Life2
... Quantum fluctuations in early universe produced “framework” of galaxy formation. Attracted gas and dark matter that coalesced to form first galaxies at only 500 million years. Formed in “cosmic web”. ...
... Quantum fluctuations in early universe produced “framework” of galaxy formation. Attracted gas and dark matter that coalesced to form first galaxies at only 500 million years. Formed in “cosmic web”. ...
Origins of the Universe
... typically containing millions to hundreds of billions of member stars – A star is a large hot ball of gas which generates energy in its core by nuclear reactions Around 100 billion in the universe Held together by the gravitational attraction of all its member stars on one another Formed around 200 ...
... typically containing millions to hundreds of billions of member stars – A star is a large hot ball of gas which generates energy in its core by nuclear reactions Around 100 billion in the universe Held together by the gravitational attraction of all its member stars on one another Formed around 200 ...
Chapter 7 Vocabulary212
... 1. Spectroscope- used to study star’s characteristics by spreading light into different wavelengths 2. Nuclear fusion- nuclei of several atoms combine to form on large nucleus 3. astronomical unit- average distance between Earth and Sun (150 million km) 4. light year- distance light travels in 1 yea ...
... 1. Spectroscope- used to study star’s characteristics by spreading light into different wavelengths 2. Nuclear fusion- nuclei of several atoms combine to form on large nucleus 3. astronomical unit- average distance between Earth and Sun (150 million km) 4. light year- distance light travels in 1 yea ...
Stellar Properties and Stellar Evolution Study Guide Name Why
... 7. Planets shine by reflected star light. How can planets be brighter than stars? ...
... 7. Planets shine by reflected star light. How can planets be brighter than stars? ...
tire
... 15. The grouping of stars on a H-R diagram extending diagonally across the graph. Stars will spend most of their lives on this diagonal. 16. A subatomic particle with no electric charge that is produced in the core of the Sun and trillions pass through us undetected each second. 17. The nearly explo ...
... 15. The grouping of stars on a H-R diagram extending diagonally across the graph. Stars will spend most of their lives on this diagonal. 16. A subatomic particle with no electric charge that is produced in the core of the Sun and trillions pass through us undetected each second. 17. The nearly explo ...
A Solar System is Born 4/29/11
... • Hubble image of protoplanetary discs in the Orion Nebula, a light-years-wide "stellar nursery" probably very similar to the primordial nebula from which our Sun formed. ...
... • Hubble image of protoplanetary discs in the Orion Nebula, a light-years-wide "stellar nursery" probably very similar to the primordial nebula from which our Sun formed. ...
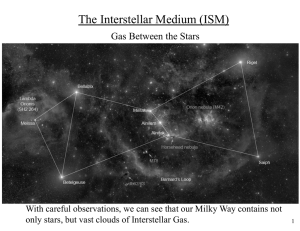
The Interstellar Medium (ISM)
... Hot, massive stars produce huge amounts of these. Such short-lived stars spend all their lives in the stellar nursery of their birth, so emission nebulae mark sites of ongoing star formation. Many stars of lower mass are forming too, but emit few UV photons. Why “H II Region”? H I: Hydrogen atom H I ...
... Hot, massive stars produce huge amounts of these. Such short-lived stars spend all their lives in the stellar nursery of their birth, so emission nebulae mark sites of ongoing star formation. Many stars of lower mass are forming too, but emit few UV photons. Why “H II Region”? H I: Hydrogen atom H I ...
Two prevailing theories on how the universe was created
... galaxy. This is a photo graph made by the Hubble telescope of deep space. What was once thought to be individual stars turned out to be huge collections of stars. ...
... galaxy. This is a photo graph made by the Hubble telescope of deep space. What was once thought to be individual stars turned out to be huge collections of stars. ...
Study Notes for Integrated Science Astronomy Unit These notes will
... come to be. We discussed from the beginning at singularity to the point at which the first stars began to form. The Big Bang Theory came about by scientists and observers realizing that our universe is expanding and cooling. This expansion and the microwave radiation left behind from its origins is ...
... come to be. We discussed from the beginning at singularity to the point at which the first stars began to form. The Big Bang Theory came about by scientists and observers realizing that our universe is expanding and cooling. This expansion and the microwave radiation left behind from its origins is ...
STARS
... • Core runs out of He, and is no longer able to fuse the remaining heavier elements • The star blows its outer layer away • The core remains behind and burns as a white dwarf • Eventually it cools to become a black dwarf ...
... • Core runs out of He, and is no longer able to fuse the remaining heavier elements • The star blows its outer layer away • The core remains behind and burns as a white dwarf • Eventually it cools to become a black dwarf ...
Another exAmple: expository mode
... known as nuclear fusion to produce light. As stars use up this hydrogen, in a process that takes billions of years, they pass through certain phases or stages. In each stage, the star’s brightness, temperature, and size change. The redgiant phase occurs when the star begins to run out of hydrogen. I ...
... known as nuclear fusion to produce light. As stars use up this hydrogen, in a process that takes billions of years, they pass through certain phases or stages. In each stage, the star’s brightness, temperature, and size change. The redgiant phase occurs when the star begins to run out of hydrogen. I ...
g9u4c12part3
... consume their fuel faster than smaller stars Become red giants. (supergiants) last for only 7 billion years. they collapse in on themselves causing a massive explosion called a supernova. the remaining core of the supernova will eventually collapse to form a neutron star. A sphere only 10 km ...
... consume their fuel faster than smaller stars Become red giants. (supergiants) last for only 7 billion years. they collapse in on themselves causing a massive explosion called a supernova. the remaining core of the supernova will eventually collapse to form a neutron star. A sphere only 10 km ...
NGC 5746 :: NGC 5746 Handout - Chandra X
... Spiral galaxies are thought to form from enormous clouds of intergalactic gas that collapse to form spinning disks of stars and gas. The Chandra data and computer simulations show that the likely origin of NGC 5746's hot halo is the gradual inflow of intergalactic matter left over from the formation ...
... Spiral galaxies are thought to form from enormous clouds of intergalactic gas that collapse to form spinning disks of stars and gas. The Chandra data and computer simulations show that the likely origin of NGC 5746's hot halo is the gradual inflow of intergalactic matter left over from the formation ...
The perfect K-12 presentation ever (replace this with your title)
... Stars form through the collapse of stellar nebula The Life Cycle of Stars describes the evolutionary paths for stars. ...
... Stars form through the collapse of stellar nebula The Life Cycle of Stars describes the evolutionary paths for stars. ...
Solar System and Astronomy puzzle 001
... a star system consisting of two stars orbiting around their common center of mass 10. natural satellite 12. a massive, gravitationally bound system consisting of stars, stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust 13. growth of a massive object by gravitationally attracting more matter ...
... a star system consisting of two stars orbiting around their common center of mass 10. natural satellite 12. a massive, gravitationally bound system consisting of stars, stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust 13. growth of a massive object by gravitationally attracting more matter ...
Discussion Activity #13
... least 10 times as much matter as we see in the Milky Way disk, suggesting that the halo is full of dark matter. B. The orbital speeds of stars far from the galactic center are surprisingly high, suggesting that these stars are feeling gravitational effects from unseen matter in the halo. C. Our view ...
... least 10 times as much matter as we see in the Milky Way disk, suggesting that the halo is full of dark matter. B. The orbital speeds of stars far from the galactic center are surprisingly high, suggesting that these stars are feeling gravitational effects from unseen matter in the halo. C. Our view ...
Mystic nebula
... • Made of light and gases • 21 light years wide on average • Irregular shapes of gas and light • -272 degrees Celsius • Only one degrees above zero ...
... • Made of light and gases • 21 light years wide on average • Irregular shapes of gas and light • -272 degrees Celsius • Only one degrees above zero ...
AST101 Lecture 20 The Ecology of the Galaxy
... • About 1010 years old • 105 - 106 stars • Radius ~ 10 light years • Most massive star: ~ 1 solar mass • ~150 globular clusters known in Milky Way ...
... • About 1010 years old • 105 - 106 stars • Radius ~ 10 light years • Most massive star: ~ 1 solar mass • ~150 globular clusters known in Milky Way ...
Space Science Chapter 4 Reading Guide BIG IDEA: Our Sun is
... 4. How do stars form inside a nebula? ...
... 4. How do stars form inside a nebula? ...
Disk Galaxies: Structural Components
... • Other elliptical galaxies and spiral galaxy halos are thought to have formed by merging smaller galaxies; merging process results in disordered stellar orbits • Important distinction between stars and hydrogen gas: gas is dissipative (a clump of gas tends to drag surrounding material with it due t ...
... • Other elliptical galaxies and spiral galaxy halos are thought to have formed by merging smaller galaxies; merging process results in disordered stellar orbits • Important distinction between stars and hydrogen gas: gas is dissipative (a clump of gas tends to drag surrounding material with it due t ...
4.1 – 4.3 - s3.amazonaws.com
... –resemble an egg or a football –not as structured • irregular galaxies –groups of stars that have no defined shapes –the Large Magellanic Cloud and Small Magellanic Cloud »the two closest galaxies to ours ...
... –resemble an egg or a football –not as structured • irregular galaxies –groups of stars that have no defined shapes –the Large Magellanic Cloud and Small Magellanic Cloud »the two closest galaxies to ours ...
H II region

An H II region is a large, low-density cloud of partially ionized gas in which star formation has recently taken place. The short-lived blue stars forged in these regions emit copious amounts of ultraviolet light that ionize the surrounding gas. H II regions—sometimes several hundred light-years across—are often associated with giant molecular clouds. The first known H II region was the Orion Nebula, which was discovered in 1610 by Nicolas-Claude Fabri de Peiresc.H II regions are named for the large amount of ionised atomic hydrogen they contain, referred to as H II, pronounced H-two by astronomers (an H I region being neutral atomic hydrogen, and H2 being molecular hydrogen). Such regions have extremely diverse shapes, because the distribution of the stars and gas inside them is irregular. They often appear clumpy and filamentary, sometimes showing bizarre shapes such as the Horsehead Nebula. H II regions may give birth to thousands of stars over a period of several million years. In the end, supernova explosions and strong stellar winds from the most massive stars in the resulting star cluster will disperse the gases of the H II region, leaving behind a cluster of birthed stars such as the Pleiades.H II regions can be seen to considerable distances in the universe, and the study of extragalactic H II regions is important in determining the distance and chemical composition of other galaxies. Spiral and irregular galaxies contain many H II regions, while elliptical galaxies are almost devoid of them. In the spiral galaxies, including the Milky Way, H II regions are concentrated in the spiral arms, while in the irregular galaxies they are distributed chaotically. Some galaxies contain huge H II regions, which may contain tens of thousands of stars. Examples include the 30 Doradus region in the Large Magellanic Cloud and NGC 604 in the Triangulum Galaxy.