Intervention in the Foreign Exchange Market
... by fundamental factors, such as Canada’s economic growth and inflation, level of interest rates, fiscal position, productivity performance, etc. These factors are assessed by the market relative to other countries, particularly the United States, our major trade partner. Because Canada is a key prod ...
... by fundamental factors, such as Canada’s economic growth and inflation, level of interest rates, fiscal position, productivity performance, etc. These factors are assessed by the market relative to other countries, particularly the United States, our major trade partner. Because Canada is a key prod ...
Lecture 3: Int`l Finance
... Exchange rate regimes • Nations can choose to let market forces determine exchange rates, as above. This is a floating regime (e.g. U.S.) • Or a nation can choose to adopt a fixed regime. Here, the govt sets the price of its currency and maintains that price via ...
... Exchange rate regimes • Nations can choose to let market forces determine exchange rates, as above. This is a floating regime (e.g. U.S.) • Or a nation can choose to adopt a fixed regime. Here, the govt sets the price of its currency and maintains that price via ...
File - Paul Scanlon
... a. What implications does this change have for i) the demand for and ii) the supply of domestic currency in the foreign exchange market? b. According to the model of the foreign exchange market, what are the implications for the nominal exchange rate? c. According to the theory of purchasing power p ...
... a. What implications does this change have for i) the demand for and ii) the supply of domestic currency in the foreign exchange market? b. According to the model of the foreign exchange market, what are the implications for the nominal exchange rate? c. According to the theory of purchasing power p ...
Dr. Mitchell - people.vcu.edu
... other ways, such as by selling forward contracts on the local currency or taking out loans denominated in the local currency (do you see why?) Government Response: Floating Rates or Exchange controls These days, worldwide market forces are much larger than the resources of a typical country. The gov ...
... other ways, such as by selling forward contracts on the local currency or taking out loans denominated in the local currency (do you see why?) Government Response: Floating Rates or Exchange controls These days, worldwide market forces are much larger than the resources of a typical country. The gov ...
suggested answers and solutions to
... coordinate exchange rate policies against the non-EMS currencies, and (iii) pave the way for the eventual European Monetary Union. The main instruments of EMS are the European Currency Unit (ECU) and the Exchange Rate Mechanism (ERM). Like SDR, the ECU is a basket currency constructed as a weighted ...
... coordinate exchange rate policies against the non-EMS currencies, and (iii) pave the way for the eventual European Monetary Union. The main instruments of EMS are the European Currency Unit (ECU) and the Exchange Rate Mechanism (ERM). Like SDR, the ECU is a basket currency constructed as a weighted ...
From Bretton Woods to the Euro
... Will there be further world currency groups? What has happened to the SP after the recent crisis? ...
... Will there be further world currency groups? What has happened to the SP after the recent crisis? ...
Appreciation
... •The Case for Fixed Exchange Rates • Facilitates trade by creating certainty about the exchange rate ...
... •The Case for Fixed Exchange Rates • Facilitates trade by creating certainty about the exchange rate ...
ECONOMIC DEVELOPMENT & INTERNATIONAL POLITICS
... Brazilian exports getting crushed by currency appreciation ...
... Brazilian exports getting crushed by currency appreciation ...
Chapter 6 - FacStaff Home Page for CBU
... a. the replacement of a foreign currency withU.S. dollars. b. This process is a step beyond a currency board because it forces the local currency to be replaced by the U.S. dollar. c. Although dollarization and a currency board both attempt to peg the local currency’s value, the currency board does ...
... a. the replacement of a foreign currency withU.S. dollars. b. This process is a step beyond a currency board because it forces the local currency to be replaced by the U.S. dollar. c. Although dollarization and a currency board both attempt to peg the local currency’s value, the currency board does ...
Tension and new alliances - the currency wars
... countries back at the high pre-crisis pushed by global monetary and financial conditions that remain very accommodating. Monetary authorities are refrained from increasing interest rates further by the fear of spurring larger inflows. As a consequence capital controls and other prudential measures a ...
... countries back at the high pre-crisis pushed by global monetary and financial conditions that remain very accommodating. Monetary authorities are refrained from increasing interest rates further by the fear of spurring larger inflows. As a consequence capital controls and other prudential measures a ...
Exchange Market as a Part of International Financial Markets
... Non-bank foreign exchange companies offer currency exchange and international payments to private individuals and companies. These are also known as foreign exchange brokers but are distinct in that they do not offer speculative trading but currency exchange with payments. ...
... Non-bank foreign exchange companies offer currency exchange and international payments to private individuals and companies. These are also known as foreign exchange brokers but are distinct in that they do not offer speculative trading but currency exchange with payments. ...
SDF - delhicargo.com
... The foreign exchange representing the full export value of the goods on or before @_____________________________________________________________________ in the manner specified in the Regulation made under the Foreign Exchange Management Act.1999. I/We further declare that I/WE am/are resident in In ...
... The foreign exchange representing the full export value of the goods on or before @_____________________________________________________________________ in the manner specified in the Regulation made under the Foreign Exchange Management Act.1999. I/We further declare that I/WE am/are resident in In ...
ch01 - Class Index
... indexes, on metals, interest rates, or on futures contracts Futures contracts trade on products such as ...
... indexes, on metals, interest rates, or on futures contracts Futures contracts trade on products such as ...
Fixed Rate System: Preview of Results
... The Law of One Price … in long run A good should cost the same in all countries (aside from tariffs or transportation costs) Exchange rates should make prices equal across countries … law of one price ...
... The Law of One Price … in long run A good should cost the same in all countries (aside from tariffs or transportation costs) Exchange rates should make prices equal across countries … law of one price ...
PowerPoint
... An international currency unit already exists, The World Bank Special Drawing Right (SDR) ...
... An international currency unit already exists, The World Bank Special Drawing Right (SDR) ...
EXCHANGE RATES
... 6 and could be exchanged for 1/35th of an 7 of gold. Under this system, overvalued currencies could only be adjusted with the agreement of the 8 9 10. Such adjustments were called 11 or 12. The BrettonWoods system of gold 13 and 14 against the dollar was abandoned in 1971, because following inflatio ...
... 6 and could be exchanged for 1/35th of an 7 of gold. Under this system, overvalued currencies could only be adjusted with the agreement of the 8 9 10. Such adjustments were called 11 or 12. The BrettonWoods system of gold 13 and 14 against the dollar was abandoned in 1971, because following inflatio ...
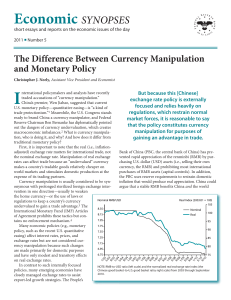
The Difference Between Currency Manipulation and Monetary Policy
... First, it is important to note that the real (i.e., inflationBank of China (PBC, the central bank of China) has preadjusted) exchange rate matters for international trade, not vented rapid appreciation of the renminbi (RMB) by purthe nominal exchange rate. Manipulation of real exchange chasing U.S. ...
... First, it is important to note that the real (i.e., inflationBank of China (PBC, the central bank of China) has preadjusted) exchange rate matters for international trade, not vented rapid appreciation of the renminbi (RMB) by purthe nominal exchange rate. Manipulation of real exchange chasing U.S. ...
FSDX: The Benefits of Foreign Exhcange Transactions That Settle
... Today, some banks estimate that only a small portion of their foreign exchange transactions are related to actual foreign trade volume. Investment or position taking and hedging and/or speculative activity, where settlement of principal is not necessary, has become the primary business in the foreig ...
... Today, some banks estimate that only a small portion of their foreign exchange transactions are related to actual foreign trade volume. Investment or position taking and hedging and/or speculative activity, where settlement of principal is not necessary, has become the primary business in the foreig ...
may 2013 treasury management 2 solutions
... On 3rd June 2012, Jombo Bank entered into a Forex Swap Agreement of EUR for USD with Bwengu Bank to mature on 04 July 2012. Given that the EUR interest rate is 4.5 % and USD interest rate is 2.5 % and that the current Spot rate is 1.3585, calculate the Forex Swap points. ...
... On 3rd June 2012, Jombo Bank entered into a Forex Swap Agreement of EUR for USD with Bwengu Bank to mature on 04 July 2012. Given that the EUR interest rate is 4.5 % and USD interest rate is 2.5 % and that the current Spot rate is 1.3585, calculate the Forex Swap points. ...
Determine RMB Real Equilibrium Exchange Rate
... productivity. Unfortunately, this assumption may not be true in reality, and existing theories likely fail to account for trade imbalance especially between developed and developing countries. This paper does not take that assumption for granted, but will instead consider a more realistic situation: ...
... productivity. Unfortunately, this assumption may not be true in reality, and existing theories likely fail to account for trade imbalance especially between developed and developing countries. This paper does not take that assumption for granted, but will instead consider a more realistic situation: ...