Meteorology - The Federation of Galaxy Explorers
... deal with fronts anyway? Well that is where the bad weather is. A cold front is associated with showers and thunder storms. Warm fronts usually bring steady rain. You can see that the clouds lie along the fronts on this weather map. Of course, the weather forecasters have a lot more information abo ...
... deal with fronts anyway? Well that is where the bad weather is. A cold front is associated with showers and thunder storms. Warm fronts usually bring steady rain. You can see that the clouds lie along the fronts on this weather map. Of course, the weather forecasters have a lot more information abo ...
All About Meteorology - Library Video Company
... 1.Why is it helpful to have accurate weather forecasts? 2.What do meteorologists do? 3.What is the atmosphere? Why is the atmosphere important? 4.What tool do meteorologists use to check temperature of the air? 5.What is humidity? Where does it come from? 6. How do meteorologists measure humidity? 7 ...
... 1.Why is it helpful to have accurate weather forecasts? 2.What do meteorologists do? 3.What is the atmosphere? Why is the atmosphere important? 4.What tool do meteorologists use to check temperature of the air? 5.What is humidity? Where does it come from? 6. How do meteorologists measure humidity? 7 ...
L`atmosphère et l`espace
... 12. What does each of the following definitions describe? a) a large expanse of the atmosphere where temperature and humidity are relatively uniform b) the leading edge of a cold air mass where it meets a warm air mass, causing puffy clouds, or cumulus, to form c) the leading edge of a warm air mass ...
... 12. What does each of the following definitions describe? a) a large expanse of the atmosphere where temperature and humidity are relatively uniform b) the leading edge of a cold air mass where it meets a warm air mass, causing puffy clouds, or cumulus, to form c) the leading edge of a warm air mass ...
SOF: Chapter 1-3 Practice Quiz
... 3. The National Weather Agency (NWA) is the civilian weather agency. (Pg 1-29) a. True b. False 4. The Air Force's weather organization is the Air Force Weather Agency. (Pg 1-30) a. True b. False 5. A ______________ satellite travels above the equator at the same speed as the Earth. (Pg 1-35) a. Pol ...
... 3. The National Weather Agency (NWA) is the civilian weather agency. (Pg 1-29) a. True b. False 4. The Air Force's weather organization is the Air Force Weather Agency. (Pg 1-30) a. True b. False 5. A ______________ satellite travels above the equator at the same speed as the Earth. (Pg 1-35) a. Pol ...
Meteorology Chapter 5 Worksheet 2 Name: Circle the letter that
... 7) How are jet contrails thought to influence the surface temperatures of cities near major airports? a. Decrease the daily temperature range. b. Definitely make the daily mean temperature warmer. c. Definitely make the daily mean temperature cooler. d. They have no measurable influence on surf ...
... 7) How are jet contrails thought to influence the surface temperatures of cities near major airports? a. Decrease the daily temperature range. b. Definitely make the daily mean temperature warmer. c. Definitely make the daily mean temperature cooler. d. They have no measurable influence on surf ...
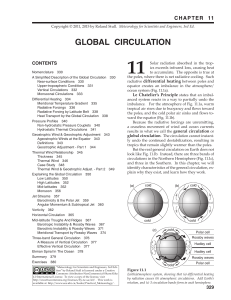
11. Global Circulation
... weather (clouds, rain, high humidity, strong winds) and fronts. The anticyclones are regions of good weather (clear skies or fair-weather clouds, no precipitation, dry air, and light winds). The high- and low-pressure centers move on average from west to east, driven by large-scale winds from the ...
... weather (clouds, rain, high humidity, strong winds) and fronts. The anticyclones are regions of good weather (clear skies or fair-weather clouds, no precipitation, dry air, and light winds). The high- and low-pressure centers move on average from west to east, driven by large-scale winds from the ...
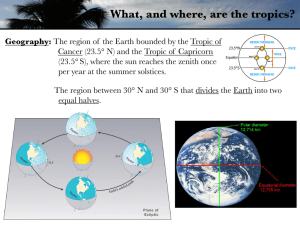
What, and where, are the tropics?
... topography, in the tropics will significantly influence the meteorology. ...
... topography, in the tropics will significantly influence the meteorology. ...
Air Pressure and Winds-I
... Air moves from high to low pressure in middle of column, causing surface pressure to change. Difference in pressure in ...
... Air moves from high to low pressure in middle of column, causing surface pressure to change. Difference in pressure in ...
TRIP PREPERATION
... - Clear sky, little wind, settled weather… LOWS - Say goodbye to the sunny skies ! - Say hello to likelihood of stronger winds and rain - Rain, showers or strong winds usually associated with Lows. ...
... - Clear sky, little wind, settled weather… LOWS - Say goodbye to the sunny skies ! - Say hello to likelihood of stronger winds and rain - Rain, showers or strong winds usually associated with Lows. ...
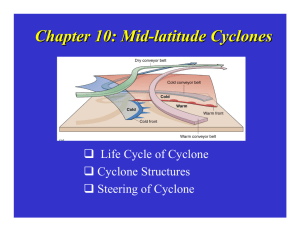
Chapter 10: Mid-latitude Cyclones
... The movement of surface systems can be predicted by the 500 mb pattern. The surface systems move in about the same direction as the 500 mb flow, at about 1/2 the speed. Upper-level winds are about twice as strong in winter than summer. This results in stronger pressure gradients (and winds), ...
... The movement of surface systems can be predicted by the 500 mb pattern. The surface systems move in about the same direction as the 500 mb flow, at about 1/2 the speed. Upper-level winds are about twice as strong in winter than summer. This results in stronger pressure gradients (and winds), ...
Chapter 10: Mid-latitude Cyclones Mid
... winds), resulting in stronger and more rapidly moving surface cyclones. ...
... winds), resulting in stronger and more rapidly moving surface cyclones. ...
Lecture:Moisture
... As the number of water vapor molecules in the air increase in number, they will have more chance of being close to another molecule and being attracted to each other. After there are a certain number of molecules in the air, any more molecules will cause the molecules to clump together forming a liq ...
... As the number of water vapor molecules in the air increase in number, they will have more chance of being close to another molecule and being attracted to each other. After there are a certain number of molecules in the air, any more molecules will cause the molecules to clump together forming a liq ...
FREE Sample Here
... today’s atmosphere, probably began an extremely slow increase in concentration as energetic rays from the sun split water vapor (H2O) into hydrogen and oxygen during a process called photodissociation. The hydrogen, being lighter, probably rose and escaped into space, while the oxygen remained in th ...
... today’s atmosphere, probably began an extremely slow increase in concentration as energetic rays from the sun split water vapor (H2O) into hydrogen and oxygen during a process called photodissociation. The hydrogen, being lighter, probably rose and escaped into space, while the oxygen remained in th ...
Y7GeU2B Weather typesPP Wk4
... Weather is the condition of the air around us over a short period of time (from day to day) ...
... Weather is the condition of the air around us over a short period of time (from day to day) ...
Atmosphere
... a. Cool air, which is denser, sinks. b. This forces the warm air, which is less dense to move up. c. Air moves from areas of high density to areas of low density. d. In its simplest form, wind can be thought of as air moving from an area of high pressure to an area of low pressure. ...
... a. Cool air, which is denser, sinks. b. This forces the warm air, which is less dense to move up. c. Air moves from areas of high density to areas of low density. d. In its simplest form, wind can be thought of as air moving from an area of high pressure to an area of low pressure. ...
Lesson 4 For students of Geography, 2 course. Subject
... more effectively than nitrogen or oxygen, so that the amount of carbon dioxide present in the atmosphere is an important factor in air temperature. In recent decades indeed, ever since the onset of the Industrial Revolution-factories, automobiles, and other burners of coal, petroleum, and gas have b ...
... more effectively than nitrogen or oxygen, so that the amount of carbon dioxide present in the atmosphere is an important factor in air temperature. In recent decades indeed, ever since the onset of the Industrial Revolution-factories, automobiles, and other burners of coal, petroleum, and gas have b ...
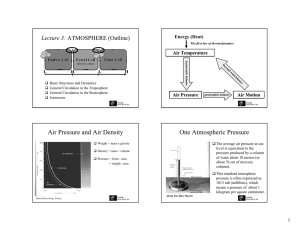
Air Pressure and Air Density One Atmospheric Pressure
... Only the Hadley Cell can be identified in the lower latitude part of the circulation. Circulation in most other latitudes are dominated by westerlies with wave patterns. Dominated by large-scale waver patterns (wave number 3 in the Northern hemisphere). ...
... Only the Hadley Cell can be identified in the lower latitude part of the circulation. Circulation in most other latitudes are dominated by westerlies with wave patterns. Dominated by large-scale waver patterns (wave number 3 in the Northern hemisphere). ...
syllabus_MET_4410 - My FIT (my.fit.edu)
... Mid-Latitude Weather Systems, T.N.Carlson (1991). Mountain Meteorology Fundamentals and Applications (2000) Sea Breeze and Local Winds, John. E. Simpson, (1994) Severe Convective Storms, C. A. Doswell, III, (2001) Basic Journal Articles ...
... Mid-Latitude Weather Systems, T.N.Carlson (1991). Mountain Meteorology Fundamentals and Applications (2000) Sea Breeze and Local Winds, John. E. Simpson, (1994) Severe Convective Storms, C. A. Doswell, III, (2001) Basic Journal Articles ...
Jet Stream Activity Packet Handout
... atmosphere. Therefore, atmospheric pressure is greatest at sea level. Air is highly compressible, as is readily seen by inflating a tire. Therefore, it is most dense at the bottom of the atmosphere where the weight of the air above compresses it to high densities. At higher altitudes, the air is les ...
... atmosphere. Therefore, atmospheric pressure is greatest at sea level. Air is highly compressible, as is readily seen by inflating a tire. Therefore, it is most dense at the bottom of the atmosphere where the weight of the air above compresses it to high densities. At higher altitudes, the air is les ...
Lec 18 - Agro Meteorology - Development of e
... isothermal because air is thin, clear, cold and dry near tropopause. 4). The temperature of this layer increases with height and also depends upon the troposphere because the troposphere is higher at the equator than at the poles. 5). In the upper parts of the stratosphere the temperatures are almos ...
... isothermal because air is thin, clear, cold and dry near tropopause. 4). The temperature of this layer increases with height and also depends upon the troposphere because the troposphere is higher at the equator than at the poles. 5). In the upper parts of the stratosphere the temperatures are almos ...
Oceanography Posters.. - University of Delaware
... to travel is dependent upon the clarity of the air. If the air is hazy there are more molecules, so there will be more scattering and the visible light will not travel very far. If the air is clear there are less molecules and there will be less opportunities for the visible light to scatter, allowi ...
... to travel is dependent upon the clarity of the air. If the air is hazy there are more molecules, so there will be more scattering and the visible light will not travel very far. If the air is clear there are less molecules and there will be less opportunities for the visible light to scatter, allowi ...
Meteorology Chapter 6 – Air Pressure and Winds Air pressure – the
... • Rising air is associated with cloudy conditions and precipitation, whereas subsidence produces adiabatic heating and clearing conditions. ⇒ In a surface low pressure system, air is spiraling inward, and the net inward transport of air causes shrinking of the area occupied by the air mass in a p ...
... • Rising air is associated with cloudy conditions and precipitation, whereas subsidence produces adiabatic heating and clearing conditions. ⇒ In a surface low pressure system, air is spiraling inward, and the net inward transport of air causes shrinking of the area occupied by the air mass in a p ...
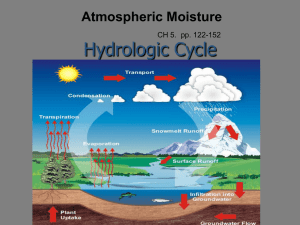
Chapter 5: Atmospheric Moisture
... The hydrologic cycle refers to the regular cycle of water through the earth-atmosphere system Liquification of water occurs frequently at normal Earth temperatures – Occurs when air is saturated with respect to water vapor – The addition of water vapor, or the lowering of temperature, in saturat ...
... The hydrologic cycle refers to the regular cycle of water through the earth-atmosphere system Liquification of water occurs frequently at normal Earth temperatures – Occurs when air is saturated with respect to water vapor – The addition of water vapor, or the lowering of temperature, in saturat ...
Atmospheric circulation

Atmospheric circulation is the large-scale movement of air, and the means (together with the smaller ocean circulation) by which thermal energy is distributed on the surface of the Earth.The large-scale structure of the atmospheric circulation varies from year to year, but the basic climatological structure remains fairly constant. Individual weather systems – mid-latitude depressions, or tropical convective cells – occur ""randomly"", and it is accepted that weather cannot be predicted beyond a fairly short limit: perhaps a month in theory, or (currently) about ten days in practice (see Chaos theory and Butterfly effect). Nonetheless, as the climate is the average of these systems and patterns – where and when they tend to occur again and again – it is stable over longer periods of time.As a rule, the ""cells"" of Earth's atmosphere shift polewards in warmer climates (e.g. interglacials compared to glacials), but remain largely constant even due to continental drift; they are, fundamentally, a property of the Earth's size, rotation rate, heating and atmospheric depth, all of which change little. However, a tectonic uplift can significantly alter their major elements, for example, the jet stream, and plate tectonics may shift ocean currents. In the extremely hot climates of the Mesozoic, indications of a third desert belt at the Equator has been found; it was perhaps caused by convection. But even then, the overall latitudinal pattern of Earth's climate was not much different from the one today.