Tibialis anterior (7
... Tibialis anterior is the primary dorsi flexor of the ankle and an adequate knowledge of its normal anatomy and variations in attachments and course is required for clinicians. Ebraheim et al. (2003) found the muscle to be a relatively easy flap to use for covering anterior tibial open wounds. It is ...
... Tibialis anterior is the primary dorsi flexor of the ankle and an adequate knowledge of its normal anatomy and variations in attachments and course is required for clinicians. Ebraheim et al. (2003) found the muscle to be a relatively easy flap to use for covering anterior tibial open wounds. It is ...
Proximal Humerus Resection. The Tikhoff–Linberg
... glenohumeral joint or capsule. These mechanisms are direct extension through the articular cartilage, along the capsule and synovium, along an intra-articular structure (biceps tendon), through a fracture hematoma, and direct articular spread. The proximal humerus is at a much higher risk for local ...
... glenohumeral joint or capsule. These mechanisms are direct extension through the articular cartilage, along the capsule and synovium, along an intra-articular structure (biceps tendon), through a fracture hematoma, and direct articular spread. The proximal humerus is at a much higher risk for local ...
The evolution of the skull and the cephalic muscles
... if the mesoderm be completely excised, the development of the segmental 'ganglion and of the peripheral fibres is more or less completely inhibited. The negative controlling force has not as yet been located. It is here suggested that this may reside in the growing nerves themselves and be exercised ...
... if the mesoderm be completely excised, the development of the segmental 'ganglion and of the peripheral fibres is more or less completely inhibited. The negative controlling force has not as yet been located. It is here suggested that this may reside in the growing nerves themselves and be exercised ...
Shoulder/Elbow
... » Ulnar nerve (C8 and T1) – Lateral part: ( the muscle serving digits 2 and 3 ) » Median nerve (C8 and T1 ) ...
... » Ulnar nerve (C8 and T1) – Lateral part: ( the muscle serving digits 2 and 3 ) » Median nerve (C8 and T1 ) ...
The shoulder joint
... • Therefore, glenohumeral joint muscles are superficial to shoulder girdle muscles • Deltoid: forms a superficial cap over the anterior, lateral and posterior sides of the shoulder • Anteriorly, pectoralis major covers most of the superficial chest wall • Biceps brachii and triceps brachii encompass ...
... • Therefore, glenohumeral joint muscles are superficial to shoulder girdle muscles • Deltoid: forms a superficial cap over the anterior, lateral and posterior sides of the shoulder • Anteriorly, pectoralis major covers most of the superficial chest wall • Biceps brachii and triceps brachii encompass ...
11 - HandLab
... A. Insert as part of the central slip insertion B. Originate at the PIP joint and insert with the terminal tendon insertion C. Connect the lateral band to the transverse fibers D. Insert into the proximal base of the proximal phalanx 9. The lateral bands can be defined as: A. The thickened edges of ...
... A. Insert as part of the central slip insertion B. Originate at the PIP joint and insert with the terminal tendon insertion C. Connect the lateral band to the transverse fibers D. Insert into the proximal base of the proximal phalanx 9. The lateral bands can be defined as: A. The thickened edges of ...
A Cadaveric Analysis of the Vastus Medialis Longus and
... The different fiber orientation between the VML and VMO has been noted by several researchers. The VML muscle fibers were more vertically aligned with the angles ranging from 14-34°4. The VMO’s fibers were more horizontally orientated with the range from 28-50° for the VMO superior and 39-69° for VM ...
... The different fiber orientation between the VML and VMO has been noted by several researchers. The VML muscle fibers were more vertically aligned with the angles ranging from 14-34°4. The VMO’s fibers were more horizontally orientated with the range from 28-50° for the VMO superior and 39-69° for VM ...
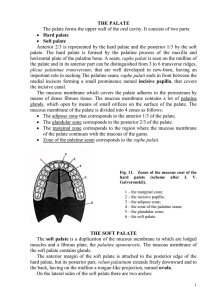
the palate
... Anterior 2/3 is represented by the hard palate and the posterior 1/3 by the soft palate. The hard palate is formed by the palatine process of the maxilla and horizontal plate of the palatine bone. A seam, raphe palati is seen on the midline of the palate and in its anterior part can be distinguished ...
... Anterior 2/3 is represented by the hard palate and the posterior 1/3 by the soft palate. The hard palate is formed by the palatine process of the maxilla and horizontal plate of the palatine bone. A seam, raphe palati is seen on the midline of the palate and in its anterior part can be distinguished ...
The Peripheral Nervous System and Reflex Activity
... The human brain, for all its sophistication, would be useless without its links to the outside world. In one experiment that illustrates this point, blindfolded volunteers suspended in warm water in a sensory deprivation tank (a situation that limits sensory inputs) hallucinated. One saw charging pi ...
... The human brain, for all its sophistication, would be useless without its links to the outside world. In one experiment that illustrates this point, blindfolded volunteers suspended in warm water in a sensory deprivation tank (a situation that limits sensory inputs) hallucinated. One saw charging pi ...
chapt10_lecture
... – sphincters – internal muscular rings that control the movement of food, bile, blood, and other materials ...
... – sphincters – internal muscular rings that control the movement of food, bile, blood, and other materials ...
Nerves
... The supratrochlear and the supraorbital veins unite at the medial margin of the orbit to form the facial vein. The superficial temporal vein unites with the maxillary vein in the substance of the parotid gland to form the retromandibular vein. The posterior auricular vein unites with the posterior d ...
... The supratrochlear and the supraorbital veins unite at the medial margin of the orbit to form the facial vein. The superficial temporal vein unites with the maxillary vein in the substance of the parotid gland to form the retromandibular vein. The posterior auricular vein unites with the posterior d ...
Transversus Abdominus Plane Block
... Muscles of the Abdominal Wall relative to the TAP Block As we will discuss later, the TAP Block is performed in the lateral part of the anterior abdominal wall. In this region of the abdominal wall there are 3 muscle layers (Fig 1). The External Oblique Muscle The external oblique muscle is the larg ...
... Muscles of the Abdominal Wall relative to the TAP Block As we will discuss later, the TAP Block is performed in the lateral part of the anterior abdominal wall. In this region of the abdominal wall there are 3 muscle layers (Fig 1). The External Oblique Muscle The external oblique muscle is the larg ...
Transversus Abdominis Plane (TAP) block - e-safe
... Muscles of the Abdominal Wall relative to the TAP Block As we will discuss later, the TAP Block is performed in the lateral part of the anterior abdominal wall. In this region of the abdominal wall there are 3 muscle layers (Fig 1). The External Oblique Muscle The external oblique muscle is the larg ...
... Muscles of the Abdominal Wall relative to the TAP Block As we will discuss later, the TAP Block is performed in the lateral part of the anterior abdominal wall. In this region of the abdominal wall there are 3 muscle layers (Fig 1). The External Oblique Muscle The external oblique muscle is the larg ...
Transversus Abdominis Plane (TAP)
... Muscles of the Abdominal Wall relative to the TAP Block As we will discuss later, the TAP Block is performed in the lateral part of the anterior abdominal wall. In this region of the abdominal wall there are 3 muscle layers (Fig 1). The External Oblique Muscle The external oblique muscle is the larg ...
... Muscles of the Abdominal Wall relative to the TAP Block As we will discuss later, the TAP Block is performed in the lateral part of the anterior abdominal wall. In this region of the abdominal wall there are 3 muscle layers (Fig 1). The External Oblique Muscle The external oblique muscle is the larg ...
34 Scapulectomy
... biopsy. The majority of sarcomas in this location have an extraosseous (soft-tissue) component; therefore a small-needle or core biopsy should be performed. Fine-needle or core biopsies should be performed under fluoroscopic or CT guidance unless the mass is easily palpable and located away from the ...
... biopsy. The majority of sarcomas in this location have an extraosseous (soft-tissue) component; therefore a small-needle or core biopsy should be performed. Fine-needle or core biopsies should be performed under fluoroscopic or CT guidance unless the mass is easily palpable and located away from the ...
Additional head of biceps brachii in elderly female
... additional head is variable. It might take origin either from the shaft of humerus near the insertion of coracobrachialis Discussion or along with brachialis or from intertubercular groove of Variations in the origin of biceps brachii have been reported humerus or from the capsule of shoulder joint ...
... additional head is variable. It might take origin either from the shaft of humerus near the insertion of coracobrachialis Discussion or along with brachialis or from intertubercular groove of Variations in the origin of biceps brachii have been reported humerus or from the capsule of shoulder joint ...
Small branches
... 3-The spinal root –arises by several filaments from the spinal cord in the first five cervical vertebrae, then directed cranially along the lateral surface of the spinal cord, and enters the cranium through the foramen magna and unites with the medullary root to make the accessory nerve. 4-the acces ...
... 3-The spinal root –arises by several filaments from the spinal cord in the first five cervical vertebrae, then directed cranially along the lateral surface of the spinal cord, and enters the cranium through the foramen magna and unites with the medullary root to make the accessory nerve. 4-the acces ...
Fascial Compartments of Upper Arm
... Contents of anterior fascial compartment of upper arm • Muscles: biceps brachii, coracobrachialis, brachialis. • Blood supply: brachial a. • N. supply to the muscles: musculocutaneous n. • Structures passing through compartment: musculocutaneous n., median n., ulnar n., brachial a., basilic v., rad ...
... Contents of anterior fascial compartment of upper arm • Muscles: biceps brachii, coracobrachialis, brachialis. • Blood supply: brachial a. • N. supply to the muscles: musculocutaneous n. • Structures passing through compartment: musculocutaneous n., median n., ulnar n., brachial a., basilic v., rad ...
Branches in the popliteal fossa
... 1-Superior gluteal vessels and nerves. 2-the piriformis muscle 3-.inferior gluteal vessels and nerves 4-sciatic nerve, 5-the posterior cutanous of the thigh 6-pudendal nerve 7—nerve to quadrates femoris ...
... 1-Superior gluteal vessels and nerves. 2-the piriformis muscle 3-.inferior gluteal vessels and nerves 4-sciatic nerve, 5-the posterior cutanous of the thigh 6-pudendal nerve 7—nerve to quadrates femoris ...
Muscle

Muscle is a soft tissue found in most animals. Muscle cells contain protein filaments of actin and myosin that slide past one another, producing a contraction that changes both the length and the shape of the cell. Muscles function to produce force and motion. They are primarily responsible for maintaining and changing posture, locomotion, as well as movement of internal organs, such as the contraction of the heart and the movement of food through the digestive system via peristalsis.Muscle tissues are derived from the mesodermal layer of embryonic germ cells in a process known as myogenesis. There are three types of muscle, skeletal or striated, cardiac, and smooth. Muscle action can be classified as being either voluntary or involuntary. Cardiac and smooth muscles contract without conscious thought and are termed involuntary, whereas the skeletal muscles contract upon command. Skeletal muscles in turn can be divided into fast and slow twitch fibers.Muscles are predominantly powered by the oxidation of fats and carbohydrates, but anaerobic chemical reactions are also used, particularly by fast twitch fibers. These chemical reactions produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP) molecules that are used to power the movement of the myosin heads.The term muscle is derived from the Latin musculus meaning ""little mouse"" perhaps because of the shape of certain muscles or because contracting muscles look like mice moving under the skin.