Pelvic and Perineal Anatomy of the Male Gorilla
... In the gorilla it is a completely separate muscle not entirely comparable to the puborectalis of man. The puborectalis in the gorilla arises by means of an aponeurosis (fig. 2D) from the connective tissue in the region of the sub-symphysial angle (arcuate pubic ligament), the fibrous tissue associat ...
... In the gorilla it is a completely separate muscle not entirely comparable to the puborectalis of man. The puborectalis in the gorilla arises by means of an aponeurosis (fig. 2D) from the connective tissue in the region of the sub-symphysial angle (arcuate pubic ligament), the fibrous tissue associat ...
Gripping Matters - Starting Strength
... First, “The Rule of 3-5-7” describes the excursion (in centimeters) of the musculotendinous units of the muscles acting on the wrist, carpal, and metacarpal joints. The wrist flexors and extensors – extensor pollicis brevis, palmar and dorsal interossei, abductor pollicis longus, and flexor carpi ul ...
... First, “The Rule of 3-5-7” describes the excursion (in centimeters) of the musculotendinous units of the muscles acting on the wrist, carpal, and metacarpal joints. The wrist flexors and extensors – extensor pollicis brevis, palmar and dorsal interossei, abductor pollicis longus, and flexor carpi ul ...
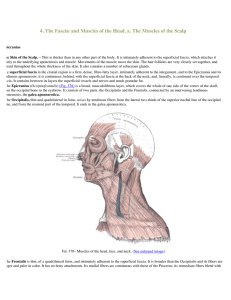
4. The Fascię and Muscles of the Head. a. The Muscles of the Scalp
... The Triangularis (Depressor anguli oris) arises from the oblique line of the mandible, whence its fibers converge, to be inserted, by a narrow fasciculus, into the angle of the mouth. At its origin it is continuous with the Platysma, and at its insertion with the Orbicularis oris and Risorius; some ...
... The Triangularis (Depressor anguli oris) arises from the oblique line of the mandible, whence its fibers converge, to be inserted, by a narrow fasciculus, into the angle of the mouth. At its origin it is continuous with the Platysma, and at its insertion with the Orbicularis oris and Risorius; some ...
Biology 3B Laboratory Muscles of Vertebrate Animals: Shark
... require more time than others. You will have to work as a team in order to spread out the work load and make sure that you all have equal time to learn the material. In the histology lab you learned to recognize smooth, cardiac, and skeletal (striated) muscle. In this lab we only look at skeletal mu ...
... require more time than others. You will have to work as a team in order to spread out the work load and make sure that you all have equal time to learn the material. In the histology lab you learned to recognize smooth, cardiac, and skeletal (striated) muscle. In this lab we only look at skeletal mu ...
COMMENTARY The diversity of hydrostatic skeletons
... amplification of the force and displacement of muscle contraction. In hydrostatic skeletons, force is transmitted not through rigid skeletal elements but instead by internal pressure. Functioning of these systems depends on the fact that they are essentially constant in volume as they consist of rel ...
... amplification of the force and displacement of muscle contraction. In hydrostatic skeletons, force is transmitted not through rigid skeletal elements but instead by internal pressure. Functioning of these systems depends on the fact that they are essentially constant in volume as they consist of rel ...
Scapular region
... Scapular movements: Elevation Depression Protraction Retraction Medial rotation Lateral rotation ...
... Scapular movements: Elevation Depression Protraction Retraction Medial rotation Lateral rotation ...
Tear flexor digitorum profundus icd 10
... tunnel syndrome, unspecified. please see my response to the the post by coderguy from the other day titled "Carpometacarpal Resection Arthroplasty". There is a lot of good info about wrist. Tendon Injury ICD Codes. Valgus deformity of wrist (736.03) Varus deformity of wrist (736.04) Wrist drop (736. ...
... tunnel syndrome, unspecified. please see my response to the the post by coderguy from the other day titled "Carpometacarpal Resection Arthroplasty". There is a lot of good info about wrist. Tendon Injury ICD Codes. Valgus deformity of wrist (736.03) Varus deformity of wrist (736.04) Wrist drop (736. ...
Membranes of the Larynx: Extrinsic membranes connect the
... on the inferior border of the thyroid lamina. It is described as having two parts, a pars recta, whose fibers course vertically and a pars oblique, whose fibers course upwards and backwards. Contraction of its fibers rotates the anterior part of the thyroid cartilage downward, causing rotation at th ...
... on the inferior border of the thyroid lamina. It is described as having two parts, a pars recta, whose fibers course vertically and a pars oblique, whose fibers course upwards and backwards. Contraction of its fibers rotates the anterior part of the thyroid cartilage downward, causing rotation at th ...
sympathetic nervous system
... Nervous system of the digestive tract Composed of 100 million neurons found in the walls of the digestive tract (no components found in CNS) ...
... Nervous system of the digestive tract Composed of 100 million neurons found in the walls of the digestive tract (no components found in CNS) ...
Fetal anatomy of the upper pharyngeal muscles with special
... begins from the peripheral or medial side of the nerve courses. Pharyngeal nerves were identified as the numerous dots in the CPS and CPM (Figs. 2, 3). Multiple pharyngeal nerves (3–5 in number) in the CPS entered the LVP at the most peripheral site of the nerve courses (Fig. 2A). Because the CPS an ...
... begins from the peripheral or medial side of the nerve courses. Pharyngeal nerves were identified as the numerous dots in the CPS and CPM (Figs. 2, 3). Multiple pharyngeal nerves (3–5 in number) in the CPS entered the LVP at the most peripheral site of the nerve courses (Fig. 2A). Because the CPS an ...
Bi 212, Lab 1
... section based on the parts you could see for each. Specific tissue layers best seen in cross-section. Be sure also to label all places where you have epidermis, mesoderm and gastrodermis (i.e. both the pharynx and the body itself). a. epidermis derived from ectoderm (multiple places in cross-section ...
... section based on the parts you could see for each. Specific tissue layers best seen in cross-section. Be sure also to label all places where you have epidermis, mesoderm and gastrodermis (i.e. both the pharynx and the body itself). a. epidermis derived from ectoderm (multiple places in cross-section ...
Cranial nerve flashcards 2005 (intermediate and challenging nerves)
... Motor to the muscles of the palate (levator veli palatini, musculus uvuli, palatoglossus, and palatopharyngeus; i.e. all palatal muscles except tensor veli palatini). Motor to the muscles of the pharynx (superior, middle, and inferior constrictor, palatopharyngeus; and salpingopharyngeus; i.e. all p ...
... Motor to the muscles of the palate (levator veli palatini, musculus uvuli, palatoglossus, and palatopharyngeus; i.e. all palatal muscles except tensor veli palatini). Motor to the muscles of the pharynx (superior, middle, and inferior constrictor, palatopharyngeus; and salpingopharyngeus; i.e. all p ...
Peripheral NS - Fullfrontalanatomy.com
... Include: -Muscle spindles -Golgi tendon organs -Joint kinesthetic receptors ...
... Include: -Muscle spindles -Golgi tendon organs -Joint kinesthetic receptors ...
Anatomy and Physiology of The Eye
... 4-outer nuclear layer. 5-outer plexiform layer. 6-inner nuclear layer. 7-inner plexiform layer. 8-Gangelion cells. 9-nerve fiber layer. 10-internal limiting membrane. ...
... 4-outer nuclear layer. 5-outer plexiform layer. 6-inner nuclear layer. 7-inner plexiform layer. 8-Gangelion cells. 9-nerve fiber layer. 10-internal limiting membrane. ...
Muscle

Muscle is a soft tissue found in most animals. Muscle cells contain protein filaments of actin and myosin that slide past one another, producing a contraction that changes both the length and the shape of the cell. Muscles function to produce force and motion. They are primarily responsible for maintaining and changing posture, locomotion, as well as movement of internal organs, such as the contraction of the heart and the movement of food through the digestive system via peristalsis.Muscle tissues are derived from the mesodermal layer of embryonic germ cells in a process known as myogenesis. There are three types of muscle, skeletal or striated, cardiac, and smooth. Muscle action can be classified as being either voluntary or involuntary. Cardiac and smooth muscles contract without conscious thought and are termed involuntary, whereas the skeletal muscles contract upon command. Skeletal muscles in turn can be divided into fast and slow twitch fibers.Muscles are predominantly powered by the oxidation of fats and carbohydrates, but anaerobic chemical reactions are also used, particularly by fast twitch fibers. These chemical reactions produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecules that are used to power the movement of the myosin heads.The term muscle is derived from the Latin musculus meaning ""little mouse"" perhaps because of the shape of certain muscles or because contracting muscles look like mice moving under the skin.