Multi-axis passive and active stiffnesses of the glenohumeral joint
... excessive loading of the joint structure. The experimental protocol was tested using two shoulder specimens in order to find appropriate initial position. It was also tested to find reasonable range of translations along the anatomical axes. In order to evaluate contributions of the passive GH capsulo ...
... excessive loading of the joint structure. The experimental protocol was tested using two shoulder specimens in order to find appropriate initial position. It was also tested to find reasonable range of translations along the anatomical axes. In order to evaluate contributions of the passive GH capsulo ...
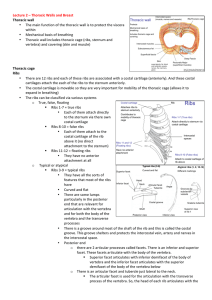
Thoracic Walls and Breast Thoracic wall • The main function of the
... • Intercostal nerves are extensions of the spinal segmental nerves which comes out of the intervertebral foramina of the vertebral column • As the spinal nerve leaves the intervertebral foramina it also gives off a dorsal ramus to supply the skin and muscles over the vertebral column = erecto ...
... • Intercostal nerves are extensions of the spinal segmental nerves which comes out of the intervertebral foramina of the vertebral column • As the spinal nerve leaves the intervertebral foramina it also gives off a dorsal ramus to supply the skin and muscles over the vertebral column = erecto ...
Aberrant Rotator Cuff Muscles: Coexistence of Triple
... The capsule of the gleno-humeral joint is also reinforced by the reported additional slips of muscles. Nonetheless, individuals possessing this kind of variations who are exposed to excessive sporting activities involving extensive movements of the gleno-humeral joint, such as javelin or shot-put th ...
... The capsule of the gleno-humeral joint is also reinforced by the reported additional slips of muscles. Nonetheless, individuals possessing this kind of variations who are exposed to excessive sporting activities involving extensive movements of the gleno-humeral joint, such as javelin or shot-put th ...
STUDY THIS FOR THE TEST! PRACTICE! HAS ANSWERS!!! File
... Epithelial Tissue Lines the digestive tract. Contains goblet cells that produce mucus. ...
... Epithelial Tissue Lines the digestive tract. Contains goblet cells that produce mucus. ...
General Anatomy Handout
... -bone forming cell derived from mesenchyme Osteoclast: -multinucleated cell that breaks down bone Lamella: -concentric matrix around osteoblast Lacuna: -small space or cavity around cells. (contains osteocytes) -Lacuna of Howship Trabeculae: -fibrous strands in medullary compartment that are interco ...
... -bone forming cell derived from mesenchyme Osteoclast: -multinucleated cell that breaks down bone Lamella: -concentric matrix around osteoblast Lacuna: -small space or cavity around cells. (contains osteocytes) -Lacuna of Howship Trabeculae: -fibrous strands in medullary compartment that are interco ...
TOES
... - Patient Starting Position: Back lying, affected leg extended. - Therapist Position and Grasps: Standing beside the table at the level of the patient feet. The proximal hand grasps the patient’s forefoot to stabilize the metatarsal bones. Resistance for testing “Grades 4 and 5” will be given by the ...
... - Patient Starting Position: Back lying, affected leg extended. - Therapist Position and Grasps: Standing beside the table at the level of the patient feet. The proximal hand grasps the patient’s forefoot to stabilize the metatarsal bones. Resistance for testing “Grades 4 and 5” will be given by the ...
AandPExam3takehomecC7sf7Y
... There are four extrinsic muscles of the tongue: genioglossus, hyoglossus, styoglossus, and palatoglossus. The extrinsic muscles originate from the bone and extend to the tongue. Their main functions are altering the tongue’s position. This allows for protrusion, retraction, and side to side movement ...
... There are four extrinsic muscles of the tongue: genioglossus, hyoglossus, styoglossus, and palatoglossus. The extrinsic muscles originate from the bone and extend to the tongue. Their main functions are altering the tongue’s position. This allows for protrusion, retraction, and side to side movement ...
20 the humerus - Rush Pin, LLC
... still occurs. Fixation is not stable and rotation of the fragment can occur. ...
... still occurs. Fixation is not stable and rotation of the fragment can occur. ...
The_Knee_Joint_handout
... • The tendon of the biceps femoris is split in two by the LCL • To locate the inferior attachment, follow the tendon of the biceps femoris muscle • FCL separated from the joint capsule inferiorly by fatty tissue • Tendon of popliteus muscle passes deep to the FCL, separating it from the lateral meni ...
... • The tendon of the biceps femoris is split in two by the LCL • To locate the inferior attachment, follow the tendon of the biceps femoris muscle • FCL separated from the joint capsule inferiorly by fatty tissue • Tendon of popliteus muscle passes deep to the FCL, separating it from the lateral meni ...
19 Topography of lower limb.
... +the synovial sheaths of the tendons of the tibialis anterior muscle, the extensor hallucis longus muscle and the extensor digitorum longus muscle -the synovial sheaths of the tendons of the extensor digitorum longus muscle, the extensor hallucis longus muscle and the tibialis anterior muscle -the s ...
... +the synovial sheaths of the tendons of the tibialis anterior muscle, the extensor hallucis longus muscle and the extensor digitorum longus muscle -the synovial sheaths of the tendons of the extensor digitorum longus muscle, the extensor hallucis longus muscle and the tibialis anterior muscle -the s ...
1. The general name for an alternate pathway of blood flow in or
... epidermis is thin and weak, so it would not be able to hold sutures by itself. Superficial fascia/ subcutaneous tissue is the loose and fatty connective tissue below the dermis, and not an appropriate location for sutures. The deep fascia invests muscles or groups of muscles, and it would be too de ...
... epidermis is thin and weak, so it would not be able to hold sutures by itself. Superficial fascia/ subcutaneous tissue is the loose and fatty connective tissue below the dermis, and not an appropriate location for sutures. The deep fascia invests muscles or groups of muscles, and it would be too de ...
BIOL 4260 Human Evolu onary Anatomy Lecture 12: Limb
... (AER), axes established 3. Fibroblast growth factors induce distal growth 4. More proximal areas slow division rates and differentiate ...
... (AER), axes established 3. Fibroblast growth factors induce distal growth 4. More proximal areas slow division rates and differentiate ...
Selective Neck Dissection - Vula
... plane between the deep aspect of the submandibular gland and the fascia covering the XIIn is opened with finger dissection, taking care not to tear the thin-walled veins accompanying XIIn. The XIIn is now visible in the floor of the submandibular triangle (Figure 14). Inferior traction on the gland ...
... plane between the deep aspect of the submandibular gland and the fascia covering the XIIn is opened with finger dissection, taking care not to tear the thin-walled veins accompanying XIIn. The XIIn is now visible in the floor of the submandibular triangle (Figure 14). Inferior traction on the gland ...
Interactive Cadaveric Dissection Guide
... observations about the musculoskeletal system and organs. Most of these were made by combining external observation with conjecture based on the dissection of nonhuman animals.2 Herophilus and Erasistratus, working as surgeons in Alexandria in approximately 300 BCE, made systematic studies designed ...
... observations about the musculoskeletal system and organs. Most of these were made by combining external observation with conjecture based on the dissection of nonhuman animals.2 Herophilus and Erasistratus, working as surgeons in Alexandria in approximately 300 BCE, made systematic studies designed ...
pdf
... The axial images are excellent to see the anterior malleal ligament (AML), posterior incudal ligament (PIL) and the stapedius muscle tendon. Coronal images are excellent to see the superior malleal ligament (SML) and the lateral malleal ligament (LML). The tensor tympani muscle tendon is well seen o ...
... The axial images are excellent to see the anterior malleal ligament (AML), posterior incudal ligament (PIL) and the stapedius muscle tendon. Coronal images are excellent to see the superior malleal ligament (SML) and the lateral malleal ligament (LML). The tensor tympani muscle tendon is well seen o ...
Dr. Kaan Yücel http://yeditepeanatomy1.org Anatomy of the hand
... synovial sheaths of the thumb and little finger are continuous with the sheaths associated with the tendons in the carpal tunnel. Extensor hoods The tendons of the extensor digitorum and extensor pollicis longus muscles pass onto the dorsal aspect of the digits and expand over the proximal phalanges ...
... synovial sheaths of the thumb and little finger are continuous with the sheaths associated with the tendons in the carpal tunnel. Extensor hoods The tendons of the extensor digitorum and extensor pollicis longus muscles pass onto the dorsal aspect of the digits and expand over the proximal phalanges ...
FibulA FlAP
... membrane (anterior intermuscular septum) all the way down to the ankle. You can also divide the muscles (extensor hallucis longus and extensor digitorum longus) and interosseus membrane (IOM) at this point if you are able to see them. Figure 8 Cut the distal fibula at your selected level. After you ...
... membrane (anterior intermuscular septum) all the way down to the ankle. You can also divide the muscles (extensor hallucis longus and extensor digitorum longus) and interosseus membrane (IOM) at this point if you are able to see them. Figure 8 Cut the distal fibula at your selected level. After you ...
Cubital fossa and forearm
... The two arteries in the thumb aren’t continuous( spaces between them) but the arteries are continuous in the three middle fingers that why we use them for measuring. • Forearm: we divided forearm to anterior and posterior compartments by radius and ulna and the interosseous membrane that connects th ...
... The two arteries in the thumb aren’t continuous( spaces between them) but the arteries are continuous in the three middle fingers that why we use them for measuring. • Forearm: we divided forearm to anterior and posterior compartments by radius and ulna and the interosseous membrane that connects th ...
Optimal Methods for Shoulder Tendon Palpation: A
... acromion as reported.""S.'l.'2 With the cadaver limbs in these positions, the infraspinatus tendon is repositioned under the acromion and the teres minor tendon is inferior to the angle of the acromion. ...
... acromion as reported.""S.'l.'2 With the cadaver limbs in these positions, the infraspinatus tendon is repositioned under the acromion and the teres minor tendon is inferior to the angle of the acromion. ...
Muscle

Muscle is a soft tissue found in most animals. Muscle cells contain protein filaments of actin and myosin that slide past one another, producing a contraction that changes both the length and the shape of the cell. Muscles function to produce force and motion. They are primarily responsible for maintaining and changing posture, locomotion, as well as movement of internal organs, such as the contraction of the heart and the movement of food through the digestive system via peristalsis.Muscle tissues are derived from the mesodermal layer of embryonic germ cells in a process known as myogenesis. There are three types of muscle, skeletal or striated, cardiac, and smooth. Muscle action can be classified as being either voluntary or involuntary. Cardiac and smooth muscles contract without conscious thought and are termed involuntary, whereas the skeletal muscles contract upon command. Skeletal muscles in turn can be divided into fast and slow twitch fibers.Muscles are predominantly powered by the oxidation of fats and carbohydrates, but anaerobic chemical reactions are also used, particularly by fast twitch fibers. These chemical reactions produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecules that are used to power the movement of the myosin heads.The term muscle is derived from the Latin musculus meaning ""little mouse"" perhaps because of the shape of certain muscles or because contracting muscles look like mice moving under the skin.