Lecture 29
... Released in cells when there is low O2 concentration Binds to purinogenic receptors A1, A2A, A2B, A3 Slows the heart down, at the same time increases capillary dilation Caffeine is a adenine derivative, and antagonizes the effects of adenine. ...
... Released in cells when there is low O2 concentration Binds to purinogenic receptors A1, A2A, A2B, A3 Slows the heart down, at the same time increases capillary dilation Caffeine is a adenine derivative, and antagonizes the effects of adenine. ...
An evolutionarily conserved mechanism for cAMP elicited axonal
... Wnd/JNK signaling indicates that activated PKA stimulates Wnd signaling. A pan-neuronal driver (BG380-Gal4) is used to express UAS-dnc-RNAi, UASPKACA or UAS-PKACA together with UAS-wnd-RNAi or a control-RNAi. Example images are shown of cell bodies in the dorsal midline of the ventral nerve cord; (a ...
... Wnd/JNK signaling indicates that activated PKA stimulates Wnd signaling. A pan-neuronal driver (BG380-Gal4) is used to express UAS-dnc-RNAi, UASPKACA or UAS-PKACA together with UAS-wnd-RNAi or a control-RNAi. Example images are shown of cell bodies in the dorsal midline of the ventral nerve cord; (a ...
Benchmarking two commonly used Saccharomyces
... more than 50% of the analyzes with CEN.PK series being the most popular (approx. 37%-CEN.PK vs. 24%-S288c and its derivatives) (Kim et al., 2012; Hong and Nielsen, 2012). The importance of the two strains as cell factories is further substantiated by an extensive multi-laboratory efforts which were ...
... more than 50% of the analyzes with CEN.PK series being the most popular (approx. 37%-CEN.PK vs. 24%-S288c and its derivatives) (Kim et al., 2012; Hong and Nielsen, 2012). The importance of the two strains as cell factories is further substantiated by an extensive multi-laboratory efforts which were ...
Design and analysis of metabolic pathways supporting
... that the reductive glycine pathway (without the terminal serine deaminase) is a common metabolic route for glycine and serine synthesis in various prokaryotes, including autotrophic ones [94]. The pathway was further suggested to operate in the last universal common ancestor (LUCA) [94]. However, th ...
... that the reductive glycine pathway (without the terminal serine deaminase) is a common metabolic route for glycine and serine synthesis in various prokaryotes, including autotrophic ones [94]. The pathway was further suggested to operate in the last universal common ancestor (LUCA) [94]. However, th ...
Substrate specificity and inhibitors of LRRK2, a protein kinase
... To investigate further and improve the optimal phosphorylation motif for LRRK2, we utilized a positional scanning peptide library approach [17,18]. This assay utilizes 198 biotinylated peptide libraries. Each library contains a 1:1 mixture of serine and threonine at the central position and one addi ...
... To investigate further and improve the optimal phosphorylation motif for LRRK2, we utilized a positional scanning peptide library approach [17,18]. This assay utilizes 198 biotinylated peptide libraries. Each library contains a 1:1 mixture of serine and threonine at the central position and one addi ...
Comparative genomics provides evidence for the 3
... Roseiflexus sp. RS-1 has two copies of the accA and accD as determined by HMMs (Table S1), and they are 73 and 62% identical to each other at the amino acid level respectively. The accA and accD most closely related to the sequences in C. aurantiacus are reported in Table 2. The colocalization of an ...
... Roseiflexus sp. RS-1 has two copies of the accA and accD as determined by HMMs (Table S1), and they are 73 and 62% identical to each other at the amino acid level respectively. The accA and accD most closely related to the sequences in C. aurantiacus are reported in Table 2. The colocalization of an ...
Can sugars be produced from fatty acids? A test case for pathway
... The publisher regrets that Figure 3 was incorrect and the correct Figure 3 is included in the full article below. ...
... The publisher regrets that Figure 3 was incorrect and the correct Figure 3 is included in the full article below. ...
Document
... c) dehydration w NAD --> NADH d) thiol clevage w CoASH - releases a 2c piece = AcoA Net result: each turn of the cycle shortens a long chain fatty acid by 2 carbons generating 1 AcoA, 1 NADH and 1 FADH2 Cellular Energetics ...
... c) dehydration w NAD --> NADH d) thiol clevage w CoASH - releases a 2c piece = AcoA Net result: each turn of the cycle shortens a long chain fatty acid by 2 carbons generating 1 AcoA, 1 NADH and 1 FADH2 Cellular Energetics ...
Can sugars be produced from fatty acids? A test
... In the 1950s, experiments using a new method involving isotopically labelled compounds started to reveal the mechanism by which carbons of fatty acids are incorporated in carbohydrates. Experiments showed that labelled carbons arrived at glucose when the system was supplied with 14 C-labelled fatty ...
... In the 1950s, experiments using a new method involving isotopically labelled compounds started to reveal the mechanism by which carbons of fatty acids are incorporated in carbohydrates. Experiments showed that labelled carbons arrived at glucose when the system was supplied with 14 C-labelled fatty ...
S08 Glycolysis
... 1. Regulation by energy level: - ATP allosterically inhibits the PFK-1 signals indicating an abundance of high energy compounds, citrate inhibits the PFK-1. - High conc. of AMP allosterically activate the PFK1. 2. Regulation by fructose 2,6-bisphosphate: - it is a potent activator for PFK-1 and it ...
... 1. Regulation by energy level: - ATP allosterically inhibits the PFK-1 signals indicating an abundance of high energy compounds, citrate inhibits the PFK-1. - High conc. of AMP allosterically activate the PFK1. 2. Regulation by fructose 2,6-bisphosphate: - it is a potent activator for PFK-1 and it ...
03Glycolysis
... 1. Regulation by energy level: - ATP allosterically inhibits the PFK-1 signals indicating an abundance of high energy compounds, citrate inhibits the PFK-1. - High conc. of AMP allosterically activate the PFK1. 2. Regulation by fructose 2,6-bisphosphate: - it is a potent activator for PFK-1 and it ...
... 1. Regulation by energy level: - ATP allosterically inhibits the PFK-1 signals indicating an abundance of high energy compounds, citrate inhibits the PFK-1. - High conc. of AMP allosterically activate the PFK1. 2. Regulation by fructose 2,6-bisphosphate: - it is a potent activator for PFK-1 and it ...
Glycolysis
... 1. Regulation by energy level: - ATP allosterically inhibits the PFK-1 signals indicating an abundance of high energy compounds, citrate inhibits the PFK-1. - High conc. of AMP allosterically activate the PFK1. 2. Regulation by fructose 2,6-bisphosphate: - it is a potent activator for PFK-1 and it ...
... 1. Regulation by energy level: - ATP allosterically inhibits the PFK-1 signals indicating an abundance of high energy compounds, citrate inhibits the PFK-1. - High conc. of AMP allosterically activate the PFK1. 2. Regulation by fructose 2,6-bisphosphate: - it is a potent activator for PFK-1 and it ...
The semi-phosphorylative Entner–Doudoroff pathway in
... 103 M−1 · cm−1 ) [29,30]. Galactonate (10 mM) was prepared from galactonate γ -lactone by incubation in 1 M NaOH for 1 h (4 M stock solution) and subsequent dilution in 50 mM Hepes/KOH (pH 7.0, 70 ◦C) as described in [31]. The activity of the T. tenax and S. solfataricus KDG kinases was determined a ...
... 103 M−1 · cm−1 ) [29,30]. Galactonate (10 mM) was prepared from galactonate γ -lactone by incubation in 1 M NaOH for 1 h (4 M stock solution) and subsequent dilution in 50 mM Hepes/KOH (pH 7.0, 70 ◦C) as described in [31]. The activity of the T. tenax and S. solfataricus KDG kinases was determined a ...
Short-term regulation of the mammalian pyruvate dehydrogenase
... components seems to be an essential addition to the allosteric regulation of PDH kinase by acetyl-CoA and NADH, as discussed above. Both mechanisms concern the same, universal and clear principle of regulation — “negative feedback inhibition”. ...
... components seems to be an essential addition to the allosteric regulation of PDH kinase by acetyl-CoA and NADH, as discussed above. Both mechanisms concern the same, universal and clear principle of regulation — “negative feedback inhibition”. ...
Gluconeogenesis
... and (b) presence of 25 mM AMP. In (a) and (b), enzyme activity is plotted against substrate (fructose-1,6-bisphosphate) concentration. Concentrations of fructose-2,6-bisphosphate (in mM) are indicated above each curve. (c) The effect of AMP (0, 10, and 25 mM) on the inhibition of fructose-1,6-bispho ...
... and (b) presence of 25 mM AMP. In (a) and (b), enzyme activity is plotted against substrate (fructose-1,6-bisphosphate) concentration. Concentrations of fructose-2,6-bisphosphate (in mM) are indicated above each curve. (c) The effect of AMP (0, 10, and 25 mM) on the inhibition of fructose-1,6-bispho ...
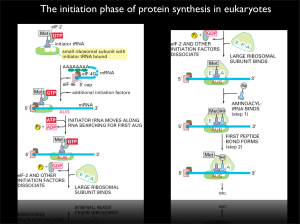
The initiation phase of protein synthesis in eukaryotes
... Gcn1p function without affecting ribosome binding or Gcn20p binding by Gcn1p, thus showing that the Gcn1p-Gcn2p interaction is crucial. The extreme N-terminal (amino acids 1–672) and C-terminal (amino acids ...
... Gcn1p function without affecting ribosome binding or Gcn20p binding by Gcn1p, thus showing that the Gcn1p-Gcn2p interaction is crucial. The extreme N-terminal (amino acids 1–672) and C-terminal (amino acids ...
Glycolysi
... Conservation of metabolic energy in phosphate esters Binding energy of phosphate group ...
... Conservation of metabolic energy in phosphate esters Binding energy of phosphate group ...
falciparum - Griffith Research Online
... PfM17LAP, critical to generating a free amino acid pool used by the intraerythrocytic stage of the parasite for proteins synthesis, growth and development. These exopeptidases are potential targets for the development of a new class of antimalaria drugs. Methodology/Principal Findings: To define the ...
... PfM17LAP, critical to generating a free amino acid pool used by the intraerythrocytic stage of the parasite for proteins synthesis, growth and development. These exopeptidases are potential targets for the development of a new class of antimalaria drugs. Methodology/Principal Findings: To define the ...
12-Glycolysis2016-11-15 13:225.6 MB
... Pyruvate Kinase Regulation by: Covalent Modification Pyruvate kinase is the enzyme that catalyzes the final step of glycolysis. It catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group from phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) to adenosine diphosphate (ADP), yielding one molecule of pyruvate and one molecule of ...
... Pyruvate Kinase Regulation by: Covalent Modification Pyruvate kinase is the enzyme that catalyzes the final step of glycolysis. It catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group from phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) to adenosine diphosphate (ADP), yielding one molecule of pyruvate and one molecule of ...
Red cell pyruvate kinase deficiency: molecular and clinical aspects
... the second part of glycolysis. Moreover, the substrate PEP and the product pyruvate are involved in a number of energetic and biosynthetic pathways and the tight regulation of PK activity has been shown to be of great importance not only for glycolysis itself, but also for the entire cellular metabo ...
... the second part of glycolysis. Moreover, the substrate PEP and the product pyruvate are involved in a number of energetic and biosynthetic pathways and the tight regulation of PK activity has been shown to be of great importance not only for glycolysis itself, but also for the entire cellular metabo ...
Biological Networks Underlying Abiotic Stress Tolerance in
... Stress Signaling and Gene Expression An ambient cue is recognized by a plant cell as a signal when it leads to significant changes in physical properties (changes in the fluidity of phospholipid molecules in plasma membrane bilayer under low or high temperatures) or chemical composition of the ambie ...
... Stress Signaling and Gene Expression An ambient cue is recognized by a plant cell as a signal when it leads to significant changes in physical properties (changes in the fluidity of phospholipid molecules in plasma membrane bilayer under low or high temperatures) or chemical composition of the ambie ...
Marine alga Sargassum horneri active component
... the S-nitrosylation of JNK1 and IKKβ. JNK1 phosphorylates Bcl2, which binds and inhibits Beclin 1. Phosphorylated Bcl-2 releases Beclin 1, which then initiates autophagosome formation. In addition, IKKβ phosphorylates AMPK, which then phosphorylates tuberous sclerosis 2 (TSC2). Phosphorylated TSC2 i ...
... the S-nitrosylation of JNK1 and IKKβ. JNK1 phosphorylates Bcl2, which binds and inhibits Beclin 1. Phosphorylated Bcl-2 releases Beclin 1, which then initiates autophagosome formation. In addition, IKKβ phosphorylates AMPK, which then phosphorylates tuberous sclerosis 2 (TSC2). Phosphorylated TSC2 i ...
Separate Domains of the Insulin Receptor Contain
... [32P]phosphoproteinswere separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, detected by autoradiography, and analyzed by tryptic peptide mapping by use of reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. Mild trypsin digestion reduced the apparent molecular mass of the &sub ...
... [32P]phosphoproteinswere separated by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, detected by autoradiography, and analyzed by tryptic peptide mapping by use of reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography. Mild trypsin digestion reduced the apparent molecular mass of the &sub ...