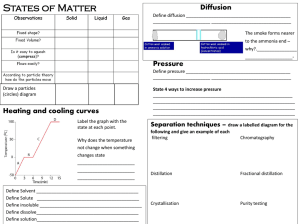
The Elements of Group 15 (5A, V, VA) The Nitrogen Group
... Phosphine (PH3) is a highly toxic, volatile gas. Its melting and boiling points are lower than for NH3 due to lack of H-bonding. ...
... Phosphine (PH3) is a highly toxic, volatile gas. Its melting and boiling points are lower than for NH3 due to lack of H-bonding. ...
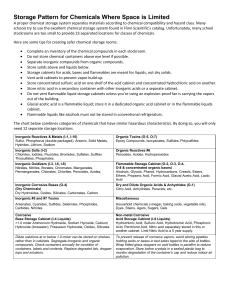
Storage Pattern for Chemicals Where Space is Limited
... Storage cabinets for acids, bases and flammables are meant for liquids, not dry solids. Vent acid cabinets to prevent vapor build-up. Store concentrated sulfuric acid on one shelf of the acid cabinet and concentrated hydrochloric acid on another. Store nitric acid in a secondary container with other ...
... Storage cabinets for acids, bases and flammables are meant for liquids, not dry solids. Vent acid cabinets to prevent vapor build-up. Store concentrated sulfuric acid on one shelf of the acid cabinet and concentrated hydrochloric acid on another. Store nitric acid in a secondary container with other ...
I CAN write Chemical formulas
... the oxidation numbers and write the oxidation number (without plus or minus) of one element as the subscript of the other element. 3. Reduce the subscripts (number of atoms) to their simplest form, if needed. WHAT IS THE CHEMICAL FORMULA FOR CALCIUM CHLORIDE? ...
... the oxidation numbers and write the oxidation number (without plus or minus) of one element as the subscript of the other element. 3. Reduce the subscripts (number of atoms) to their simplest form, if needed. WHAT IS THE CHEMICAL FORMULA FOR CALCIUM CHLORIDE? ...
Redox - Plusnet
... O is -2, except in OF2 Group 7 are -1, except with O or F Group 1 metals are +1 Group 2 metals are +2 H is +1, except in hydrides, e.g. NaH Al is +3 The total for an ion is its charge (e.g. -1 for CN-) More electronegative atoms get negative numbers The total for a compound is 0, even in O2, Cl2 etc ...
... O is -2, except in OF2 Group 7 are -1, except with O or F Group 1 metals are +1 Group 2 metals are +2 H is +1, except in hydrides, e.g. NaH Al is +3 The total for an ion is its charge (e.g. -1 for CN-) More electronegative atoms get negative numbers The total for a compound is 0, even in O2, Cl2 etc ...
CHEM 120 WEEK 11 LECTURES (INORGANIC WEEK 2) Dr. MD
... • Each halogen is the most electronegative element in its row. • Halogens exist as diatomic molecules. • In solids and liquids, the molecules are held together by weak London-dispersion forces • Iodine has the highest melting point and the strongest intermolecular forces. • At room temperature, I2 i ...
... • Each halogen is the most electronegative element in its row. • Halogens exist as diatomic molecules. • In solids and liquids, the molecules are held together by weak London-dispersion forces • Iodine has the highest melting point and the strongest intermolecular forces. • At room temperature, I2 i ...
+ CuO Cu + O
... 2- When copper hydroxide is heated, it will decompose into ……………… and …………………………. 3- When calcium carbonate is heated, ……………………………. And ……………………………. Are obtained. 4- Copper sulphate is decomposed by heat into …………………………………… 5- Active metals react with water as they substitute hydrogen of water which ...
... 2- When copper hydroxide is heated, it will decompose into ……………… and …………………………. 3- When calcium carbonate is heated, ……………………………. And ……………………………. Are obtained. 4- Copper sulphate is decomposed by heat into …………………………………… 5- Active metals react with water as they substitute hydrogen of water which ...
Introduction to Dental Materials
... They are bonded by covalent bonding along the backbone, and ionic bonding . Polymers are prepared in form of dough then shaped into desired shapes. They harden by: -physical reaction,(cooling, or evapration). Waxes, -chemical reaction, ...
... They are bonded by covalent bonding along the backbone, and ionic bonding . Polymers are prepared in form of dough then shaped into desired shapes. They harden by: -physical reaction,(cooling, or evapration). Waxes, -chemical reaction, ...
Chemistry IGCSE Revision PDF File
... Electrolysis y10 What is a conductor? ____________________________ What is an insulator? ___________________________ Why are the only solids that conduct are metals and graphite ___________________________________ ________________________________________________ Why do ionic substances only conduct ...
... Electrolysis y10 What is a conductor? ____________________________ What is an insulator? ___________________________ Why are the only solids that conduct are metals and graphite ___________________________________ ________________________________________________ Why do ionic substances only conduct ...
IGCSE Revision document
... Electrolysis What is a conductor? ____________________________ What is an insulator? ___________________________ Why are the only solids that conduct are metals and graphite ___________________________________ ________________________________________________ Why do ionic substances only conduct whe ...
... Electrolysis What is a conductor? ____________________________ What is an insulator? ___________________________ Why are the only solids that conduct are metals and graphite ___________________________________ ________________________________________________ Why do ionic substances only conduct whe ...
In situ Raman Spectroscopic Study of Supported Molten Salt
... generation, large amounts of SO2 are also emitted from sulfuric acid manufacturers and smelters of non-ferrous metals. Production of sulfuric acid is currently performed not only from traditional sulfuric acid manufacturers but also from NOx and SOx removal stations, combined with SCR technology lik ...
... generation, large amounts of SO2 are also emitted from sulfuric acid manufacturers and smelters of non-ferrous metals. Production of sulfuric acid is currently performed not only from traditional sulfuric acid manufacturers but also from NOx and SOx removal stations, combined with SCR technology lik ...
ALKALI EARTH METALS Introduction Properties Beryllium
... The melting point, boiling point and the hardness of the elements decrease top to bottom. Beryllium is the hardest alkaline earth metal Barium is the softest alkaline earth metal. ...
... The melting point, boiling point and the hardness of the elements decrease top to bottom. Beryllium is the hardest alkaline earth metal Barium is the softest alkaline earth metal. ...
Electrochemical synthesis of Cu and Fe metal organic frame
... tailoring of novel solids with regular porosity from the micro to nanopore scale. Nowadays several hundred different types of MOF are known. The self assembly of metal ions, which act as coordination centres, linked together with a variety of polyatomic organic bridging ligands, results in tailorabl ...
... tailoring of novel solids with regular porosity from the micro to nanopore scale. Nowadays several hundred different types of MOF are known. The self assembly of metal ions, which act as coordination centres, linked together with a variety of polyatomic organic bridging ligands, results in tailorabl ...
HW4 Problem 1 and 2.docx
... particle wear. Finally, the very large applied normal load causes a high amount of friction. This increase in friction can cause the materials to heat up and become brittle and harder. It can be seen from the equation above that the hardness is indirectly proportional to the volume of wear. Thus an ...
... particle wear. Finally, the very large applied normal load causes a high amount of friction. This increase in friction can cause the materials to heat up and become brittle and harder. It can be seen from the equation above that the hardness is indirectly proportional to the volume of wear. Thus an ...
g - Santa Rosa Junior College
... Sodium ore is halite, which is obtained either by the evaporation of brines or by mining salt deposits. Na is extracted and purified in an electrolytic apparatus called the Downs cell. Sylvite (mostly KCl) is the major ore of potassium. Chemical reduction of K+ ions by Na at high temperature produce ...
... Sodium ore is halite, which is obtained either by the evaporation of brines or by mining salt deposits. Na is extracted and purified in an electrolytic apparatus called the Downs cell. Sylvite (mostly KCl) is the major ore of potassium. Chemical reduction of K+ ions by Na at high temperature produce ...
ch22 lecture 7e
... Sodium ore is halite, which is obtained either by the evaporation of brines or by mining salt deposits. Na is extracted and purified in an electrolytic apparatus called the Downs cell. Sylvite (mostly KCl) is the major ore of potassium. Chemical reduction of K+ ions by Na at high temperature produce ...
... Sodium ore is halite, which is obtained either by the evaporation of brines or by mining salt deposits. Na is extracted and purified in an electrolytic apparatus called the Downs cell. Sylvite (mostly KCl) is the major ore of potassium. Chemical reduction of K+ ions by Na at high temperature produce ...
File
... 2. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion equals the charge on the ion. Example: Mg2+ has the oxidation number of +2. 3. The more electronegative element in a binary compound is assigned the number equal to the charge it would have if it were an ion. 4. The oxidation number of fluorine in a compoun ...
... 2. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion equals the charge on the ion. Example: Mg2+ has the oxidation number of +2. 3. The more electronegative element in a binary compound is assigned the number equal to the charge it would have if it were an ion. 4. The oxidation number of fluorine in a compoun ...
ch22_lecture_6e_final
... Sodium ore is halite, which is obtained either by the evaporation of brines or by mining salt deposits. Na is extracted and purified in an electrolytic apparatus called the Downs cell. Sylvite (mostly KCl) is the major ore of potassium. Chemical reduction of K+ ions by Na at high temperature produce ...
... Sodium ore is halite, which is obtained either by the evaporation of brines or by mining salt deposits. Na is extracted and purified in an electrolytic apparatus called the Downs cell. Sylvite (mostly KCl) is the major ore of potassium. Chemical reduction of K+ ions by Na at high temperature produce ...
Wet Corrosion Conditions for Wet Corrosion Just as we live in an
... depends on the molecular weight of the active chemical specie. Electrochemical attack, the scientific name for wet corrosion, depends on three circumstances occurring simultaneously. This might seem restrictive, but the evidence of wet corrosion that we see all around us proves that these conditions ...
... depends on the molecular weight of the active chemical specie. Electrochemical attack, the scientific name for wet corrosion, depends on three circumstances occurring simultaneously. This might seem restrictive, but the evidence of wet corrosion that we see all around us proves that these conditions ...
Modelling Mass Transfer in Nitrification Processes Using
... • Metal oxides, especially transition metal oxides, form the basis of selective oxidation catalysts. • The catalyst performance in terms of activity and selectivity is strongly related to the lattice structure. • Most selective oxidation reactions kinetics can be described in terms of the “REDOX” me ...
... • Metal oxides, especially transition metal oxides, form the basis of selective oxidation catalysts. • The catalyst performance in terms of activity and selectivity is strongly related to the lattice structure. • Most selective oxidation reactions kinetics can be described in terms of the “REDOX” me ...
SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER CHEMISTRY (043) CLASS XII (2013-14)
... (a) Explain why aniline is less basic than ammonia (b) How would you convert (i) Aniline to benzene diazonium chloride (ii) Aniline to fluorobenzene (a) Out of C6H5CH2I & C6H5CH2Cl which one is more reactive in SN2 substitutions reaction (b) Alcohols have higher boiling points why? (c) What do you m ...
... (a) Explain why aniline is less basic than ammonia (b) How would you convert (i) Aniline to benzene diazonium chloride (ii) Aniline to fluorobenzene (a) Out of C6H5CH2I & C6H5CH2Cl which one is more reactive in SN2 substitutions reaction (b) Alcohols have higher boiling points why? (c) What do you m ...
Single Replacement Reactions
... In nature, elements can occur either free, meaning uncombined with other elements, or chemically combined in a compound. The tendency of a particular element to combine with other substances is a measure of the activity of the element. The more active an element is, the more likely it is to combine. ...
... In nature, elements can occur either free, meaning uncombined with other elements, or chemically combined in a compound. The tendency of a particular element to combine with other substances is a measure of the activity of the element. The more active an element is, the more likely it is to combine. ...
7.4 Acids and bases
... CH3COOH + NaHCO3 CO2 + H2O + NaCH3COO Acid and metal reactions Acids react with metals to produce hydrogen gas and a salt. An example of this is seen between HCl and K which produces H2 gas KCl and a lot of energy which is seen as light and heat. In this specific reaction the energy from this reac ...
... CH3COOH + NaHCO3 CO2 + H2O + NaCH3COO Acid and metal reactions Acids react with metals to produce hydrogen gas and a salt. An example of this is seen between HCl and K which produces H2 gas KCl and a lot of energy which is seen as light and heat. In this specific reaction the energy from this reac ...
Sample Paper - Army Public School Jammu Cantt
... Shalini is confused as she has been reading in the newspaper about the ban on the usage of plastic substances. She further finds that despite the durability, the use of these materials has presented mankind with serious waste disposal problem as these materials do not disintegrate by themselves. In ...
... Shalini is confused as she has been reading in the newspaper about the ban on the usage of plastic substances. She further finds that despite the durability, the use of these materials has presented mankind with serious waste disposal problem as these materials do not disintegrate by themselves. In ...
Flux (metallurgy)

In metallurgy, a flux (derived from Latin fluxus meaning “flow”) is a chemical cleaning agent, flowing agent, or purifying agent. Fluxes may have more than one function at a time. They are used in both extractive metallurgy and metal joining.Some of the earliest known fluxes were carbonate of soda, potash, charcoal, coke, borax, lime, lead sulfide and certain minerals containing phosphorus. Iron ore was also used as a flux in the smelting of copper. These agents served various functions, the simplest being a reducing agent which prevented oxides from forming on the surface of the molten metal, while others absorbed impurities into the slag which could be scraped off the molten metal.As cleaning agents, fluxes facilitate soldering, brazing, and welding by removing oxidation from the metals to be joined. Common fluxes are: ammonium chloride or rosin for soldering tin; hydrochloric acid and zinc chloride for soldering galvanized iron (and other zinc surfaces); and borax for brazing or braze-welding ferrous metals. In the process of smelting, inorganic chlorides, fluorides (see fluorite), limestone and other materials are designated as ""fluxes"" when added to the contents of a smelting furnace or a cupola for the purpose of purging the metal of chemical impurities such as phosphorus, and of rendering slag more liquid at the smelting temperature. The slag is a liquid mixture of ash, flux, and other impurities. This reduction of slag viscosity with temperature, increasing the flow of slag in smelting, is the original origin of the word flux in metallurgy. Fluxes are also used in foundries for removing impurities from molten nonferrous metals such as aluminum, or for adding desirable trace elements such as titanium.In high-temperature metal joining processes (welding, brazing and soldering), the primary purpose of flux is to prevent oxidation of the base and filler materials. Tin-lead solder (e.g.) attaches very well to copper, but poorly to the various oxides of copper, which form quickly at soldering temperatures. Flux is a substance which is nearly inert at room temperature, but which becomes strongly reducing at elevated temperatures, preventing the formation of metal oxides. Additionally, flux allows solder to flow easily on the working piece rather than forming beads as it would otherwise.The role of a flux in joining processes is typically dual: dissolving of the oxides on the metal surface, which facilitates wetting by molten metal, and acting as an oxygen barrier by coating the hot surface, preventing its oxidation. In some applications molten flux also serves as a heat transfer medium, facilitating heating of the joint by the soldering tool or molten solder.Fluxes for soft soldering are typically of organic nature, though inorganic fluxes, usually based on halogenides and/or acids, are also used in non-electronics applications. Fluxes for brazing operate at significantly higher temperatures and are therefore mostly inorganic; the organic compounds tend to be of supplementary nature.