Managing biodiversity correctly – Efficient portfolio - Bio
... holistic approach, as expressed returns cannot be predicted in the concept of sustainable with certainty, financial service development. Long-term consideproviders combine risks which rations and future expectations are independent of each other represent the basis on which in portfolios. The result ...
... holistic approach, as expressed returns cannot be predicted in the concept of sustainable with certainty, financial service development. Long-term consideproviders combine risks which rations and future expectations are independent of each other represent the basis on which in portfolios. The result ...
Credit Loss Distribution and Copula in Risk Management
... closed analytic form. This results has been extensively used in deriving approximations for more complex portfolios and instruments like derivatives such as collateralized debt obligations (CDO), as well as in regulatory capital estimates and portfolio risk management. Importantly, Vasicek’s result ...
... closed analytic form. This results has been extensively used in deriving approximations for more complex portfolios and instruments like derivatives such as collateralized debt obligations (CDO), as well as in regulatory capital estimates and portfolio risk management. Importantly, Vasicek’s result ...
Over/Under-Reaction of Stock Markets
... If these pension fund assets are primarily invested by portfolio managers who follow relative strength rules, then the winners portfolio may benefit from additional price pressure in this month. Similarly, the larger than average returns in November and December may in part be due to price press ...
... If these pension fund assets are primarily invested by portfolio managers who follow relative strength rules, then the winners portfolio may benefit from additional price pressure in this month. Similarly, the larger than average returns in November and December may in part be due to price press ...
The n-period Binomial Model
... This section shows an important difference between the arithmetic and the geometric mean rate of return. It is shown that the geometric mean is always less than the arithmetic mean and that the difference between the two is approximately half the variance of the return. This is an important distinct ...
... This section shows an important difference between the arithmetic and the geometric mean rate of return. It is shown that the geometric mean is always less than the arithmetic mean and that the difference between the two is approximately half the variance of the return. This is an important distinct ...
Chapter 3 Asset Pricing Theories, Models, and Tests
... The SDF approach to asset pricing indicates that the price of a security is obtained by "discounting" its future payoff by a valid SDF so that the expected present value of the payoff is equal to the current price. In practice, finding a valid SDF, i.e., an SDF that prices each asset correctly, is i ...
... The SDF approach to asset pricing indicates that the price of a security is obtained by "discounting" its future payoff by a valid SDF so that the expected present value of the payoff is equal to the current price. In practice, finding a valid SDF, i.e., an SDF that prices each asset correctly, is i ...
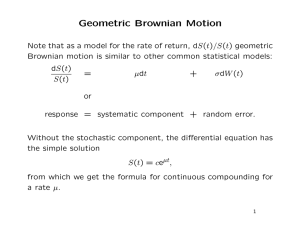
Geometric Brownian Motion
... Likewise, for an American option, we could maximize the expected value over all stopping times, 0 < τ < T : P (0, s) = sup e−rτ E(h(S(τ ))). τ ≤T ...
... Likewise, for an American option, we could maximize the expected value over all stopping times, 0 < τ < T : P (0, s) = sup e−rτ E(h(S(τ ))). τ ≤T ...
Fundamentalist/Chartist
... initial wealth is 40. In addition, short selling is permitted in the model. The total number of investors is 40, including 20 fundamentalists and 20 chartists. One step in this model can be seen as one week in reality. Every experiment runs 1000 periods, corresponding 20 years in reality. The risk- ...
... initial wealth is 40. In addition, short selling is permitted in the model. The total number of investors is 40, including 20 fundamentalists and 20 chartists. One step in this model can be seen as one week in reality. Every experiment runs 1000 periods, corresponding 20 years in reality. The risk- ...
have Higher Stock Returns? - IC
... Muchinsky, 1985; Harrison, Newman, & Roth, 2006). We will understand the impact of job satisfaction in organisational performance, specifically, in firm value. This variable will be measured by future stock returns. Generally, the variable job satisfaction is measured by surveys (Ostroff, 1992; Tala ...
... Muchinsky, 1985; Harrison, Newman, & Roth, 2006). We will understand the impact of job satisfaction in organisational performance, specifically, in firm value. This variable will be measured by future stock returns. Generally, the variable job satisfaction is measured by surveys (Ostroff, 1992; Tala ...
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES FINANCIAL INNOVATION, MARKET PARTICIPATION AND ASSET PRICES Laurent Calvet
... interest rate. Second, there also exist J risky assets (j = 1, ...J) with price π j and random payoff ãj . We assume for simplicity that all assets are in zero net supply.11 Investors can freely operate in the bond market but have to pay a fixed entry cost κ in order to invest in one or more risky a ...
... interest rate. Second, there also exist J risky assets (j = 1, ...J) with price π j and random payoff ãj . We assume for simplicity that all assets are in zero net supply.11 Investors can freely operate in the bond market but have to pay a fixed entry cost κ in order to invest in one or more risky a ...
What type of p ensions would most people prefer? ( Life insurance and pension contracts II: the life cycle model with recursive utility)
... • This investment policy implies the required consumption smoothening that the agent wants, provided γ > ρ. With preference for early resolution of uncertainty, this agent is a ’bit ahead’ in consumption/investment decisions. • His preferences is related to more than one period at the time. • The op ...
... • This investment policy implies the required consumption smoothening that the agent wants, provided γ > ρ. With preference for early resolution of uncertainty, this agent is a ’bit ahead’ in consumption/investment decisions. • His preferences is related to more than one period at the time. • The op ...
Fat Tails and their (Un)happy Endings
... value of equity is determined by a portfolio of options in several projects, or that each tranche comprises long and short options on the value of the portfolio.3 The natural advantage vis-à-vis the contingent claim approach is that the copula approach naturally accommodates several types of claims ...
... value of equity is determined by a portfolio of options in several projects, or that each tranche comprises long and short options on the value of the portfolio.3 The natural advantage vis-à-vis the contingent claim approach is that the copula approach naturally accommodates several types of claims ...
Finding Your Way Through the Bond Market
... member of our fixed-income team—with a goal of generating maximum alpha, or return, from each pod. Individual pod decisions are then incorporated into the portfolio-building process. The objective is to extract alpha from each stage of the decision-making process, using a diversified source of alpha ...
... member of our fixed-income team—with a goal of generating maximum alpha, or return, from each pod. Individual pod decisions are then incorporated into the portfolio-building process. The objective is to extract alpha from each stage of the decision-making process, using a diversified source of alpha ...
Multi-Period Trading via Convex Optimization
... We consider a basic model of multi-period trading, which can be used to evaluate the performance of a trading strategy. We describe a framework for single-period optimization, where the trades in each period are found by solving a convex optimization problem that trades off expected return, risk, tr ...
... We consider a basic model of multi-period trading, which can be used to evaluate the performance of a trading strategy. We describe a framework for single-period optimization, where the trades in each period are found by solving a convex optimization problem that trades off expected return, risk, tr ...
StrongPCMP4e-ch02
... Dispersion Investors are interested in the best and the worst in addition to the average A common measure of dispersion is the ...
... Dispersion Investors are interested in the best and the worst in addition to the average A common measure of dispersion is the ...
Actuary_v2
... in America =>The need for a more ‘zen’ view: Asset Liability Management. ALM looks at the evolution of Asset and Liability at the same time for long periods. It integrates all the long term models in a Big picture. More specifically, ALM managers now pay attention not only to interest rates and liqu ...
... in America =>The need for a more ‘zen’ view: Asset Liability Management. ALM looks at the evolution of Asset and Liability at the same time for long periods. It integrates all the long term models in a Big picture. More specifically, ALM managers now pay attention not only to interest rates and liqu ...
Document
... * Target asset allocation weights adjusted following annual review of Counsel portfolios and with the renewal of the Simplified Prospectus. This Portfolio is managed using a multi-manager process. The current sub-advisor or underlying mutual fund manager for each mandate is listed beside the mandate ...
... * Target asset allocation weights adjusted following annual review of Counsel portfolios and with the renewal of the Simplified Prospectus. This Portfolio is managed using a multi-manager process. The current sub-advisor or underlying mutual fund manager for each mandate is listed beside the mandate ...