4- Worms_AP Bio
... blood and •Endemic in central Africa, Turkey, India, lymph vessels Southeast Asia, Australia, Philippines, and of birds and South America mammals •transmitted by mosquitoes •After infection, the adult filarial worms migrate •Usually to and live in the lymphatic ducts of causes humans. There, they cl ...
... blood and •Endemic in central Africa, Turkey, India, lymph vessels Southeast Asia, Australia, Philippines, and of birds and South America mammals •transmitted by mosquitoes •After infection, the adult filarial worms migrate •Usually to and live in the lymphatic ducts of causes humans. There, they cl ...
RENAL - ACID BASE – ADRENAL PHYSIOLOGY
... a. Its precursor, Angiotensinogen, is produced by the Adrenals. b. Is inactive in its Angiotensin III form. c. It stimulates both aldosterone & vasopressin release d. Is most active as Angiotensin I 50. What is true regarding erythropoietin? a. 85% comes from the kidneys, the remainder from the live ...
... a. Its precursor, Angiotensinogen, is produced by the Adrenals. b. Is inactive in its Angiotensin III form. c. It stimulates both aldosterone & vasopressin release d. Is most active as Angiotensin I 50. What is true regarding erythropoietin? a. 85% comes from the kidneys, the remainder from the live ...
Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 11: Endocrine System Directions
... Blood pressure rises, Breathing rate increases, Air passages dilate, Pupils dilate, Blood flow redistributes 6. What are 2 long-term effects? Increase in blood concentration of amino acids, increased release of fatty acids, increased glucose formed from noncarbohydrates--amino acids (from proteins) ...
... Blood pressure rises, Breathing rate increases, Air passages dilate, Pupils dilate, Blood flow redistributes 6. What are 2 long-term effects? Increase in blood concentration of amino acids, increased release of fatty acids, increased glucose formed from noncarbohydrates--amino acids (from proteins) ...
Unit One: Introduction to Physiology: The Cell and General Physiology
... Velocity of Blood Flow-because the same volume of blood flow (F) must pass thru each segment of circulation each minute, the velocity (V) is inversely proportional to vascular crosssectional area V = F/A ...
... Velocity of Blood Flow-because the same volume of blood flow (F) must pass thru each segment of circulation each minute, the velocity (V) is inversely proportional to vascular crosssectional area V = F/A ...
Ch.21
... If the pH of arterial blood drops to 6.8 or rises to 8.0 for more than a few hours, the person usually cannot survive ...
... If the pH of arterial blood drops to 6.8 or rises to 8.0 for more than a few hours, the person usually cannot survive ...
File - Wk 1-2
... ↑ temp also → ↓ tendency for O2 to remain bound to Hb. Hence, the ↑ amount of O2 released into the tissues with ↑ metabolism (e.g. during exercise). This causes a shift to the RHS. As much as 75-85% of the oxygen is released into the tissues from the Hb. In the lungs, the curve shifts to the LHS du ...
... ↑ temp also → ↓ tendency for O2 to remain bound to Hb. Hence, the ↑ amount of O2 released into the tissues with ↑ metabolism (e.g. during exercise). This causes a shift to the RHS. As much as 75-85% of the oxygen is released into the tissues from the Hb. In the lungs, the curve shifts to the LHS du ...
Worms - Cloudfront.net
... – Hooks attach to inner walls of intestines – Food absorbed through skin – Grow up to 12 meters ...
... – Hooks attach to inner walls of intestines – Food absorbed through skin – Grow up to 12 meters ...
المحاضرة السادسة عشر Sixteenth lecture
... مرئ, crop حوصلة, gizzard قانصة, and intestine أمعاء. The closed circulatory system carries blood with oxygen- ...
... مرئ, crop حوصلة, gizzard قانصة, and intestine أمعاء. The closed circulatory system carries blood with oxygen- ...
cardiac output
... 60 bpm x 70 mL/beat = 4,200 mL/min (approximately 1 gallon of blood per min) During maximum exercise, cardiac output can increase up to 4 to 7 times above resting level. ...
... 60 bpm x 70 mL/beat = 4,200 mL/min (approximately 1 gallon of blood per min) During maximum exercise, cardiac output can increase up to 4 to 7 times above resting level. ...
Notes to Endo 3
... Due to a hypersecretion or hyposecretion of aldosterone. Hypersecretion results in • increased Na+ re-absorption and increased secretion of potassium • results in excess water retention, hypertension • if K+ secretion is severe, low response to stimuli, weak muscle tone, paralysis ( hyper polarizati ...
... Due to a hypersecretion or hyposecretion of aldosterone. Hypersecretion results in • increased Na+ re-absorption and increased secretion of potassium • results in excess water retention, hypertension • if K+ secretion is severe, low response to stimuli, weak muscle tone, paralysis ( hyper polarizati ...
BIOL212test2keyMAY2012
... 42.) Three chambered hearts with incomplete septa were once viewed as being less adapted to circulatory function than mammalian hearts. What advantage of such hearts did this viewpoint not consider? (You should have read this in the text.) Found in amphibian & reptilian species: when submerged, wher ...
... 42.) Three chambered hearts with incomplete septa were once viewed as being less adapted to circulatory function than mammalian hearts. What advantage of such hearts did this viewpoint not consider? (You should have read this in the text.) Found in amphibian & reptilian species: when submerged, wher ...
Key – underlined answers are the correct answers 1) In the diagram
... c) 225 miles per hour d) Faster if temperature is lowered e) Not important for animal respiration 30) In respiration a) Reduced carbon (such as glucose) is produced b) Oxygen and reduced carbon (such as glucose) are consumed c) Carbon dioxide is consumed d) A 1 meter spherical organism can rely on j ...
... c) 225 miles per hour d) Faster if temperature is lowered e) Not important for animal respiration 30) In respiration a) Reduced carbon (such as glucose) is produced b) Oxygen and reduced carbon (such as glucose) are consumed c) Carbon dioxide is consumed d) A 1 meter spherical organism can rely on j ...
Chapter 15- Lateral mesoderm and endoderm
... Blood vessel formation 1. Vasculogenesis Fig. 15.14 Blood vessels and blood cells are intimately ...
... Blood vessel formation 1. Vasculogenesis Fig. 15.14 Blood vessels and blood cells are intimately ...
The Renal System
... plasma level is constant. urine is collected for a timed period to get urine flow rate and urinary concentration of inulin. ...
... plasma level is constant. urine is collected for a timed period to get urine flow rate and urinary concentration of inulin. ...
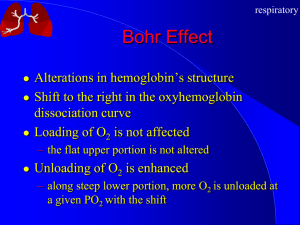
Respiration - Weber State University
... dissociation curve Loading of O2 is not affected – the flat upper portion is not altered ...
... dissociation curve Loading of O2 is not affected – the flat upper portion is not altered ...
1 FORM W KEY deducted if you fail to do this!!!!!!
... 15. The functional unit of the kidney is the a) glomerulus b) proximal tubule c) collecting ducts d) nephron e) loop of Henle 16. Blood enters the glomerulus from ________. a) The peritubular capillary b) The efferent arteriole c) The afferent arteriole d) Bowman’s capsule e) The vasa recta 17. Whi ...
... 15. The functional unit of the kidney is the a) glomerulus b) proximal tubule c) collecting ducts d) nephron e) loop of Henle 16. Blood enters the glomerulus from ________. a) The peritubular capillary b) The efferent arteriole c) The afferent arteriole d) Bowman’s capsule e) The vasa recta 17. Whi ...
Chapter 16 - Dr. Dorena Rode
... Perhaps the most remarkable molecule in the body is hemoglobin. Featuring an iron atom core that attracts oxygen, thousands of hemoglobin-O2 molecules are transported in the cytoplasm of each erythrocyte (red blood cell) past every tissue cell in the body. As erythrocytes tumble single file through ...
... Perhaps the most remarkable molecule in the body is hemoglobin. Featuring an iron atom core that attracts oxygen, thousands of hemoglobin-O2 molecules are transported in the cytoplasm of each erythrocyte (red blood cell) past every tissue cell in the body. As erythrocytes tumble single file through ...
Abdomen Thorax Head
... circulatory systems. Why are open circulatory systems found mostly in small animals that move slowly? In an open system, blood is pumped through vessels by a simple heart and works its way through different sinuses. In a closed system, blood is circulated through a network of blood vessels. A closed ...
... circulatory systems. Why are open circulatory systems found mostly in small animals that move slowly? In an open system, blood is pumped through vessels by a simple heart and works its way through different sinuses. In a closed system, blood is circulated through a network of blood vessels. A closed ...
19 Comp Review 3b
... aerobic activity have less oxygen and more CO2, lower pH, and increased temperature. When the CO2 levels in the tissues are too high, the smooth muscle sphincters relax to allow more blood flow to increase gas exchange. ...
... aerobic activity have less oxygen and more CO2, lower pH, and increased temperature. When the CO2 levels in the tissues are too high, the smooth muscle sphincters relax to allow more blood flow to increase gas exchange. ...
Blood Vessel - Oregon State University
... Methods of Autoregulation: 1) Metabolic Control: • Nutritional status of tissues regulate flow ...
... Methods of Autoregulation: 1) Metabolic Control: • Nutritional status of tissues regulate flow ...
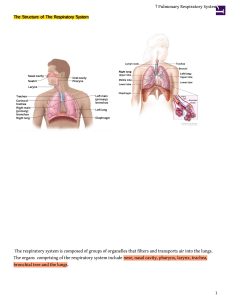
The Respiratory System
... 1. Pulmonary ventilation - Movement of air into and out of the lungs (also referred to as “breathing”). 2. External respiration - Gas exchange in the lungs between the blood of the capillaries and the spaces in the air sacs (alveoli) 3. Transport - The movement of gases by the circulatory system Str ...
... 1. Pulmonary ventilation - Movement of air into and out of the lungs (also referred to as “breathing”). 2. External respiration - Gas exchange in the lungs between the blood of the capillaries and the spaces in the air sacs (alveoli) 3. Transport - The movement of gases by the circulatory system Str ...
① Pulmonary Respiratory System
... water vapor (H2O) to inspired air, warming it to body temperature, and trapping particulate material (dust, yeast, and bacteria) as well as noxious fumes (smoke, ozone). The pulmonary tree anatomy provides a large surface area for respiratory gas exchange between alveoli and blood (pulmonary capilla ...
... water vapor (H2O) to inspired air, warming it to body temperature, and trapping particulate material (dust, yeast, and bacteria) as well as noxious fumes (smoke, ozone). The pulmonary tree anatomy provides a large surface area for respiratory gas exchange between alveoli and blood (pulmonary capilla ...