taxes & subject to various restrictions Couldn’t spread religion, but could be officials, scholars, bureaucrats, etc. ...
... Spread Islam Muslims allowed conquered people to worship their own religion Christians & Jews received special treatment Still had to pay taxes & subject to various restrictions Couldn’t spread religion, but could be officials, scholars, bureaucrats, etc. ...
6.2 Sunni Shia split
... One prince named Abd al-Rahman escaped the slaughter and fled to Spain. There he set up an Umayyad caliphate. Spain had already been conquered and settled by Muslims from North Africa, who were known as Berbers. The Berber armies advanced north to within 200 miles of Paris before being halted at the ...
... One prince named Abd al-Rahman escaped the slaughter and fled to Spain. There he set up an Umayyad caliphate. Spain had already been conquered and settled by Muslims from North Africa, who were known as Berbers. The Berber armies advanced north to within 200 miles of Paris before being halted at the ...
timeline for islam and ottoman empires
... 610 - Muhammad begins to preach monotheism. 622 - Muhammad forced to flee to Medina. 630 - Muhammad and his followers capture Mecca in 630. 632 - Muhammad dies and he is succeeded by four caliphs, elected successors. These leaders form the Orthodox Caliphate. They were good generals and they conquer ...
... 610 - Muhammad begins to preach monotheism. 622 - Muhammad forced to flee to Medina. 630 - Muhammad and his followers capture Mecca in 630. 632 - Muhammad dies and he is succeeded by four caliphs, elected successors. These leaders form the Orthodox Caliphate. They were good generals and they conquer ...
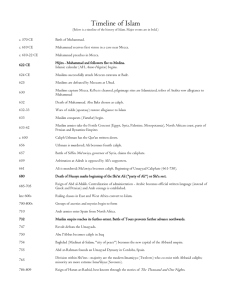
Timeline of Islam
... Reign of Ma'mun. Theological controversy over whether the Qur'an is created or uncreated and eternal. Center for translation of texts from Greek to Arabic founded in Baghdad. ...
... Reign of Ma'mun. Theological controversy over whether the Qur'an is created or uncreated and eternal. Center for translation of texts from Greek to Arabic founded in Baghdad. ...
slides - www3.telus.net
... 2. Created man from a blood-clot. 3. Read, for thy Lord is the Most Generous, 4. Who taught by the pen, 5. Taught man that which he knew not. ...
... 2. Created man from a blood-clot. 3. Read, for thy Lord is the Most Generous, 4. Who taught by the pen, 5. Taught man that which he knew not. ...
Islamic Civilization GRAPES Geography Islam religion began in
... Living a proper life meant following God’s law as revealed in the Qur’an and the Sunnah The laws were collected in a legal code called the Sharia First four caliphate had close ties to Muhammad After death of fourth caliphate, the Umayyad family gained control of the caliphate and moved the capital ...
... Living a proper life meant following God’s law as revealed in the Qur’an and the Sunnah The laws were collected in a legal code called the Sharia First four caliphate had close ties to Muhammad After death of fourth caliphate, the Umayyad family gained control of the caliphate and moved the capital ...