* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit-2 Macro Review
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
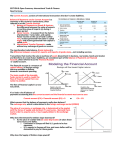
Unit-5 Macro Review Foreign Exchange & Balance of Payments Determinants of Exchange Rates 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Changes in Consumer Tastes Relative Income Changes Relative Inflation Relative Real Interest Rates Speculation & Investment U.S. Income Rises Demand Imports Market Housefor of Money Foreign Exchange Demand Foreign Currency Dollar Depreciates Foreign Appreciates Graphing Exchange Rates House of Money = Market for Foreign Exchange Dollars Euros Euro Price of a dollar S1 Dollar Price of a Euro -------------- D1 Q1 D2 Qty of Dollars S2 -------------- -------------- 1.3 $ .75 Euro -------------- S1 Q1 D1 Qty of Euros U.S. Price Level Falls => U.S. goods look “cheap” => Europeans ↑U.S. exports => Demand for dollars ↑ => Dollar appreciates Balance of Payments • Current Account If one account is positive the other must Be negative. They generally sum to ZERO! (NX) – U.S. Trade Balance – Exports - Imports & Investment Income (bond interest, stock dividends) • Financial Account (formerly called capital account) – Foreign purchase of US assets – U.S. purchase of foreign assets – Assets = Stocks, bonds, factories, land, etc… – Example: Capital Surplus = Capital flows into US China & Balance of Payments • The USA imports more goods from China than we export to them… • Balance of Payments: China buys U.S. Bonds Capital Account Surplus Imports > Exports Current Account Deficit Balance of Payments • Current Account If one is positive the other is negative. They generally sum to ZERO! (NX) – U.S. Trade Balance – Exports - Imports & Investment Income (bond interest, stock dividends) • Financial Account (formerly called capital account) – Foreign purchase of US assets – U.S. purchase of foreign assets If both accounts do Not sum to zero, reserves are used to Offset minor difference – Assets = Stocks, bonds, factories, land, etc… – Example: Capital Surplus = Capital flows into US • Official Reserves – Fed holds quantities of foreign currency called reserves – Used to offset discrepancy in current account vs. capital account