* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download STOMP ROCKET STATION What energies are present? Where
Dark energy wikipedia , lookup
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Gibbs free energy wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
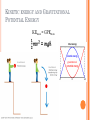
STOMP ROCKET STATION 1. What energies are present? 2. Where does the KE come from? 3. Where does the initial energy come from? MOVEMENT (KINETIC) GRAVITATIONAL POTENTIAL The stored energy due to height above a reference point GPE becoming KE GPE = mgh Maximum GPE Minimum GPE KINETIC ENERGY AND GRAVITATIONAL POTENTIAL ENERGY KEmax = GPEmax Gravitational gravitational Gravitational PULL BACK CAR 1. What energies are present? 2. Where did the initial energy come from? 3. What is the pullback energy similar to? What else can you think of that bounces back? ELASTIC POTENTIAL ENERGY The energy stored in a deformed object, for objects that have the tendency to return to original shape POP-UP TOY 1. What energies are present? 2. Where did the initial energy come from? 3. How is this related to the previous station? METAL IN WATER 1. What energies are present? 2. Where did the energy start? 3. Where did the energy end up? 4. Did the energy change forms at all? THERMAL ENERGY LAB REVIEW 3 factors determine the amount of thermal energy in a substance Type of substance – Different materials can hold more or less thermal energy. The more it holds, the slower its temperature changes. Kettle gets hot fast! – hold less thermal Water slower to heat – holds more thermal Mass of substance – More Mass = More particles holding energy Temperature of substance CLAY BALL DROP 1. What energies are present? 2. Where did the energy come from? 3. What happened to the clay? WHAT IS DEFORMATION? The transfer of KE to thermal energy causes a change in shape of substances (visible in soft substances) SOUND Organized movement of particles – Turns to thermal energy once organization is lost SOUND Organized movement of particles – Turns to thermal energy once organization is lost CIRCUIT 1. What energies are present? 2. Where did the energy start? 3. Where did the energy end up? 4. How did the energy travel? CHEMICAL POTENTIAL ENERGY The energy stored in the arrangement of atoms NEW MOLECULES ATOMS TELL YOU ABOUT MATTER BONDS TELL YOU ABOUT ENERGY CHEMICAL REACTION NEW FORMS OF ENERGY THERMAL and LIGHT ELECTRICAL ENERGY The transfer of energy through wires LIGHT Electromagnetic radiation in the form of waves Visible and Invisible Spreads out into environment FORMS OF ENERGY AND WAYS TO TRANSFER ENERGY Forms of energy observed in objects at the stations: Gravitational Energy Kinetic Energy Thermal Energy Elastic Energy Chemical Energy Ways to transfer energy: Mechanical Energy (Work) Heat Energy (Heating) Electrical Energy (Electricity) Light Energy (Radiation)