The atmosphere! - Studentportalen
... •" The troposphere has a great deal of vertical mixing due to solar heating at the surface, or convection. This is the main source for most of the weather! The heating warms bubbles of air, which makes them less dense so they rise. When a bubble of warm air rises the pressure upon it decreases so it ...
... •" The troposphere has a great deal of vertical mixing due to solar heating at the surface, or convection. This is the main source for most of the weather! The heating warms bubbles of air, which makes them less dense so they rise. When a bubble of warm air rises the pressure upon it decreases so it ...
MAST_-_Introduction2MET
... Air Temperature – the degree of hotness or coldness of the air. Air pressure – the force of the air above an area. Humidity – a measure of the amount of water vapor in the air. Clouds – a visible mass of tiny water droplets and/or ice crystals that are above the earth’s surface. Precipitat ...
... Air Temperature – the degree of hotness or coldness of the air. Air pressure – the force of the air above an area. Humidity – a measure of the amount of water vapor in the air. Clouds – a visible mass of tiny water droplets and/or ice crystals that are above the earth’s surface. Precipitat ...
5.07 Wind - 94 Newmarket Air Cadet Squadron
... –Longer than a gust –May be caused by a fast moving cold front or thunderstorm –May be accompanied by a rapid change in direction ...
... –Longer than a gust –May be caused by a fast moving cold front or thunderstorm –May be accompanied by a rapid change in direction ...
5.07 Wind
... –Longer than a gust –May be caused by a fast moving cold front or thunderstorm –May be accompanied by a rapid change in direction ...
... –Longer than a gust –May be caused by a fast moving cold front or thunderstorm –May be accompanied by a rapid change in direction ...
IM_08 - earthjay science
... mass will carry characteristics of its source with it and often has a strong influence on conditions in the region it invades. Continental polar air moving down from Canada, for example, often brings clear skies but bitterly cold temperatures to the United States in winter. Fronts, the boundaries be ...
... mass will carry characteristics of its source with it and often has a strong influence on conditions in the region it invades. Continental polar air moving down from Canada, for example, often brings clear skies but bitterly cold temperatures to the United States in winter. Fronts, the boundaries be ...
weather quiz - Travelling across time
... 15. Which pressure system brings rain/stormy weather? High pressure A. Low pressure B. 16. __________ is used to photograph and track large scale air movements such as typhoons etc. 17. The process in which liquid water changes into a gas or water vapor Transpiration A. Evaporation B. Condensation C ...
... 15. Which pressure system brings rain/stormy weather? High pressure A. Low pressure B. 16. __________ is used to photograph and track large scale air movements such as typhoons etc. 17. The process in which liquid water changes into a gas or water vapor Transpiration A. Evaporation B. Condensation C ...
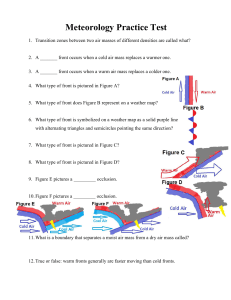
Meteorology Practice Test
... 60. Under El Niño conditions, temperatures in British Columbia during its winter are generally ___________ than usual. ...
... 60. Under El Niño conditions, temperatures in British Columbia during its winter are generally ___________ than usual. ...
WHAT IS WEATHER?
... calm or stormy, and clear or cloudy. There are certain things that are involved in weather, and these are: temperature, humidity, cloudiness, precipitation, wind and pressure. Humidity is the amount of water that is present in the air in the form of tiny water droplets. Precipitation is when water f ...
... calm or stormy, and clear or cloudy. There are certain things that are involved in weather, and these are: temperature, humidity, cloudiness, precipitation, wind and pressure. Humidity is the amount of water that is present in the air in the form of tiny water droplets. Precipitation is when water f ...
chapter 17 test
... by the statistical collection of weather conditions for a given region during a specified interval of time, usually several decades (see the Glossary of Meteorology, American Meteorological Society, 1986, or National Climate Data Center U.S. Climate Normals for more details). Given this definition o ...
... by the statistical collection of weather conditions for a given region during a specified interval of time, usually several decades (see the Glossary of Meteorology, American Meteorological Society, 1986, or National Climate Data Center U.S. Climate Normals for more details). Given this definition o ...
Climate and Meteorology 03: Meteorology
... Why is predicting the weather important? Why is accuracy in predicting the weather important? Are weather predictions ...
... Why is predicting the weather important? Why is accuracy in predicting the weather important? Are weather predictions ...
Welcome to Meteorology 10
... • Without it, the poles would be much colder and the tropics much warmer • Maintains earth’s heat balance along with the oceans • Earth tries to achieve balance, but never fully does. This is VERY GOOD for me as a meteorologist. ...
... • Without it, the poles would be much colder and the tropics much warmer • Maintains earth’s heat balance along with the oceans • Earth tries to achieve balance, but never fully does. This is VERY GOOD for me as a meteorologist. ...
Sky Watch: Weather
... By knowing how strong and in what direction the wind moves, we can often classify the type of wind as a breeze, a gale, a storm, tornado, or a hurricane. Go on a windy day adventure! Can you feel the push of the wind pulling you in a particular direction? Wind can be very powerful and can work to ma ...
... By knowing how strong and in what direction the wind moves, we can often classify the type of wind as a breeze, a gale, a storm, tornado, or a hurricane. Go on a windy day adventure! Can you feel the push of the wind pulling you in a particular direction? Wind can be very powerful and can work to ma ...
The Atmosphere: Climate and Weather
... • Basic understanding of main processes: energy flow, air movement, water cycle, air pressure • Present some of the terminology ...
... • Basic understanding of main processes: energy flow, air movement, water cycle, air pressure • Present some of the terminology ...
Name: Introduction to Meteorology Homework #1 (Chapters 1 and 2
... so that it can heat the earth but then absorbing _____________________________________, emitted by the earth, as it tries to escape into outer space. 26. The “greenhouse effect” is a ______________________ thing because, without it, the temperature of earth’s surface would average ____________ inste ...
... so that it can heat the earth but then absorbing _____________________________________, emitted by the earth, as it tries to escape into outer space. 26. The “greenhouse effect” is a ______________________ thing because, without it, the temperature of earth’s surface would average ____________ inste ...
Weather Satellite Weather Stations around Fiji
... A weather satellite is a type of satellite that is primarily used to monitor the weather and climate of the Earth. Satellites can be either polar orbiting, seeing the same swath of the Earth every 12 hours, or geostationary, hovering over the same spot on Earth by orbiting over the equator while mov ...
... A weather satellite is a type of satellite that is primarily used to monitor the weather and climate of the Earth. Satellites can be either polar orbiting, seeing the same swath of the Earth every 12 hours, or geostationary, hovering over the same spot on Earth by orbiting over the equator while mov ...
Andy Modaff, Tony Schneider, Richie Moore, and
... they first have to organize all their data. They use computer programming to put together a map with a moving timeline for the duration of their forecasts. Storm systems detected by radar are shown in their entirety with their moving path charted out according to real time. The colors of a storm sys ...
... they first have to organize all their data. They use computer programming to put together a map with a moving timeline for the duration of their forecasts. Storm systems detected by radar are shown in their entirety with their moving path charted out according to real time. The colors of a storm sys ...
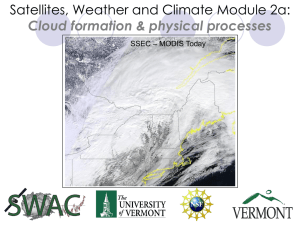
Satellites, Weather and Climate Module 2a: Cloud formation & physical processes SSEC
... Domed tops where air eventually becomes non buoyant Evaporating cloud elements on cloud edges in downward motion ...
... Domed tops where air eventually becomes non buoyant Evaporating cloud elements on cloud edges in downward motion ...
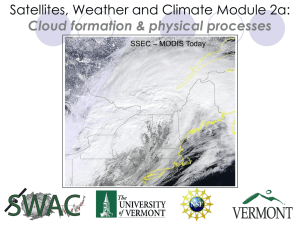
Satellite Weather And Climate (SWAC) Initial Training Modules
... Domed tops where air eventually becomes non buoyant Evaporating cloud elements on cloud edges in downward motion ...
... Domed tops where air eventually becomes non buoyant Evaporating cloud elements on cloud edges in downward motion ...
Unit 6: Weather & Climate
... Lightning stroke: flow of current thru air (a poor conductor) from the – to the + Lightning can flow from cloud to ground, cloud to cloud, and from ground to cloud Bright light is caused by glowing air molecules heated by the current Lightning follows the path of least resistance (easiest way ...
... Lightning stroke: flow of current thru air (a poor conductor) from the – to the + Lightning can flow from cloud to ground, cloud to cloud, and from ground to cloud Bright light is caused by glowing air molecules heated by the current Lightning follows the path of least resistance (easiest way ...
Wind Web Quest
... 1. What is air pressure? Click on "pressure" (questions 2-6) 2. If the number of air molecules above a surface increases, there are more molecules to exert a force on that surface and consequently, the pressure does what? 3. What device is used to measure atmospheric pressure? 4. What unit of measur ...
... 1. What is air pressure? Click on "pressure" (questions 2-6) 2. If the number of air molecules above a surface increases, there are more molecules to exert a force on that surface and consequently, the pressure does what? 3. What device is used to measure atmospheric pressure? 4. What unit of measur ...
History of Meteorology
... Lows that track across the northern US usually produce less rain or snowfall than lows that track further south Weather to the left side (west and north) of a storm’s track tends to be relatively cold Weather to the right (east and south) of a ...
... Lows that track across the northern US usually produce less rain or snowfall than lows that track further south Weather to the left side (west and north) of a storm’s track tends to be relatively cold Weather to the right (east and south) of a ...
8th Grade Science Meteorology Review
... Average weather in a region over a long period of time. ...
... Average weather in a region over a long period of time. ...
Earth Science SOL Review Power Point (Oceanography and
... Stratus 21. What does water vapor condense on? _______________________________ 22. Winds blow from _____________ pressure to ___________ pressure. 23. These are the major winds that affect the continental United States ________________________________ 24. How do hurricanes differ from tornadoes? ___ ...
... Stratus 21. What does water vapor condense on? _______________________________ 22. Winds blow from _____________ pressure to ___________ pressure. 23. These are the major winds that affect the continental United States ________________________________ 24. How do hurricanes differ from tornadoes? ___ ...
Surface weather analysis

Surface weather analysis is a special type of weather map that provides a view of weather elements over a geographical area at a specified time based on information from ground-based weather stations.Weather maps are created by plotting or tracing the values of relevant quantities such as sea level pressure, temperature, and cloud cover onto a geographical map to help find synoptic scale features such as weather fronts.The first weather maps in the 19th century were drawn well after the fact to help devise a theory on storm systems. After the advent of the telegraph, simultaneous surface weather observations became possible for the first time, and beginning in the late 1840s, the Smithsonian Institution became the first organization to draw real-time surface analyses. Use of surface analyses began first in the United States, spreading worldwide during the 1870s. Use of the Norwegian cyclone model for frontal analysis began in the late 1910s across Europe, with its use finally spreading to the United States during World War II.Surface weather analyses have special symbols that show frontal systems, cloud cover, precipitation, or other important information. For example, an H may represent high pressure, implying good and fair weather. An L on the other hand may represent low pressure, which frequently accompanies precipitation. Various symbols are used not just for frontal zones and other surface boundaries on weather maps, but also to depict the present weather at various locations on the weather map. Areas of precipitation help determine the frontal type and location.