* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Atmosphere
Precipitation wikipedia , lookup
Global Energy and Water Cycle Experiment wikipedia , lookup
Automated airport weather station wikipedia , lookup
Air quality law wikipedia , lookup
Thunderstorm wikipedia , lookup
Convective storm detection wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric circulation wikipedia , lookup
Severe weather wikipedia , lookup
Lockheed WC-130 wikipedia , lookup
Cold-air damming wikipedia , lookup
Atmosphere of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Weather lore wikipedia , lookup
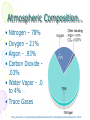
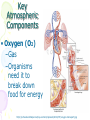
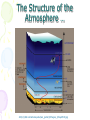
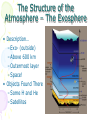
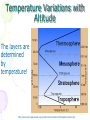
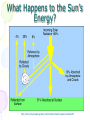
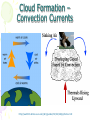
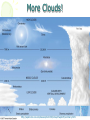
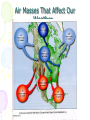
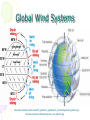
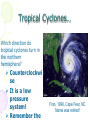
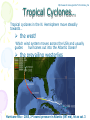
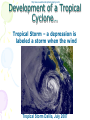
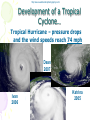
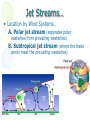
Atmosphere Atmospheric Basics Atmospheric Composition… • Nitrogen – 78% • Oxygen – 21% • Argon - .93% • Carbon Dioxide .03% • Water Vapor - .0 to 4% • Trace Gases http://www.bbc.co.uk/schools/gcsebitesize/science/21c/atmosphere/chemicalsairrev1.shtml Key Atmospheric Components • Oxygen (O2) –Gas –Organisms need it to break down food for energy http://schoolworkhelper.net/wp-content/uploads/2010/07/oxygen-transport.jpg Key Atmospheric Components • Carbon Dioxide (CO2) –Gas –Minor role in absorbing heat –plant fertilizer http://ed101.bu.edu/StudentDoc/current/ED101fa10/ccburke/Photosynthesis.html Key Atmospheric Components • Ozone (O3) –Gas –Absorbs ultraviolet radiation from the sun http://mmedia.pl/ozone-layer-diagram-for-kids Key Atmospheric Components • Water Vapor(H2O) –Gas –Major role in absorbing heat –source of condensation for clouds Key Atmospheric Components • Water –Liquid –source of rain Singing in the Rain! http://mypeartreehouse.blogspot.com/ Key Atmospheric Components • Ice –Solid –Makes up snow, sleet, & hail http://www.austinskiers.org/trips0910/vail0910.htm Legendary Vail Powder! Key Atmospheric Components • Dust, Salt, Volcanic Ash – Solids – Provide solid surface for water vapor to condense (so that clouds can form) – Condensation nuclei – See next slide… http://www.kidsgeo.com/images/ocean-waves.jpg http://www.weatherfreaks.net/images/dust_storm3.jpg Salt Spray from Waves Dust Storm The Structure of the Atmosphere … •http://ds9.ssl.berkeley.edu/lws_gems/3/images_3/layat510.jpg The Structure of the Atmosphere – The Troposphere • Description… – Tropo- (change) – 0-11 km – highest air pressure – Contains most gases of the atmosphere • Objects Found There – Weather – life forms The Structure of the Atmosphere – The Stratosphere • Description… – Strato- (layer) – 11-48 km – Molecular heat rises due to ozone layer absorbing UV radiation • Objects Found There – Ozone layer – Weather balloons The Structure of the Atmosphere – The Mesosphere • Description… – Meso- (middle) – 48-95 km – Temperature falls b/c there’s not a whole lot here! • Objects Found There – Meteors (shooting stars) burn here The Structure of the Atmosphere – The Thermosphere • Description… – Thermo- (heat) – 95-550 km – Molecular heat rises • Objects Found There – Ionosphere – Auroras The Structure of the Atmosphere – The Exosphere • Description… – Exo- (outside) – Above 600 km – Outermost layer – Space! • Objects Found There – Some H and He – Satellites Temperature Variations with Altitude The layers are determined by temperature! http://www.aerospaceweb.org/question/atmosphere/atmosphere/layers.gif What Happens to the Sun’s Energy? http://www.physicalgeography.net/fundamentals/images/cascade.GIF The State of the Atmosphere The Temperature of the Atmosphere The thermosphere is the hottest layer of the atmosphere but it feels so cold… b/c even though molecules are moving very fast (which means they are very hot), they are so far apart that there is no heat transfer. http://www.newworldencyclopedia.org/entry/Astronaut Astronaut Bruce McCandless II is feeling no heat! The Temperature of the Atmosphere Dew Point - temperature to which air must be cooled (at constant pressure) to reach saturation. a. Dew point tells us how much water is in the air. o This is when dew is formed! o The higher the dew point, more humid and uncomfortable the air. Vertical Temperature Changes How is dew point determined? … determine the temperature at which dew (condensation) forms by cooling the air. Humidity Changes with Temperature… What is humidity? The amount of water air can hold at a given temperature. This is a constant! What is relative humidity? The amount of water the air is actually holding compared to how much it can hold Relative humidity is determined by....using a wet/dry bulb thermometer & a relative humidity chart Air Pressure and Density… Density is mass (of air) per volume. Air pressure is… … force exerted by molecules of atmosphere as they are pulled toward Earth’s center by gravity. Air Pressure and Density… Air at the bottom of the atmosphere (troposphere) has higher density and pressure because... … of the greater mass of the atmosphere above you (it contains the most gases) … This is similar to being at the bottom of the ocean with tons of water above you! … We are accustomed to the high air pressure so it doesn’t squash us. Temperature-Density Relationship Warm Air… As temperature increases… air becomes less dense. b. Warm air is less dense and will rise. c. The upward movement of warm air lowers pressure. d. So, warm air rising causes low pressure. a. Temperature-Density Relationship Cold Air… a. As temperature decreases… air becomes more dense. b. Cold air is more dense and will sink. c. The downward movement of cold air raises pressure. d. So, cold air sinking causes high pressure. http://scifiles.larc.nasa.gov/text/kids/Problem_Board/problems/light/sim3.html Creating Wind… a. Cool air, which is denser, sinks. b. This forces the warm air, which is less dense to move up. c. Air moves from areas of high density to areas of low density. d. In its simplest form, wind can be thought of as air moving from an area of high pressure to an area of low pressure. Wind… The density imbalances that move air to produce wind are created by… The unequal heating of Earth’s surface Wind is measured by… anemometers (mph or kph) Wind speeds increase at high altitudes b/c… There are few to no obstacles there Moisture in the Atmosphere Three Ways Clouds Can Form… a. from convection currents b. from warm air rising over mountains (orographic lifting) c. when air masses of different temperatures meet Cloud Formation – Convection Currents http://ww2010.atmos.uiuc.edu/(Gh)/guides/mtr/cld/cldtyp/home.rxml Cloud Formation – Orographic Lifting Clouds form over a mountain. http://www.envi.hufs.ac.kr/gwlee/session6/lift.html Cloud Formation – Frontal http://www.windows2universe.org/earth/Atmosphere/images/cloudformation_Fronts_small.jpg Cloud Types…Altitude • Cirro- high –Above 6000m • Alto - middle –Between 2000-6000m • Stratus - low –Below 2000m http://www.windows2universe.org/earth/Atmosphere/clouds/cloud_heights.html More Clouds! http://apollo.lsc.vsc.edu/classes/met130/notes/chapter5/summary.html Meteorology The Causes of Weather Energy in the Atmosphere… What two things are always in motion to distribute heat energy on and around the Earth? ocean currents global wind systems What explains why the poles are never very warm? The Sun’s rays don’t hit Earth as directly at the poles as at the tropics. (So the same amount of solar Air Masses… • Continental Tropical –Abbreviation cT –Origin - land –Origin - tropical –Moisture Content - dry –Temperature - http://earth.usc.edu/~stott/Catalina/WeatherPatterns.html Air Masses… • Maritime Tropical –Abbreviation mT –Origin – ocean/water –Origin - tropical –Moisture Content humid Air Masses… Continental Polar –Abbreviation - cP –Origin - land –Origin – high latitudes –Moisture Content - dry –Temperature – cool or cold Air Masses… • Maritime Polar –Abbreviation mP –Origin – ocean/water –Origin – high latitudes –Moisture Content - humid –Temperature – Air Masses… • Arctic (Continental) –Abbreviation - cA –Origin – land –Origin - Arctic –Moisture Content – dry –Temperature – very cold Air Masses That Affect Our Weather… Global Wind Systems http://pulse.pharmacy.arizona.edu/9th_grade/from_global/earth_science/images/wind_patterns.gif http://www.topnews.in/files/atmosphere_wind_patterns.jpg 2. Chart:Global Wind Systems… • Polar Easterlies –Comes from the east –Located between 60 degrees latitude and the pole in both hemispheres –(60° - 90°) Global Wind Systems… • Prevailing Westerlies – Comes from the west – Located between 30 and 60 degrees latitude in both hemispheres – (30° - 60°) – This is the wind system that directs Global Wind Systems… • Trade Winds –Comes from the east –Located between the equator and 30 degrees latitude in both hemispheres –(0° - 30°) The Intertropical Convergence Zone What is the intertropical convergence zone (ITCZ)? The area near the equator where the trade winds converge. Air is forced up and creates an area of low pressure. (Remember – warm air rising!) The ITCZ provides the moisture for many of the world’s tropical rain forests. Picture on next slide… The Doldrums… What are the doldrums? Another name for the ITCZ! Sailing ships would often get stranded in this area because of the light (or no!) winds. The phrase, “I’m stuck in the doldrums,” came from this phenomenon. Looking for wind! Horse Latitudes… Why were the horse latitudes so named? Around the 30 degrees latitude, sinking air creates a belt of high pressure which causes weak winds. Sailors stranded here were said to throw their horses overboard when they couldn’t feed them! Weather Systems in the USA Which global wind system is responsible for much of the movement of weather across the USA and Canada? The prevailing westerlies The Causes of Weather Pressure Systems – High Pressure Cold air sinking a. Fair weather b. Rotates clockwise c. Represented as a blue ‘H’ Good ‘H’air Day! http://www.windows2universe.org/earth/Atmosphere/high_pressure.html Pressure Systems – Low Pressure a. Warm air rising b. Clouds and precipitation c. Rotates counterclockwise d. Represented as a red ‘L’ ‘L’ousy Weather Day! http://www.windows2universe.org/earth/Atmosphere/high_pressure.html http://3.bp.blogspot.com/_275ZCyVPoFk/TNAxxCklePI/AAAAAAAAAJs/VFM3DzpqDzg/s1600/meteo.jpg http://www.cdli.ca/courses/sci2200/unit02_org01_ilo03/b_activity.html Cold Front… • Definition – Cold, dense air displaces warm air and forces it up a steep front • Symbol – blue icicles! • Weather – clouds, showers, and thunder storms http://earth.usc.edu/~stott/Catalina/WeatherPatterns.html http://www.cdli.ca/courses/sci2200/unit02_org01_ilo03/b_activity.html Warm Front… • Definition – Advancing warm air displaces cold air and moves up slowly • Symbol – red lava rocks! • Weather – extensive cloudiness and precipitation Stationary (Stalled) Front… • Definition – Two air masses meet and neither advances • Symbol – blue icicles alternate with red lava rocks • Weather – some clouds and precipitation http://www.kidsgeo.com/geography-for-kids/0129-stationary-fronts.php http://www.nvwx.com/wximages/occluded_front.png Occluded Front… • Definition – A cold air mass moves so rapidly that it overtakes a warm front and wedges the warm air up. • Symbol – purple alternating rocks/icicles • Weather – precipitation on both sides of the front http://www.aggiecat.com/Logs/logs-0016-Jan-08/occluded_front_sm.jpg Gathering Weather Data Thermometer – Measures temperature – Degrees Celsius or Fahrenheit – Thermometers contain liquids that expand when heated. Barometer • Measures air pressure • Millibars or inches of mercury • A barometer may contain mercury or a vacuum inside a metal chamber that contracts or expands with http://robertwhite.com/marineimages/precision_barometer.jpg Anemometer – Measures wind speed – … mph or km/h or knots – Has cupped arms that rotate as the wind http://www.smg.gov.mo/www/dm/equip/ws.jpg Hygrometer –Measures relative humidity – % age of water air is holding compared to how much it can hold. – Uses wet- and drybulb thermometers and determines how fast the water evaporates from the wet bulb. https://www.avogadro-lab-supply.com/item_images/Wet%20Dry3.jpg – Measures the height of cloud layers & estimates cloud cover – meters above ground level – Radar is beamed at the bottom Ceilometer http://apollo.lsc.vsc.edu/classes/met130/notes/chapter5/graphics/ceilometer.jpg Upper Level Data To make accurate forecasts, meteorologist gather data up to 30,000 m. A radiosonde is a balloon-borne package of weather sensors (upper level data) a. Radiosondes take measurement on temperature, air pressure and humidity. http://www.windows2universe.org/milagro/images/radiosonde_sm.jpg Weather Radar and Satellites Radar pinpoints where rain is falling at any given moment a. radio detecting and ranging b. A radar system works by bouncing radio waves off large rain http://www.comet.ucar.edu/nsflab/web/remote/1221.htm The Doppler Effect… … is the change in wave frequency of energy (sound or light) as it moves toward or away from an observer. https://www.youtube.com/wat ch?v=0rJPvGML9A0 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=K g9F5pN5tlI&safe=active Meteorologists use Doppler Radar to plot the speed at which raindrops move toward or away from a radar station. This allows them to detect http://24.media.tumblr.com/tumblr_lvut83IRCk1r285ovo1_400.jpg severe weather events! Weather Satellites… a. Weather radar tracks rain. b. Weather satellites track clouds. Station Models… What is a station model? A record of weather data for a particular site at a particular time What is the advantage of using a station model? A large amount of data can be http://www.free-online-private-pilot-ground-school.com/Aviation-weather-reporting.html Station Model Symbols… Cloud/Sky Cover http://0.tqn.com/d/weather/1/0/R/-/-/-/cloudcover.gif Wind Speed http://www.scalloway.org.uk/images/knots.gif The Nature of Storms Thunderstorms and Severe Weather Average Number of Thunderstorm Days Annually… Florida is #1!! Cause of Thunderstorms… • Warm air rises over a mountain • Temperature difference b/tw land & sea • Fronts Types of Thunderstorms… • Air Mass - Mountain – Where… within one air mass over a mountain – Why… warm air rises over a mountain, forming storm clouds! – When… midafternoon http://web.mst.edu/~rogersda/umrcourses/ge301/press&siever12.3.png Types of Thunderstorms… • Air Mass - Sea-Breeze – Where… coastal areas, esp. tropics/subtropics – Why… temperature differences between land and sea create convection cells and updrafts – When… summer http://apollo.lsc.vsc.edu/~wintelsw/MET1010LOL/web/notes/chapter11/ts_ingredients4summary.html http://apollo.lsc.vsc.edu/classes/met130/notes/chapter11/graphics/cf_xsect.jpg Types of Thunderstorms… • Frontal - Cold – Where… at the leading edge of a cold front – Why… cold air pushes warm air rapidly up at the steep cold-front boundary – When… anytime a cold front moves in! Types of Thunderstorms… • Frontal – Warm – Where… at the leading edge of a warm front – Why… warm air mass slides up over a cold air mass creating clouds – When… if a warm front moves in with enough moisture and instability http://www.atmoz.org/img/warm-front.png Lightning… What is lightning? A giant spark of static electricity How does a lightning bolt form? A ‘-’ channel of air from a cloud (stepped leader) connects with a ‘+’ channel on the ground (return http://i.imwx.com/web/multimedia/images/blog/stepped_lightning2.jpg Lightning… What causes thunder? Super-heated air expanding and contracting How hot is lightning? 30,000 degrees http://www.eoearth.org/files/119701_119800/119773/Step5.jpg http://www.srh.noaa.gov/jetstream/lightning/images/lightning8.jpg http://www.barransclass.com/phys1090/circus/JenkinsD/JenkinsD.html Lightning Damage… The damage that lightning can do… 7500 forest fires/year 300 injuries/ 93 deaths/year Property damage Lightning-struck trees on the Blue Ridge Parkway http://www.sciencephoto.com/images/download_lo_res.html?id=670034119 Lightning Safety… “When lightning roars, go indoors!” Tornadoes (Formation of…) A. change in wind direction & speed creates horizontal rotation. B. Strong updrafts tilt rotating air to vertical position. C. Tornado forms http://www.weatherwizkids.com/tornado_formation.jpg Tornado Alley The Midwest! A supercell is a giant, self-sustaining storm that can spawn tornados. (A cP air mass from Canada meets a mT air mass from the Gulf of Mexico) Tornado Alley is in the midwest. Most tornadoes occur in May. http://midwestweather.net/archives/tornadoclimatology.htm The Enhanced Fujita Scale… a. This scale is used to classify a tornado AFTER the tornado has passed by looking at the damage and effects of the tornado. Tornado Safety… 1. Move to a pre-designated shelter – to a basement if possible. 2. Move to an interior room/hall, lowest floor, under sturdy furniture. (A bath tub is safest!) 3. Stay away from windows. 4. Get out of vehicles! 5. Don’t try to outrun a tornado. 6. If outside, lie flat in a ditch or depression. 7. Abandon a mobile home for a shelter. Tropical Storms & Hurricanes Tropical Cyclones… A tropical cyclone can be described as a… Large, rotating, low pressure storm We call these storms… hurricanes Tropical cyclones derive energy from… Warm, tropical oceans http://www.nhc.noaa.gov/HAW2/english/history.shtml Tropical Cyclones… As a hurricane strengthens, what do the following components do? a. Air pressure in eyewall– decreases b. Surface wind speeds – Tropical Cyclones… Which direction do tropical cyclones turn in the northern hemisphere? Counterclockwi se It is a low pressure system! Remember the Fran, 1996, Cape Fear, NC Name was retired! http://www.srh.noaa.gov/shv/?n=hurricane_rita Tropical Cyclones… Tropical cyclones in the N. Hemisphere move steadily towards… the west! Which wind system moves across the USA and usually guides hurricanes out into the Atlantic Ocean? the prevailing westerlies Hurricane Rita – 2005, 3rd lowest pressure in Atlantic (897 mb), hit as cat. 3 Development of a Tropical Cyclone… Tropical Disturbance – a weak, lowpressure system – group of thunderstorms collect http://www.uvs-model.com/WFE%20on%20tropical%20cyclone%20(Hurricane).htm Development of a Tropical Cyclone… Tropical Depression – a disturbance begins to rotate around the center of low pressure Katrina as a tropical depression http://www.weatherstockphotography.com/ Development of a Tropical Cyclone… Tropical Storm – a depression is labeled a storm when the wind speeds reach 39 mph. Tropical Storm Dalila, July 2007 http://www.weatherstockphotography.com/ Development of a Tropical Cyclone… Tropical Hurricane – pressure drops and the wind speeds reach 74 mph Dean 2007 Ivan 2006 Katrina 2005 Classifying Hurricanes… The Saffir-Simpson Scale 4 characteristics of a hurricane described… a. Wind speed – how high? b. Air pressure – how low? c. Potential for damage – how much?! d. Storm surge http://www.nhc.noaa.gov/sshws_table.shtml?large Classifying Hurricanes… The Saffir-Simpson Scale… Categories 1 – 5 Category that does the most damage – 5 Wind speed of a cat 5? > 155 mph Three most powerful storms to hit USA? http://www.nhc.noaa.gov/pastint.shtml a. Florida Keys, 1935 Classifying Hurricanes… A hurricane runs out of energy When it moves over land or cold water http://backyard.weatherbug.com/profiles/blogs/the-south-central-texas-445 Hurricane Hazards… The strongest winds in a hurricane are in the… eye wall http://www.med.navy.mil/sites/nmcp/localarea/Weather/PublishingImages/def1.gif Hurricane Hazards… What is a storm surge? When hurricane force winds drive a mound of ocean water towards coastal areas http://www.chathamemergency.org/images/storm%20surge%202.png Storm Surge… a. 9 of every 10 people who die in a hurricane are killed by the storm surge. b. You should EVACUATE so you don’t get killed by the storm surge! Hurricane Hazards… What hurricane hazard is caused by great amounts of rain? floods Flooding from Hurricane Fran http://pubs.usgs.gov/of/1996/of96-499/text/PHOTOS.html Hurricane Hazards… Which agency is responsible for tracking and forecasting hurricanes? The National Hurricane Center in Miami, FL (FIU Campus) (NOAA) The World’s Best Hurricane Safety Tip… EVACUATE!! Human Impact on Air Quality Smog (Smokey Fog)… 1. Smog is a yellow-brown photochemical haze. 2. Smog is caused by solar radiation heating pollution (hydrocarbons & nitrogen oxides mostly from car exhaust). 3. Smog makes it difficult to breathe! 4. The major chemical in smog is ozone. b/c Ozone irritates the eyes, nose, Particulate Matter… Four examples of particulate matter include… 1. ash, dust, pollen, & asbestos fibers. 2. These are forms of SOLID pollutants in the air. Particulate matter is harmful to people because it can… get in lung tissues & cause breathing difficulties & lung disease. See next slide… Review Only! The Greenhouse Effect What is the greenhouse effect? It is heat from the sun being trapped by the gases in our atmosphere. – A greenhouse effect you may relate to is that of a closed car on a cold, sunny day in winter. – The greenhouse effect is a GOOD thing! It allows for life on our planet! http://www.uic.com.au/graphics/ueg1-1.gif Global Warming… Global warming is… … an increase in Earth’s average surface temperature. Some scientists believe that the cause of global warming is... Coal for electricity … the burning of fossil fuels Gasoline for vehicles Natural Gas for Write examples in margin… fireplaces and cooking a. which releases carbon dioxide (CO2) b. CO2 makes up only .04% of the atmosphere! (4 out of 10,000 molecules) Fossil Fuel Use • Fossil Fuels Used… – Coal for electricity – Gasoline for vehicles – Natural Gas for fireplaces and cooking There are many scientists who believe the Sun has the major role in global warming/cooling. To reduce levels of CO2 in the atmosphere people can … … reduce our use of fossil fuels! (And stop breathing!) How? The Ozone Issue Review! The ozone layer is found in the stratosphere. Ozone absorbs ultraviolet radiation from the sun. www.space.gc.ca Add to Margin of Notes: 3 Effects of Ultraviolet Radiation… Ultraviolet radiation from the sun can cause cataracts (a clouding of the lens of the eye) and skin cancer. Ultraviolet radiation can kill the eggs of certain animals like amphibians because they lay their eggs in shallow water. www.matthews.co.nz www.waterencyclopedia.com www.mja.com.au The Ozone Issue Man-made chemicals called (CFCs) chlorofluorocarbons react with ozone and break it apart. (The part of the CFC molecule that reacts with the ozone molecule is the chlorine atom.) observe.arc.nasa.gov The Ozone Issue CFCs are used as refrigerants, coolants, propellants in aerosol cans, and Styrofoam. www.ec.gc.ca tiki.oneworld.net The Ozone Issue We should eliminate sources of CFCs worldwide. (CFCs were banned in the late 1980’s in industrialized nations. They are still in use in some places in the world.) “Under the 1987 Montreal Protocol, developing countries committed themselves to halving consumption and production of the CFCs by 2005 and to achieving an 85 percent cut by 2007.” http://www.tribuneindia.com/2002/20020919/science.htm#2 Acid Precipitation (Rain)… 1. Acid precipitation (rain) is precipitation with a pH of less than 5. The pH of natural precipitation is 5.0 to 5.6. 2. Acid precipitation forms when sulfur dioxide (SO2) & nitrogen oxides (NO2) combine w/ atmospheric water to create sulfuric acid & nitric acid. 3. Six types of acid precipitation are Coal-burning Power Plant – Jacksonville, FL 5. The source of acid precipitation that receives the most attention is caused by coal-burning power plants in the midwestern USA. Acid Rain… 6. Three effects of acid precipitation are the damage it causes to… a. … aquatic ecosystems b. … plants & soil. c. … stone buildings & statues. Easy on the acid rain, guys! Acid Rain… 7. Prevention: Use wet scrubbers on smoke stacks of coalburning power plants. (to reduce sulfur emissions) Station Model… http://visual.merriam-webster.com/images/earth/meteorology/station-model.jpg http://www.centennialofflight.gov/essay/Dictionary/Jet_Stream/DI68G1.jpg Jet Streams… • Definition of Jet Stream… – Narrow bands of fast, high altitude westerly winds (which resemble jets of water) – Jet streams follow the boundaries between hot and cold air and are strongest in the winter. A Jet Stream As It Appears on a Weather Map… Jet Streams… • Location by Wind Systems… A. Polar jet stream (separates polar easterlies from prevailing westerlies) B. Subtropical jet stream (where the trade winds meet the prevailing westerlies)