Modernization and Innovation in the Weather Bureau: From Origins
... meteorologists, Harry Wexler, Jerome Namias, and Horace Byers are three who fulfilled this need. They studied under Rossby and soon brought the Bergen techniques to the weather bureau. Air mass analysis began in the mid‐1930s, however the United States proved to have difficulties that were only ...
... meteorologists, Harry Wexler, Jerome Namias, and Horace Byers are three who fulfilled this need. They studied under Rossby and soon brought the Bergen techniques to the weather bureau. Air mass analysis began in the mid‐1930s, however the United States proved to have difficulties that were only ...
Chapter 5
... suns radiation energy is absorbed by matter (air, land, water etc), which results in the convection of warm air which expands the air, creating a parcel that is of lower density and therefore able to rise vertically through the atmosphere, and is therefore a form of lifting. ...
... suns radiation energy is absorbed by matter (air, land, water etc), which results in the convection of warm air which expands the air, creating a parcel that is of lower density and therefore able to rise vertically through the atmosphere, and is therefore a form of lifting. ...
Atmospheric circulation structures associated with freezing rain in
... warm air advection. This yields a constant influx of moisture and above zero temperatures. The progression of spatial patterns at the surface, 850 hPa, and 500 hPa, bracket the potential interval of duration of each event. As outlined by Cheng et al. (1), duration thresholds, chosen to be 8 and 12h, ...
... warm air advection. This yields a constant influx of moisture and above zero temperatures. The progression of spatial patterns at the surface, 850 hPa, and 500 hPa, bracket the potential interval of duration of each event. As outlined by Cheng et al. (1), duration thresholds, chosen to be 8 and 12h, ...
Environmental lapse rate - FPInnovations Wildfire Operations
... adiabatic lapse rates, which are generally due to the extreme heating of the earth’s surface in calm conditions. Atmospheric stability is influenced by the environmental lapse rate. Extreme instability can influence wildfire behaviour and affect firefighter safety. Extreme instability is sometimes a ...
... adiabatic lapse rates, which are generally due to the extreme heating of the earth’s surface in calm conditions. Atmospheric stability is influenced by the environmental lapse rate. Extreme instability can influence wildfire behaviour and affect firefighter safety. Extreme instability is sometimes a ...
GOES-R and ABI Products from the NWS WFOs
... do today. In the area of air quality, we cannot do it without your help. ...
... do today. In the area of air quality, we cannot do it without your help. ...
Activity 8 Drawing Isobars Level 2 http://www.uni.edu/storm/activities
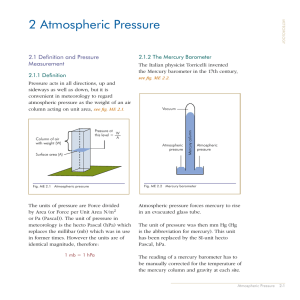
... of strikes per unit of time and area also increases. Since the particles move in all directions, they can even exert air pressure upwards as they smash into object from underneath. Air pressure can be exerted in all directions. As elevation above Earth’s surface increases, the number of particles de ...
... of strikes per unit of time and area also increases. Since the particles move in all directions, they can even exert air pressure upwards as they smash into object from underneath. Air pressure can be exerted in all directions. As elevation above Earth’s surface increases, the number of particles de ...
Weather Forecasting
... • Radiosonde instruments can be used to measure the vertical profiles of temperature, dew point, and winds. • Saturated air extends up to about 820 mb. • Below-freezing temperatures only exist in a shallow layer near the surface and the freezing rain would continue or possibly change to rain, as c ...
... • Radiosonde instruments can be used to measure the vertical profiles of temperature, dew point, and winds. • Saturated air extends up to about 820 mb. • Below-freezing temperatures only exist in a shallow layer near the surface and the freezing rain would continue or possibly change to rain, as c ...
weather or not - Northrop Grumman
... precipitation fall. As air rises, it expands and cools. The slow-moving air molecules in the cool air stick to each other and condense onto particulates in the air, forming the water droplets that make up clouds. Cloud formation can be helped along by seeding clouds which adds dust or ions onto whic ...
... precipitation fall. As air rises, it expands and cools. The slow-moving air molecules in the cool air stick to each other and condense onto particulates in the air, forming the water droplets that make up clouds. Cloud formation can be helped along by seeding clouds which adds dust or ions onto whic ...
Sounding Paper for METR 3613 - University of Oklahoma School of
... air. Since the ground heats faster than the air, heat is transferred from the ground into the lowerlevels of the atmosphere, thus creating the “lag time” in temperature change between the low levels and upper levels. In conclusion, the boundary layer was able to be identified based on thermal profil ...
... air. Since the ground heats faster than the air, heat is transferred from the ground into the lowerlevels of the atmosphere, thus creating the “lag time” in temperature change between the low levels and upper levels. In conclusion, the boundary layer was able to be identified based on thermal profil ...
Tornadoes-NB
... create instability in the atmosphere. A change in wind direction and an increase in wind speed with increasing height creates an invisible, horizontal spinning effect in the lower atmosphere. Rising air within the updraft tilts the rotating air from horizontal to vertical. An area of rotation, 2-6 m ...
... create instability in the atmosphere. A change in wind direction and an increase in wind speed with increasing height creates an invisible, horizontal spinning effect in the lower atmosphere. Rising air within the updraft tilts the rotating air from horizontal to vertical. An area of rotation, 2-6 m ...
Chapter 6: Stability
... • If a material changes its state (pressure, volume, or temperature) without any heat being added to it or withdrawn from it, the change is said to be adiabatic. • The adiabatic process often occurs when air rises or descends and is an important process in the atmosphere. ...
... • If a material changes its state (pressure, volume, or temperature) without any heat being added to it or withdrawn from it, the change is said to be adiabatic. • The adiabatic process often occurs when air rises or descends and is an important process in the atmosphere. ...
Original scientific paper 911.2:551.51 THE
... questionnaire has shown that of existing classification methods in Europe on daily data is based 84%, and 9% on short time scale of 12 to 6 hours. Only 5% of the classifications use the monthly values. However, this difference was not due to a methodological approach but the available data (Huth et ...
... questionnaire has shown that of existing classification methods in Europe on daily data is based 84%, and 9% on short time scale of 12 to 6 hours. Only 5% of the classifications use the monthly values. However, this difference was not due to a methodological approach but the available data (Huth et ...
Heat, Wind and Pressure
... 5. If we didn't have air, the sky would be black, there would be no life as we know it, and there would be no clouds. The side of the Earth facing the sun would be extremely hot, while the dark side of the planet would be bitterly cold. 6. Around low pressure we commonly find weather that is unsettl ...
... 5. If we didn't have air, the sky would be black, there would be no life as we know it, and there would be no clouds. The side of the Earth facing the sun would be extremely hot, while the dark side of the planet would be bitterly cold. 6. Around low pressure we commonly find weather that is unsettl ...
How a Barometer works: A barometer is an instrument for measuring
... by about three hectopascals between 9 am and 3 pm and will rise by a nearly similar amount between 3 pm and 9 am, even if weather systems are stationary. A smaller rise and fall occurs during the night and early morning. These daily (diurnal) changes must be allowed for before you can really say whe ...
... by about three hectopascals between 9 am and 3 pm and will rise by a nearly similar amount between 3 pm and 9 am, even if weather systems are stationary. A smaller rise and fall occurs during the night and early morning. These daily (diurnal) changes must be allowed for before you can really say whe ...
Extreme Weather on Earth Overview
... a short period of time. The term climate describes weather patterns of a particular region over a longer period, usually 30 years or more. Climate is an average pattern of weather for a particular region. Build background by providing the following example: The weather in Wisconsin can vary from day ...
... a short period of time. The term climate describes weather patterns of a particular region over a longer period, usually 30 years or more. Climate is an average pattern of weather for a particular region. Build background by providing the following example: The weather in Wisconsin can vary from day ...
SkyWatch
... The circle that forms around the sun or moon is called a halo. Halos are formed by the light from the sun or moon refracting (bending) as they pass through the ice crystals that form high-level cirrus and cirrostratus clouds. These clouds do not produce rain or snow, but they often precede an advanc ...
... The circle that forms around the sun or moon is called a halo. Halos are formed by the light from the sun or moon refracting (bending) as they pass through the ice crystals that form high-level cirrus and cirrostratus clouds. These clouds do not produce rain or snow, but they often precede an advanc ...
Click here to chapter 5
... Wind speed and direction at the earth’s surface are also influenced by friction and topography. Air flowing over the ground experiences a frictional drag that slows it down. Because friction decreases the more you move up from the surface, wind speed tends to increase with altitude. This decrease in ...
... Wind speed and direction at the earth’s surface are also influenced by friction and topography. Air flowing over the ground experiences a frictional drag that slows it down. Because friction decreases the more you move up from the surface, wind speed tends to increase with altitude. This decrease in ...
Air Barometer And Answer
... warm air is less dense than cooler air because the gas molecules in warm air have a greater velocity and are ... the barometer sinks lowest of all for wind and ... BAROMETER BASICS: HOW IT WORKS AND HELPS FORECAST WEATHER Mon, 28 Mar 2016 23:53:00 GMT a barometer is a widely used weather instrument ...
... warm air is less dense than cooler air because the gas molecules in warm air have a greater velocity and are ... the barometer sinks lowest of all for wind and ... BAROMETER BASICS: HOW IT WORKS AND HELPS FORECAST WEATHER Mon, 28 Mar 2016 23:53:00 GMT a barometer is a widely used weather instrument ...
Meteorology
... rate of evaporation increases As humidity increases, rate of evaporation decreases As wind increases, rate of evaporation increases As surface area increases, rate of evaporation increases ...
... rate of evaporation increases As humidity increases, rate of evaporation decreases As wind increases, rate of evaporation increases As surface area increases, rate of evaporation increases ...
Lesson 5
... A weather watch is issued when severe weather conditions are possible over a large area. People should have a plan of action in case of a storm. A weather warning is issued when weather conditions that pose a threat to life and property are happening or are about to happen. ...
... A weather watch is issued when severe weather conditions are possible over a large area. People should have a plan of action in case of a storm. A weather warning is issued when weather conditions that pose a threat to life and property are happening or are about to happen. ...
Yannay - onafieldtrip.ca
... The warm Pacific water remains off South Americas west coast and because of that, the cool, nutrient rich water can’t come up from below it. This means that fish don’t have the food they need to survive and not many are attracted to that area. As a result, fishing is decreased. For example, in the 1 ...
... The warm Pacific water remains off South Americas west coast and because of that, the cool, nutrient rich water can’t come up from below it. This means that fish don’t have the food they need to survive and not many are attracted to that area. As a result, fishing is decreased. For example, in the 1 ...
Atmospheric circulation

Atmospheric circulation is the large-scale movement of air, and the means (together with the smaller ocean circulation) by which thermal energy is distributed on the surface of the Earth.The large-scale structure of the atmospheric circulation varies from year to year, but the basic climatological structure remains fairly constant. Individual weather systems – mid-latitude depressions, or tropical convective cells – occur ""randomly"", and it is accepted that weather cannot be predicted beyond a fairly short limit: perhaps a month in theory, or (currently) about ten days in practice (see Chaos theory and Butterfly effect). Nonetheless, as the climate is the average of these systems and patterns – where and when they tend to occur again and again – it is stable over longer periods of time.As a rule, the ""cells"" of Earth's atmosphere shift polewards in warmer climates (e.g. interglacials compared to glacials), but remain largely constant even due to continental drift; they are, fundamentally, a property of the Earth's size, rotation rate, heating and atmospheric depth, all of which change little. However, a tectonic uplift can significantly alter their major elements, for example, the jet stream, and plate tectonics may shift ocean currents. In the extremely hot climates of the Mesozoic, indications of a third desert belt at the Equator has been found; it was perhaps caused by convection. But even then, the overall latitudinal pattern of Earth's climate was not much different from the one today.