Locus Focus Group
... Ways to construct lines Measuring lines and areas Measuring angles; using sectors to measure angles of more than 180˚ Using calculate Ways to construct circles Constructing lines of fixed length ...
... Ways to construct lines Measuring lines and areas Measuring angles; using sectors to measure angles of more than 180˚ Using calculate Ways to construct circles Constructing lines of fixed length ...
Unit 20 - Connecticut Core Standards
... and corresponding angles are congruent; points on a perpendicular bisector of a line segment are exactly those equidistant from the segment’s endpoints. G-C.2. Identify and describe relationships among inscribed angles, radii, and chords. Include the relationship between central, inscribed, and circ ...
... and corresponding angles are congruent; points on a perpendicular bisector of a line segment are exactly those equidistant from the segment’s endpoints. G-C.2. Identify and describe relationships among inscribed angles, radii, and chords. Include the relationship between central, inscribed, and circ ...
Determining locus
... In a right triangle find the inscribed rectangle, whose perimeter is a given length. (One vertex of the rectangle is at the right angle of the triangle.) ...
... In a right triangle find the inscribed rectangle, whose perimeter is a given length. (One vertex of the rectangle is at the right angle of the triangle.) ...
- wced curriculum development
... Dividing a line into equal parts Given the line to be divided Draw a light construction line at any convenient angle from one end of the given line. With dividers or scale, set off from the intersections of the lines as many equal divisions as needed (in this example, three). Connect the last divisi ...
... Dividing a line into equal parts Given the line to be divided Draw a light construction line at any convenient angle from one end of the given line. With dividers or scale, set off from the intersections of the lines as many equal divisions as needed (in this example, three). Connect the last divisi ...
Notes
... 8-2 Arcs and Chords – The arc of a chord is a minor arc that shares the _________________ of a chord. Use the three GeoGebra applets in section 8-2 to complete these conjectures: Circle Conjecture #1: If two chords in a circle are congruent, then their arcs are _______________. Circle Conjecture #2: ...
... 8-2 Arcs and Chords – The arc of a chord is a minor arc that shares the _________________ of a chord. Use the three GeoGebra applets in section 8-2 to complete these conjectures: Circle Conjecture #1: If two chords in a circle are congruent, then their arcs are _______________. Circle Conjecture #2: ...
Textbook Sections in order with CMS pacing guide
... Write variable coordinates to figures in the coordinate plane Compute area of triangles and quadrilaterals ...
... Write variable coordinates to figures in the coordinate plane Compute area of triangles and quadrilaterals ...
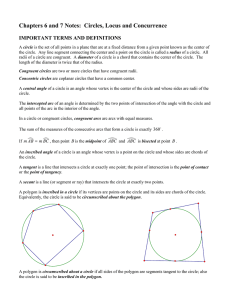
Circles - Basic Terms
... Use the diagram at the right. 17. What are tile center and radius of 18. What are the center and radius of ®B? 19, Describe tile intersection of the two circles. 20. Describe all the common tangents of the two circles, 21. Are the two circles congruent? Explain, Tell whether ~ is tangent to ®C, Expl ...
... Use the diagram at the right. 17. What are tile center and radius of 18. What are the center and radius of ®B? 19, Describe tile intersection of the two circles. 20. Describe all the common tangents of the two circles, 21. Are the two circles congruent? Explain, Tell whether ~ is tangent to ®C, Expl ...
Unit 4 Circles Geometry ACC - Long Beach Unified School District
... • Students will identify and describe relationships among inscribed angles, radii and chords. • Students will identify and explain why inscribed angles on a diameter are right angles. • Students will identify and explain why the radius of a circle is perpendicular to the tangent where the radius int ...
... • Students will identify and describe relationships among inscribed angles, radii and chords. • Students will identify and explain why inscribed angles on a diameter are right angles. • Students will identify and explain why the radius of a circle is perpendicular to the tangent where the radius int ...
3-D Figures
... Three Point Perspective – all parallel lines meet at a vanishing point. To draw in two point perspective: 1. Draw horizontal and 2 vanishing points on the horizontal. Pick a third vanishing point below the horizon. 2. Draw the point that will be the top corner of your figure. 3. Connect this point w ...
... Three Point Perspective – all parallel lines meet at a vanishing point. To draw in two point perspective: 1. Draw horizontal and 2 vanishing points on the horizontal. Pick a third vanishing point below the horizon. 2. Draw the point that will be the top corner of your figure. 3. Connect this point w ...
Construction 12: Construct a circle circumscribed about a triangle. 1
... Three Point Perspective – all parallel lines meet at a vanishing point. To draw in two point perspective: 1. Draw horizontal and 2 vanishing points on the horizontal. Pick a third vanishing point below the horizon. 2. Draw the point that will be the top corner of your figure. 3. Connect this point w ...
... Three Point Perspective – all parallel lines meet at a vanishing point. To draw in two point perspective: 1. Draw horizontal and 2 vanishing points on the horizontal. Pick a third vanishing point below the horizon. 2. Draw the point that will be the top corner of your figure. 3. Connect this point w ...
High School Geometry
... Identify and describe relationships among inscribed angles, radii, and chords. (MA10‐GR.HS‐S.4‐GLE.2‐EO.e.i) (CCSS: G‐C.2) PARCC Calculator Include the relationship between central, inscribed, and circumscribed angles; inscribed angles on a diameter are right angles; the radius of a circle is p ...
... Identify and describe relationships among inscribed angles, radii, and chords. (MA10‐GR.HS‐S.4‐GLE.2‐EO.e.i) (CCSS: G‐C.2) PARCC Calculator Include the relationship between central, inscribed, and circumscribed angles; inscribed angles on a diameter are right angles; the radius of a circle is p ...
ch9 pkt - Niskayuna Central Schools
... Thm: A line tangent to a circle the line is perpendicular to the radius @ the pt of intersection Converse: A line which is perpendicular to the radius @ a point on the circle the line is tangent to the circle * the circle & line must be Coplanar! ...
... Thm: A line tangent to a circle the line is perpendicular to the radius @ the pt of intersection Converse: A line which is perpendicular to the radius @ a point on the circle the line is tangent to the circle * the circle & line must be Coplanar! ...
Tangent lines to circles
In Euclidean plane geometry, a tangent line to a circle is a line that touches the circle at exactly one point, never entering the circle's interior. Roughly speaking, it is a line through a pair of infinitely close points on the circle. Tangent lines to circles form the subject of several theorems, and play an important role in many geometrical constructions and proofs. Since the tangent line to a circle at a point P is perpendicular to the radius to that point, theorems involving tangent lines often involve radial lines and orthogonal circles.