S8P2 Students will be familiar with the forms and transformations of
... Energy is the ability to do work or cause change. ...
... Energy is the ability to do work or cause change. ...
Heat Transfer, Greenhouse Effect, Ozone Layer Notes
... How does the Earth get heated? • Energy transfer from the sun ...
... How does the Earth get heated? • Energy transfer from the sun ...
File
... surroundings, the process is endothermic. • When heat is released by the system to the surroundings, the process is exothermic. ...
... surroundings, the process is endothermic. • When heat is released by the system to the surroundings, the process is exothermic. ...
What is Energy - Educator Pages
... an object’s vibrations. The object’s vibrations transmit some kinetic energy to the air particles, which also vibrate. These vibrations transmit sound energy. ...
... an object’s vibrations. The object’s vibrations transmit some kinetic energy to the air particles, which also vibrate. These vibrations transmit sound energy. ...
Slide 1
... Potential Energy is stored energy. Energy can be stored in various forms. 1. Energy can be stored by raising an object above the ground (gravitational potential energy). 2. Energy can be stored by compressing or stretching a spring (elastic potential energy). 3. Energy can be stored in the chemical ...
... Potential Energy is stored energy. Energy can be stored in various forms. 1. Energy can be stored by raising an object above the ground (gravitational potential energy). 2. Energy can be stored by compressing or stretching a spring (elastic potential energy). 3. Energy can be stored in the chemical ...
EM Energy
... A = mNIr/2 f (Check B = x A) Set r = R because only those terms multiply with J WM = ½ J.AV = ½(I/S0).(mNIR/2).(Nl.2pR.S0) rewrite I in terms of B ...
... A = mNIr/2 f (Check B = x A) Set r = R because only those terms multiply with J WM = ½ J.AV = ½(I/S0).(mNIR/2).(Nl.2pR.S0) rewrite I in terms of B ...
CH 7 Study Guide-Answers
... b. Electric – the energy an electric current carries c. Thermal – energy that involves heat from particles moving d. Mechanical – energy that involves movement of parts ex: a clock, riding a bike e. Nuclear – energy stored and released in the nucleus of atoms f. Radiant – light energy, carried by el ...
... b. Electric – the energy an electric current carries c. Thermal – energy that involves heat from particles moving d. Mechanical – energy that involves movement of parts ex: a clock, riding a bike e. Nuclear – energy stored and released in the nucleus of atoms f. Radiant – light energy, carried by el ...
Thermochemistry
... The potential energy of this ball of clay is increased when it is moved from the ground to the top of the wall. b) As the ball falls, its potential energy is converted to kinetic energy. c) When it hits the ground, its kinetic energy falls to zero (since it is no longer moving); some of the energy d ...
... The potential energy of this ball of clay is increased when it is moved from the ground to the top of the wall. b) As the ball falls, its potential energy is converted to kinetic energy. c) When it hits the ground, its kinetic energy falls to zero (since it is no longer moving); some of the energy d ...
Video Notes #5 – Introduction to Energy
... C__________________________ - the energy stored in _________________ that is released during a _______________ change. Examples of chemical energy include: The burning of the chemicals stored in fuel to make heat, using chemicals stored in batteries to operate a toy, the digestion of chemicals foun ...
... C__________________________ - the energy stored in _________________ that is released during a _______________ change. Examples of chemical energy include: The burning of the chemicals stored in fuel to make heat, using chemicals stored in batteries to operate a toy, the digestion of chemicals foun ...
ENERGY
... • Another form is Elastic PE • This is the PE stored in an object by its being disturbed from is natural state, • and how much it wants to return to that ...
... • Another form is Elastic PE • This is the PE stored in an object by its being disturbed from is natural state, • and how much it wants to return to that ...
Review Sheet
... Write all of your answers on a separate sheet of paper. There will not be enough room for you to write your answers on this sheet. This sheet is designed so you can then continue to use this as a question/answer review. Study with friends or family by having other people quiz you. Simply answering t ...
... Write all of your answers on a separate sheet of paper. There will not be enough room for you to write your answers on this sheet. This sheet is designed so you can then continue to use this as a question/answer review. Study with friends or family by having other people quiz you. Simply answering t ...
Ch 16 Thermal Energy and Heat
... 16.1 Thermal Energy and Matter • In the 1700’s scientists thought heat was a fluid called a caloric that flowed between objects. • In 1798, the scientist Count Rumford concluded, from his observations, that heat could not be a kind of matter but instead was related to the motion of objects ...
... 16.1 Thermal Energy and Matter • In the 1700’s scientists thought heat was a fluid called a caloric that flowed between objects. • In 1798, the scientist Count Rumford concluded, from his observations, that heat could not be a kind of matter but instead was related to the motion of objects ...
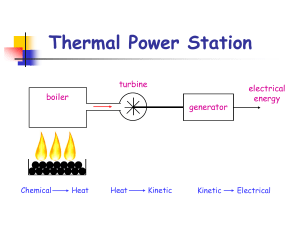
Thermal Power Station
... The major disadvantage of nuclear power is that the waste produced is radioactive. It has to be stored underground in lead and concrete containers for thousands of years. ...
... The major disadvantage of nuclear power is that the waste produced is radioactive. It has to be stored underground in lead and concrete containers for thousands of years. ...
Energy and Power
... Kinetic energy increase as mass increases. (golf and bowling ball) Kinetic energy increases as mass and velocity increase. ...
... Kinetic energy increase as mass increases. (golf and bowling ball) Kinetic energy increases as mass and velocity increase. ...
Conservation of energy

In physics, the law of conservation of energy states that the total energy of an isolated system remains constant—it is said to be conserved over time. Energy can be neither created nor be destroyed, but it transforms from one form to another, for instance chemical energy can be converted to kinetic energy in the explosion of a stick of dynamite.A consequence of the law of conservation of energy is that a perpetual motion machine of the first kind cannot exist. That is to say, no system without an external energy supply can deliver an unlimited amount of energy to its surroundings.